本章重点讲解思想、思想、思想。
12.1 linux驱动的软件架构
下述三种思想,在linux的spi、iic、usb等复杂驱动里广泛使用。后面几节分别对这些思想进行详细说明。
- 思想1:驱动与设备分离,linux采用总线、设备和驱动模型,驱动只管驱动,设备只管设备,总线负责匹配设备和驱动;驱动从标准途径拿到板级信息(设备信息,现在都已dts的形式存在),这样驱动就可以放之四海而皆准了,结构如下图。
说到“总线”,有很多种,如I2C、SPI等,linux还为没有硬件总线的设备提出一种虚拟总线,即platform总线,同时还有对应的platform设备和platform驱动。
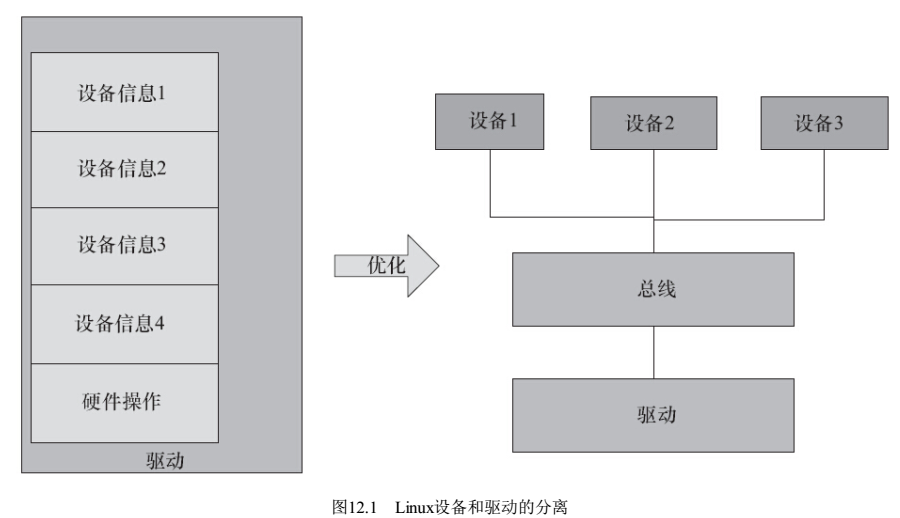
为啥? linux驱动要支持很多硬件,如果把设备信息写到驱动里,驱动会有非常多分支,一堆东西揉到一起,换成一锅粥,所以要把设备和驱动分开。
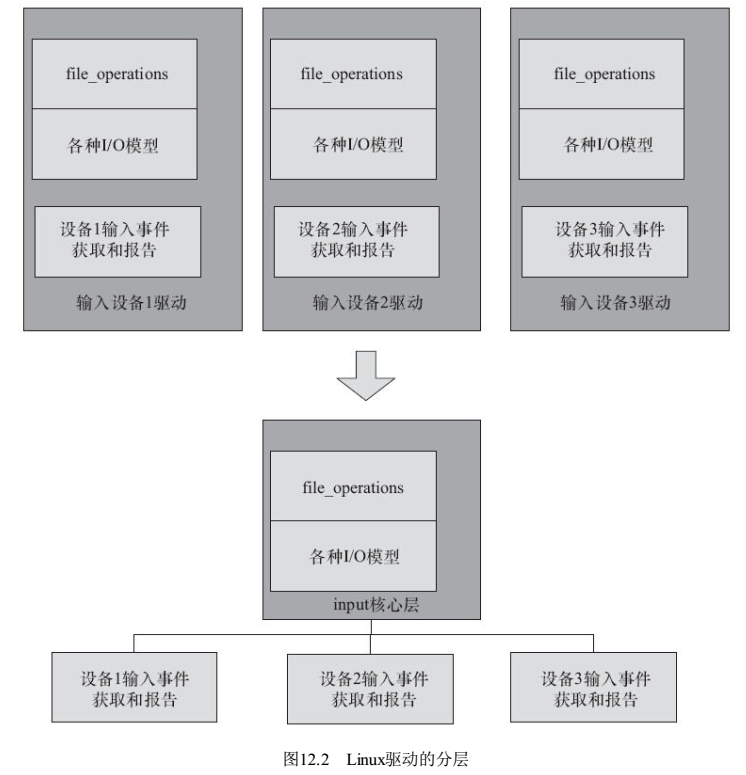
- 思想2:分层设计思想,file_opretations、IO模型等,是很多驱动共有的部分,linux提炼出一个中间层,把这些部分封装起来,供所有驱动使用。这就引出了软件分层的思想。
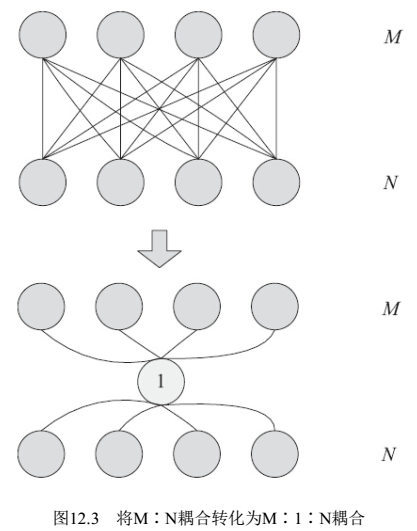
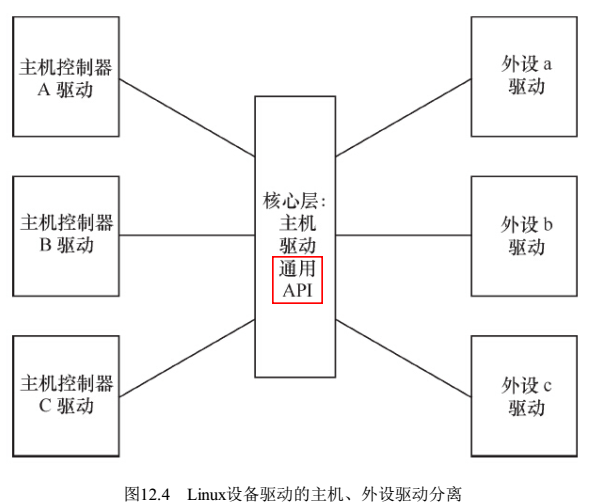
- 思想3:主机与外设分隔的思想。例如spi分为主机和外设,不同CPU有M种spi主机,同时不通外设也有N种,如果直接交叉支持,势必有M*N种组合,代码会非常复杂。需要在主机和外设中间插入一个标准API,把M和N分隔开,主机和外设都使用标准API与中间的分隔层接口,这样只需要实现M个主机和N个外设驱动即可,这种思想也叫“高内聚,低耦合”
12.2 platform设备驱动
12.2.1 platform总线、设备与驱动
- linux 2.6以后,采用总线、设备、驱动模型;
- platform的引入:有些设备本身依附一种总线,例如IIC、SPI、PCI、SPI等,很容易实现linux的总线/设备/驱动模型;但有些设备不依赖总线,例如SOC系统内部集成的独立外设控制器等,基于这种情况,linux发明了一种虚拟总线,即platform总线,对应的设备和驱动分别为platform_device和platform_driver。
- platform device不是针对linux的字符设备、块设备、网络设备的,是linux的一种附加手段。SOC内部集成的各控制器,例如IIC、RTC、LCD等一般都归纳为platform device。
- platform作为一种虚拟总线,与其他实体总线地位对等,例如SPI/IIC总线等,掌握了platform总线,其他总线也是类似的。
关键数据结构:
1. device
#include <linux/platform_device.h>struct platform_device {const char *name;int id;bool id_auto;struct device dev; // linux/device.h里定义,总线match时,实际match的是dev,所有设备共性的部分u32 num_resources; // 资源struct resource *resource;const struct platform_device_id *id_entry;/* MFD cell pointer */struct mfd_cell *mfd_cell;/* arch specific additions */struct pdev_archdata archdata; };
2.driver
#include <linux/platform_device.h>
// probe等函数由内核的platform机制实现了,驱动需要填充driver结构体 struct platform_driver {int (*probe)(struct platform_device *);int (*remove)(struct platform_device *);void (*shutdown)(struct platform_device *);int (*suspend)(struct platform_device *, pm_message_t state); // 电源管理,基本不用了,有driver里的int (*resume)(struct platform_device *); // 同上struct device_driver driver; // 所有驱动共享的部分,match以后driver.probe执行,同时调用外层platform_driver的prove执行 const struct platform_device_id *id_table; // 一组ID表bool prevent_deferred_probe; };// linux/device.h /*** struct device_driver - The basic device driver structure* @name: Name of the device driver.* @bus: The bus which the device of this driver belongs to.* @owner: The module owner.* @mod_name: Used for built-in modules.* @suppress_bind_attrs: Disables bind/unbind via sysfs.* @of_match_table: The open firmware table.* @acpi_match_table: The ACPI match table.* @probe: Called to query the existence of a specific device,* whether this driver can work with it, and bind the driver* to a specific device.* @remove: Called when the device is removed from the system to* unbind a device from this driver.* @shutdown: Called at shut-down time to quiesce the device.* @suspend: Called to put the device to sleep mode. Usually to a* low power state.* @resume: Called to bring a device from sleep mode.* @groups: Default attributes that get created by the driver core* automatically.* @pm: Power management operations of the device which matched* this driver.* @p: Driver core's private data, no one other than the driver* core can touch this.** The device driver-model tracks all of the drivers known to the system.* The main reason for this tracking is to enable the driver core to match* up drivers with new devices. Once drivers are known objects within the* system, however, a number of other things become possible. Device drivers* can export information and configuration variables that are independent* of any specific device.*/ struct device_driver {const char *name;struct bus_type *bus; // 对应总线结构体指针struct module *owner;const char *mod_name; /* used for built-in modules */bool suppress_bind_attrs; /* disables bind/unbind via sysfs */const struct of_device_id *of_match_table;const struct acpi_device_id *acpi_match_table;int (*probe) (struct device *dev); // 总线match完设备和驱动以后,这个函数会执行,
// 形参dev就是被match的设备信息!!!int (*remove) (struct device *dev);void (*shutdown) (struct device *dev);int (*suspend) (struct device *dev, pm_message_t state);int (*resume) (struct device *dev);const struct attribute_group **groups;const struct dev_pm_ops *pm;struct driver_private *p; };
3.总线
总线的类型为bus_type,内核直接为platform定义了一个总线实体
// drivers/base/platform.c,这些函数都是现成的,在platform机制里实现了。 struct bus_type platform_bus_type = {.name = "platform",.dev_groups = platform_dev_groups,.match = platform_match, // 匹配函数,关键.uevent = platform_uevent,.pm = &platform_dev_pm_ops, };/*** platform_match - bind platform device to platform driver.* @dev: device.* @drv: driver.** Platform device IDs are assumed to be encoded like this:* "<name><instance>", where <name> is a short description of the type of* device, like "pci" or "floppy", and <instance> is the enumerated* instance of the device, like '0' or '42'. Driver IDs are simply* "<name>". So, extract the <name> from the platform_device structure,* and compare it against the name of the driver. Return whether they match* or not.*/ static int platform_match(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv) {struct platform_device *pdev = to_platform_device(dev);struct platform_driver *pdrv = to_platform_driver(drv);/* Attempt an OF style match first */ // 基于dts匹配优先级最高if (of_driver_match_device(dev, drv))return 1;/* Then try ACPI style match */ if (acpi_driver_match_device(dev, drv))return 1;/* Then try to match against the id table */ // 基于platform device和platform driver的IDif (pdrv->id_table)return platform_match_id(pdrv->id_table, pdev) != NULL;/* fall-back to driver name match */ // 基于名字return (strcmp(pdev->name, drv->name) == 0); }
linux 2.6以及之前版本,platform device通常定义在板级bsp里,然后再add;而3.x以后,改为自动展开dts,形成若干device。
12.2.2 将globalmem作为platform设备
没法实验,只罗列代码。
static int globalfifo_probe(struct platform_device *pdev) // 完成原来globalmem_init的任务 {int ret;dev_t devno = MKDEV(globalfifo_major, 0);if (globalfifo_major)ret = register_chrdev_region(devno, 1, "globalfifo");else {ret = alloc_chrdev_region(&devno, 0, 1, "globalfifo");globalfifo_major = MAJOR(devno);}if (ret < 0)return ret;globalfifo_devp = devm_kzalloc(&pdev->dev, sizeof(*globalfifo_devp),GFP_KERNEL);if (!globalfifo_devp) {ret = -ENOMEM;goto fail_malloc;}globalfifo_setup_cdev(globalfifo_devp, 0);mutex_init(&globalfifo_devp->mutex);init_waitqueue_head(&globalfifo_devp->r_wait);init_waitqueue_head(&globalfifo_devp->w_wait);return 0;fail_malloc:unregister_chrdev_region(devno, 1);return ret; }static int globalfifo_remove(struct platform_device *pdev) // 完成原来globalmem_exit的任务 {cdev_del(&globalfifo_devp->cdev);unregister_chrdev_region(MKDEV(globalfifo_major, 0), 1);return 0; }static struct platform_driver globalfifo_driver = {.driver = {.name = "globalfifo",.owner = THIS_MODULE,},.probe = globalfifo_probe,.remove = globalfifo_remove, };module_platform_driver(globalfifo_driver); // !!!注册platform驱动,/sys/bus/platform/drivers/globalmem,多出一个globalmem子目录
// 在板级bsp里(arch/arm/mach-xxx/mach-yyy.c,xxx为SOC名,yyy为board名)增加platform device,
// 系统初始化时添加到系统里,/sys/device/platform/globalmem,多出一个globalmem子目录,该目录中有driver符号链接,
// 指向/sys/bus/platform/drivers/globalmem static struct platform_device globalfifo_device = { .name = "globalfifo",.id = -1, };
12.2.3 platform设备资源和数据
在platform_device结构体中,有resource结构体,表示该device的资源,start和end随flag的变化而表示不同的含义:
flag:
-
IORESOURCE_MEM,start和end表示platform device占据的开始开始地址和结束地址
- IORESOURCE_IRQ,start和end表示使用中断号的开始值和结束值,如果只有1个中断号,则开始值和结束值相同
resource在板级支持包或者dts里定义,dts的定义后续说明,板级支持包都淘汰了,不再说明。
/* Resources are tree-like, allowing
* nesting etc..*/ struct resource {resource_size_t start;resource_size_t end;const char *name;unsigned long flags;struct resource *parent, *sibling, *child; };/** IO resources have these defined flags.*/ #define IORESOURCE_BITS 0x000000ff /* Bus-specific bits */#define IORESOURCE_TYPE_BITS 0x00001f00 /* Resource type */ #define IORESOURCE_IO 0x00000100 /* PCI/ISA I/O ports */ #define IORESOURCE_MEM 0x00000200 #define IORESOURCE_REG 0x00000300 /* Register offsets */ #define IORESOURCE_IRQ 0x00000400 #define IORESOURCE_DMA 0x00000800 #define IORESOURCE_BUS 0x00001000#define IORESOURCE_PREFETCH 0x00002000 /* No side effects */ #define IORESOURCE_READONLY 0x00004000 #define IORESOURCE_CACHEABLE 0x00008000 #define IORESOURCE_RANGELENGTH 0x00010000 #define IORESOURCE_SHADOWABLE 0x00020000#define IORESOURCE_SIZEALIGN 0x00040000 /* size indicates alignment */ #define IORESOURCE_STARTALIGN 0x00080000 /* start field is alignment */#define IORESOURCE_MEM_64 0x00100000 #define IORESOURCE_WINDOW 0x00200000 /* forwarded by bridge */ #define IORESOURCE_MUXED 0x00400000 /* Resource is software muxed */#define IORESOURCE_EXCLUSIVE 0x08000000 /* Userland may not map this resource */ #define IORESOURCE_DISABLED 0x10000000 #define IORESOURCE_UNSET 0x20000000 #define IORESOURCE_AUTO 0x40000000 #define IORESOURCE_BUSY 0x80000000 /* Driver has marked this resource busy *//* PnP IRQ specific bits (IORESOURCE_BITS) */ #define IORESOURCE_IRQ_HIGHEDGE (1<<0) #define IORESOURCE_IRQ_LOWEDGE (1<<1) #define IORESOURCE_IRQ_HIGHLEVEL (1<<2) #define IORESOURCE_IRQ_LOWLEVEL (1<<3) #define IORESOURCE_IRQ_SHAREABLE (1<<4) #define IORESOURCE_IRQ_OPTIONAL (1<<5)/* PnP DMA specific bits (IORESOURCE_BITS) */ #define IORESOURCE_DMA_TYPE_MASK (3<<0) #define IORESOURCE_DMA_8BIT (0<<0) #define IORESOURCE_DMA_8AND16BIT (1<<0) #define IORESOURCE_DMA_16BIT (2<<0)#define IORESOURCE_DMA_MASTER (1<<2) #define IORESOURCE_DMA_BYTE (1<<3) #define IORESOURCE_DMA_WORD (1<<4)#define IORESOURCE_DMA_SPEED_MASK (3<<6) #define IORESOURCE_DMA_COMPATIBLE (0<<6) #define IORESOURCE_DMA_TYPEA (1<<6) #define IORESOURCE_DMA_TYPEB (2<<6) #define IORESOURCE_DMA_TYPEF (3<<6)/* PnP memory I/O specific bits (IORESOURCE_BITS) */ #define IORESOURCE_MEM_WRITEABLE (1<<0) /* dup: IORESOURCE_READONLY */ #define IORESOURCE_MEM_CACHEABLE (1<<1) /* dup: IORESOURCE_CACHEABLE */ #define IORESOURCE_MEM_RANGELENGTH (1<<2) /* dup: IORESOURCE_RANGELENGTH */ #define IORESOURCE_MEM_TYPE_MASK (3<<3) #define IORESOURCE_MEM_8BIT (0<<3) #define IORESOURCE_MEM_16BIT (1<<3) #define IORESOURCE_MEM_8AND16BIT (2<<3) #define IORESOURCE_MEM_32BIT (3<<3) #define IORESOURCE_MEM_SHADOWABLE (1<<5) /* dup: IORESOURCE_SHADOWABLE */ #define IORESOURCE_MEM_EXPANSIONROM (1<<6)/* PnP I/O specific bits (IORESOURCE_BITS) */ #define IORESOURCE_IO_16BIT_ADDR (1<<0) #define IORESOURCE_IO_FIXED (1<<1)/* PCI ROM control bits (IORESOURCE_BITS) */ #define IORESOURCE_ROM_ENABLE (1<<0) /* ROM is enabled, same as PCI_ROM_ADDRESS_ENABLE */ #define IORESOURCE_ROM_SHADOW (1<<1) /* ROM is copy at C000:0 */ #define IORESOURCE_ROM_COPY (1<<2) /* ROM is alloc'd copy, resource field overlaid */ #define IORESOURCE_ROM_BIOS_COPY (1<<3) /* ROM is BIOS copy, resource field overlaid *//* PCI control bits. Shares IORESOURCE_BITS with above PCI ROM. */ #define IORESOURCE_PCI_FIXED (1<<4) /* Do not move resource */
12.3 设备驱动的分层思想
稍后具体分析1个linux的驱动比较好。
12.4 主机驱动与外设驱动分离的设计思想
核心是定义好外设与主机之间的标准API,两边都使用标准API。具体分析一个驱动,便于理解。
12.5 总结
掌握思想,用这些思想去分析具体驱动,多读读驱动,慢慢就能理解这些思想了。
