一、引言:
在css众多属性中,position算是里面用的比较多也相对来说比较重要的属性了,它对于单个标签的“定位”、标签之间的“相对位置定位”还有网页的分层来说十分重要!
二、“定位的实现”具体介绍
position属性下常用的有fixed、relative跟absolute方式,其中fixed是实现“固定在浏览器窗口的某个位置”的功能的;而relative单独用没有任何意义,绝大多数情况下都是relative+absolute联合使用的:
2.1 fixed介绍:
2.1.1 我们在浏览网页时,通常会看到不论网页怎么上下滚动,右下角总有一个“固定”的“返回顶部”的标签,这个标签就是用fixed做的:


<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title> </head> <body><div style="width: 50px;height: 50px;background-color: #333333;color: #fafafa;position: fixed;bottom: 50px;right: 50px;">返回顶部</div><div style="height: 5000px;background-color: grey"></div> </body> </html>
2.1.2 这里还有个例子,我们想实现“网页的头部不随着鼠标滚动一直留在顶部”的效果,这在实际中用的也非常多,具体代码实现如下:


<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title><style>.pg-top{background-color: #333333;color:white;position:fixed;width:100%;height:22px;top:0;text-align: center;line-height:22px;}.pg-home{background-color:grey;color:yellow;height: 3333px;margin-top:22px ;text-align: center;}</style> </head> <body><div class="pg-top">我是顶部</div><div class="pg-home"><p>adasd</p><p>adaaasd</p><p>adcccasd</p><p>adavvsd</p><p>adaaasd</p><p>adzzzasd</p></div></body> </html>
效果如下:

2.2 relative+absolute介绍
我们用这种模式绝大多数情况下是实现子类标签相对于父类标签的位置的,看下面的效果就明白了:

我们要实现上图所示的效果,利用relative+absolute就可以了,实现代码如下:


<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title><style>.site-main{position: relative;border: 1px solid red;margin: 0 auto;/*使div居中*/height:200px;width:500px;}.main-l{position: absolute;left:0;bottom:0;width:50px;height:50px;background-color: yellow;border: 1px solid green;}.main-r{position:absolute;right:0;bottom:0;width:66px;height:66px;background-color: aqua;border: 1px dashed orangered;}.main-m{position: absolute;right:230px;bottom:0;width:66px;height:66px;background-color: fuchsia;border: 1px dashed sandybrown;}</style></head><body style="margin: 0 auto;"><div class="site-main">div1<div class="main-l">div11</div></div><div class="site-main">div2<div class="main-r">div21</div></div><div class="site-main">div3<div class="main-m">div31</div></div></body> </html>
三、页面分层介绍:
这里需要注意的是:我们写的网页如果不用position方法默认是在最底层,也就是第一层;如果利用position的fixed方法那么这个标签其实放置在了页面的第二层;如果再想在第二层上面放置一层的话,就要用到z-index了,z-index的值越大标签就在越上层!这里需要与margin属性配合使用进行定位:


<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title><style>.top{z-index: 5;/*z-index的值谁大谁在上面*/height: 255px;background-color: green;opacity:1;/*透明度*/position: fixed;top:0;bottom:0;left: 0;right:0;}.top-top{z-index: 10;/*z-index的值谁大谁在上面*/height:155px;width: 155px;background-color: white;opacity:1;/*透明度*/position: fixed;top:50px;left: 50%;margin-left: -100px;}</style> </head> <body style="margin:0 auto;"><div class="top-top"></div><div class="top"></div><div style="height: 500px;background-color: grey;">dasdas</div></body> </html>
效果如下:
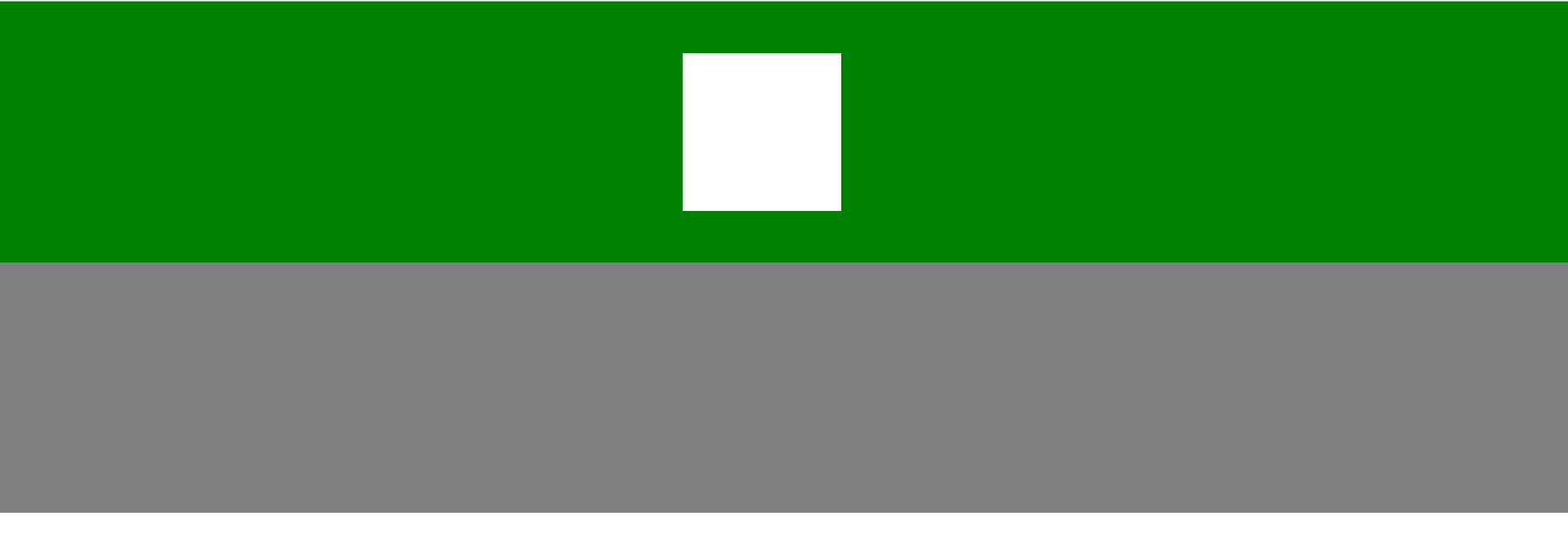
最后需要注意的是:在具体开发时,我们一般都会默认使二三层隐藏(display:none),然后在一定的触发条件下改变二、三层的display值达到相应的效果。
