网络推广与推广/盐城seo培训
前面大致的了解了Thread的一些方法和属性下面对一些方法进行运用看看具体效果
activeCount():返回当前线程所属线程组的活动线程数
源代码如下:
1 /**
2 * Returns an estimate of the number of active threads in the current3 * thread's {@linkplainjava.lang.ThreadGroup thread group} and its4 * subgroups. Recursively iterates over all subgroups in the current5 * thread's thread group.6 *7 *
The value returned is only an estimate because the number of8 * threads may change dynamically while this method traverses internal9 * data structures, and might be affected by the presence of certain10 * system threads. This method is intended primarily for debugging11 * and monitoring purposes.12 *13 *@returnan estimate of the number of active threads in the current14 * thread's thread group and in any other thread group that15 * has the current thread's thread group as an ancestor16 */
17 public static intactiveCount() {18 returncurrentThread().getThreadGroup().activeCount();19 }
这个静态方法先调用了一个currentThread()方法获取当前线程,然后调用了getThreadgroup()获取线程组,最后调用了activeCount()方法获取活动线程数。下面是调用的方法的具体实现,native方法调用的是VM的实现,需要下载VM的源码才能查看,这里先略过。
/*** Returns a reference to the currently executing thread object.
*
*@returnthe currently executing thread.*/
public static nativeThread currentThread();/*** Returns the thread group to which this thread belongs.
* This method returns null if this thread has died
* (been stopped).
*
*@returnthis thread's thread group.*/
public finalThreadGroup getThreadGroup() {returngroup;
}/*** Returns an estimate of the number of active threads in this thread
* group and its subgroups. Recursively iterates over all subgroups in
* this thread group.
*
*
The value returned is only an estimate because the number of
* threads may change dynamically while this method traverses internal
* data structures, and might be affected by the presence of certain
* system threads. This method is intended primarily for debugging
* and monitoring purposes.
*
*@returnan estimate of the number of active threads in this thread
* group and in any other thread group that has this thread
* group as an ancestor
*
*@sinceJDK1.0*/
public intactiveCount() {intresult;//Snapshot sub-group data so we don't hold this lock//while our children are computing.
intngroupsSnapshot;
ThreadGroup[] groupsSnapshot;synchronized (this) {if(destroyed) {return 0;
}
result=nthreads;
ngroupsSnapshot=ngroups;if (groups != null) {
groupsSnapshot=Arrays.copyOf(groups, ngroupsSnapshot);
}else{
groupsSnapshot= null;
}
}for (int i = 0 ; i < ngroupsSnapshot ; i++) {
result+=groupsSnapshot[i].activeCount();
}returnresult;
}
方法的使用:
1 /**
2 * thread method test3 *@authorLjcx4 *5 */
6 public class ThreadMethord implementsRunnable{7 @Override8 public voidrun() {9 System.out.println("");10 try{11 Thread.sleep(1000);12 } catch(InterruptedException e) {13 e.printStackTrace();14 }15 }16
17 public static voidmain(String[] args) {18 ThreadMethord tm = newThreadMethord();19 Thread th = newThread(tm);20 th.start();21 System.out.println("--活动线程数--"+th.activeCount());22 ThreadMethord tm2 = newThreadMethord();23 Thread th2 = newThread(tm2);24 th2.start();25 System.out.println("--活动线程数--"+th2.activeCount());26 }27 }
运行结果:
--活动线程数--2
--活动线程数--3
程序启动一共创建了三个线程:main,th,th2,主线程启动main函数,线程th启动,此时的活动线程为main,th.然后创建线程th2并启动。此时活动线程数是main,th,th2.把上面的代码稍微修改一下
1 public class ThreadMethord implementsRunnable{2 public voidrun() {3 System.out.println("");4 /*try {5 Thread.sleep(1000);6 } catch (InterruptedException e) {7 e.printStackTrace();8 }*/
9 }10
11 public static voidmain(String[] args) {12 ThreadMethord tm = newThreadMethord();13 Thread th = newThread(tm);14 th.start();15 System.out.println("--活动线程数--"+th.activeCount());16 ThreadMethord tm2 = newThreadMethord();17 Thread th2 = newThread(tm2);18 th2.start();19 System.out.println("--活动线程数--"+th2.activeCount());20 }21 }
运行结果:
1 --活动线程数--2
2 --活动线程数--2
好像跟预期的结果不一样,只是因为把线程休眠去掉了,那是因为在th2启动的时候th1已经运行结束了。
基本属性的获取方法:
方法使用:
1 public class ThreadMethord implementsRunnable{2 public voidrun() {3 System.out.println("");4 System.out.println("-当前线程的引用--"+Thread.currentThread());5 try{6 Thread.sleep(1000);7 } catch(InterruptedException e) {8 e.printStackTrace();9 }10 }11
12 public static voidmain(String[] args) {13 ThreadMethord tm = newThreadMethord();14 Thread th = newThread(tm);15 th.start();16 System.out.println("--活动线程数--"+th.activeCount());17 ThreadMethord tm2 = newThreadMethord();18 Thread th2 = newThread(tm2);19 th2.start();20 System.out.println("--活动线程数--"+th2.activeCount());21 Thread [] tarray = new Thread[3];22 System.out.println("-当前线程的引用--"+Thread.currentThread());23 Thread.enumerate(tarray);//将当前线程的所有活动线程放进数组里
24 for(Thread thread : tarray) {25 System.out.println("--tarray活动线程--"+thread);26 }27
28 System.out.println("--th线程ID--"+th.getId());29 System.out.println("--th的线程名--"+th.getName());30 System.out.println("--th的线程优先级--"+th.getPriority());31 System.out.println("--th的线程组--"+th.getThreadGroup());32
33
34 System.out.println("--th2线程ID--"+th2.getId());35 System.out.println("--th2的线程名--"+th2.getName());36 th2.setPriority(6);//设置优先级
37 System.out.println("--th2的线程优先级--"+th2.getPriority());38 System.out.println("--th2的线程组--"+th2.getThreadGroup());39 }40 }
运行结果:
1 --活动线程数--2
2 --活动线程数--3
3 -当前线程的引用--Thread[main,5,main]4
5 --tarray活动线程--Thread[main,5,main]6 --tarray活动线程--Thread[Thread-0,5,main]7 --tarray活动线程--Thread[Thread-1,5,main]8
9 --th线程ID--10
10 --th的线程名--Thread-0
11 --th的线程优先级--5
12 --th的线程组--java.lang.ThreadGroup[name=main,maxpri=10]13 --th2线程ID--11
14 --th2的线程名--Thread-1
15 --th2的线程优先级--6
16 --th2的线程组--java.lang.ThreadGroup[name=main,maxpri=10]17
18 -当前线程的引用--Thread[Thread-0,5,main]19 -当前线程的引用--Thread[Thread-1,6,main]
可以看到主线程他的引用就是main,优先级是5,所属线程组是main,th和th2他们的引用分别是Thread-0,Thread-1,这是他们的线程名,因为我们在创建现成的时候没有个他初始化名称,所以默认使用Thread-加上线程组内线程创建的序号。(说多了我以为我在胡扯,来看一波源代码)
源代码:
//这个初始化方法是我们调用的,可以看到他的命名方式:“Thread-“+nextThreadNum(),这个nextThreadNum方法是一个同步的方法,加了
//sychnorized锁,返回的是一个私有的静态的int类型的属性,所以他的默认值应该是0,说到这有的小伙伴可能有疑问了,既然默认值(初始值)0,
//那么这里返回的是threadInitNumber++,那第一个线程名应该是Thread-1,问题又回到了++i和i++的问题了,不多说了。
publicThread(Runnable target) {
init(null, target, "Thread-" + nextThreadNum(), 0);
}/*初始化方法的四个参数第一个线程组,第二个线程,第三个线程名,第四个是栈大小
private void init(ThreadGroup g, Runnable target, String name,long stackSize) {
init(g, target, name, stackSize, null);
}*/
private static intthreadInitNumber;private static synchronized intnextThreadNum() {return threadInitNumber++;
}
getState():获取线程状态
方法使用:
1 public class TestMethord2 implementsRunnable{2 @Override3 public voidrun() {4 //获取当前线程的引用
5 Thread obj =Thread.currentThread();6 System.out.println("线程:"+obj.getName()+"的状态:"+obj.getState());//RUNNABLE7 try{8 Thread.sleep(2000);9 } catch(InterruptedException e) {10 e.printStackTrace();11 }12 }13 public static voidmain(String[] args) {14 TestMethord2 t1 = newTestMethord2();15 TestMethord2 t2 = newTestMethord2();16 Thread th1 = new Thread(t1,"th1");17 System.out.println(th1.getState());//NEW18 th1.start();19 System.out.println(th1.getState());//RUNNABLE20 //等待线程执行到sleep
21 try{22 Thread.sleep(1000);23 } catch(InterruptedException e) {24 e.printStackTrace();25 }26 System.out.println(th1.getState());//TIMES_WAITING27 //等待线程th1执行完毕
28 try{29 Thread.sleep(1000);30 } catch(InterruptedException e) {31 e.printStackTrace();32 }33 System.out.println(th1.getState());//TERMINATED34 }35 }
运行结果:(跑一下代码一目了然可以看到不同的状态)
1 线程th1的状态:NEW2 线程th1的状态:RUNNABLE3 RUN线程th1的状态:RUNNABLE4 线程th1的状态:TIMED_WAITING5 线程th1的状态:TERMINATED
开始创建的时候状态是:NEW。start之后线程执行,状态是RUNNABLE,此时主线程进入休眠1秒,是为了等待th1进入到休眠状态,当th1进入休眠状态2秒,主线程已经结束了休眠此时在查看th1的状态为TIMED_WAIING,我们再让主线程等待1秒,th1结束了休眠,执行完毕,再次查看th1状态为TERMINATED。
跟状态相关的方法:
yield:暂停当前线程,让其他线程先执行。
1 public class TestMethord3 implementsRunnable{2
3 @Override4 public voidrun() {5 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"runing.....");6
7 for (int i = 0; i <10; i++) {8 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+i);9 if(i==3){10 Thread.yield();11 }12 }13 }14 public static voidmain(String[] args) {15 TestMethord3 tm1 = newTestMethord3();16 TestMethord3_2 tm2 = newTestMethord3_2();17 Thread th1 = new Thread(tm1, "th1");18 Thread th2 = new Thread(tm2, "th2");19 th1.start();20 th2.start();21 }22 }
1 public class TestMethord3_2 implementsRunnable{2 public voidrun() {3 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"runing.....");4 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {5 System.out.println("------------------"+i);6 }7 }8 }
运行结果:这个结果每次运行都不一样。
1 th2runing.....2 th1runing.....3 ------------------0
4 ------------------1
5 ------------------2
6 ------------------3
7 ------------------4
8 ------------------5
9 ------------------6
10 th1:0
11 ------------------7
12 th1:1
13 ------------------8
14 ------------------9
15 th1:2
16 th1:3
17 th1:4
18 th1:5
19 th1:6
20 th1:7
21 th1:8
22 th1:9
按照理想上来说,我们在th1运行到输出3的时候就应该停下来让th2先执行完,th1和th2是我交叉执行应该只发生在th1输出3之前。然而结果并不是如此,多运行几次就会发现,这个yield方法并没有起到应有的作用,这是由于CPU资源充足的情况下两个都能获取到CPU,暂停当前线程的执行可能只是在CPU资源不足的情况下让出CPU资源。(个人理解),但是就算是CPU资源不充足,两个同等优先级的线程在一个暂停之后仍然有同等几率被调度选中分配到资源,所以说这个yield方法同等优先级的情况下出现不管用的几率会更大。
join:等待某线程终止
1 public class TestMethord3 implementsRunnable{2 public voidrun() {3 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"runing.....");4
5 for (int i = 0; i <10; i++) {6 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+i);7 if(i==3){8 Thread.yield();9 }10 }11 }12 public static void main(String[] args) throwsInterruptedException {13 TestMethord3 tm1 = newTestMethord3();14 TestMethord3_2 tm2 = newTestMethord3_2();15 Thread th1 = new Thread(tm1, "th1");16 Thread th2 = new Thread(tm2, "th2");17 th1.start();18 th2.start();19 th2.join();20 System.out.println("th2的状态:"+th2.getState());21 }22 }23
24 public class TestMethord3_2 implementsRunnable{25 public voidrun() {26 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"runing.....");27 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {28 System.out.println("------------------"+i);29 }30 }31 }
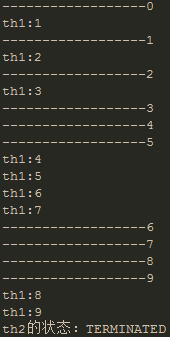
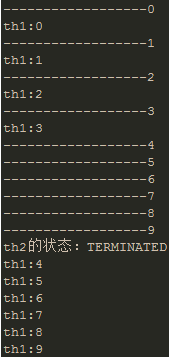
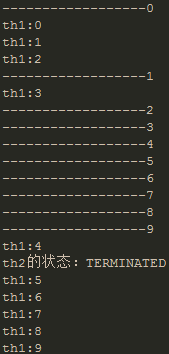
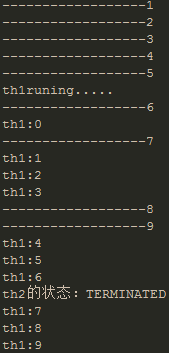
运行结果:下面是运行四次的结果显示,从结果中可以看出,无论th1,th2怎么运行,最终主线程输出的th2的状态都是TERMINATED,因为这一行输出是放在th2.join()后面的,表示的是主线程要等待th2执行完毕才能继续执行。
wait(),wait(long million),notify(),notifyAll(),这几个方法继承自Object类.
wait()和wait(long million):指的是让线程等待,与sleep的不同的是,wait方法会释放CPU,而sleep仍然占有CPU资源。
notify():指的是唤醒某个线程
notifyAll() :指的是唤醒所有的线程
这几个方法需要组合使用,在多个线程运行时涉及到的先后问题,暂时还未研究深入,先放一下。后面会补充上。
通过上面这些方法,基本上了解了线程这个类。除去基本的属性方法,其他的跟状态相关的在复杂的并发线程环境中才能体现他们的作用和价值,也才能展现出使用上的难度,这里所涉及到的不过是九牛一毛,后面继续探索。
