天津做网站seo的网络培训系统
欢迎加入Unity业内qq交流群:956187480
qq扫描二维码加群

A*算法是众多算法里面的明星算法,网络上很多流传的版本要么是实战改版出来的要么就是纯理论的,让很多初学者难以下手,我也很久没在看过这个算法,只记得零星片段,今天就重新捡起来重新过一遍。
可以做一个展想:平面的A*和3D的A*区别在哪?另外如果地图足够大,我们是否需要做A*分层处理等等,A*今天我们只是了解了入门基础,在此之上的变形扩展有很多
源工程:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_37310110/article/details/113336900
一:构建网格地形,建立起止点
//创建格子for (int i = 0; i < gridSize; i++){for (int j = 0; j < gridSize; j++){GameObject obj= GameObject.Instantiate<GameObject>(CellAsset, transform);RectTransform trans = obj.transform as RectTransform;trans.anchoredPosition = new Vector2(i,j) * cellSize;bool isWall=false;trans.Find("Pos").GetComponent<Text>().text = i + "," + j;if(wallList.Contains( i+"_"+j)){isWall = true;obj.GetComponent<Image>().color=Color.black;}Cell cell = new Cell(i, j, isWall, obj);cells.Add(cell);}}//创建起点GameObject obj1 = GameObject.Instantiate<GameObject>(PointAsset, transform);RectTransform trans1 = obj1.transform as RectTransform;trans1.anchoredPosition = startPos * cellSize;obj1.GetComponent<Image>().color = Color.red;trans1.localScale = Vector3.one * 1.2f;obj1.name = "start";//创建终点GameObject obj2 = Instantiate<GameObject>(PointAsset, transform);RectTransform trans2 = obj2.transform as RectTransform;trans2.anchoredPosition = endPos * cellSize;obj2.GetComponent<Image>().color = Color.green;trans2.localScale = Vector3.one * 1.2f;obj2.name = "end";1.如下图红色点为起点,绿色点为终点,我们的目的就是找到最优路径绘制出来。我们把搜索区域分割成方块格子,每个格子都有自己的二维位置数组,通过计算红点到绿点要走哪些路径,在A*寻路的做法,我们从开始点A做起,检查它周围的方块,并且向外普通的搜索,直到找到目标。
2.从开始点A起,添加它到待考虑的方块的“开放列表”。开放列表有点象购物列表。此时只有一个项目在里面,但很快我们会得到更多。它包含了你可能取用的沿途的方块,也可能不用它。基本上,这是需要检查的方块的列表。
//开启列表List<Cell> openLs = new List<Cell>();//关闭列表List<Cell> closeLs = new List<Cell>();3.观察开始点邻近的所有可到达或可行走的方块,忽略障碍物。也把它们添加到开放列表。对每一个方块,保存A 点作为它们的关联节点。这个关联节点方块在跟踪路径时非常重要。
4.把开始方块A从开放列表中取出,并放到“封闭列表”内,它是所有现在不需要再关注的方块的列表。

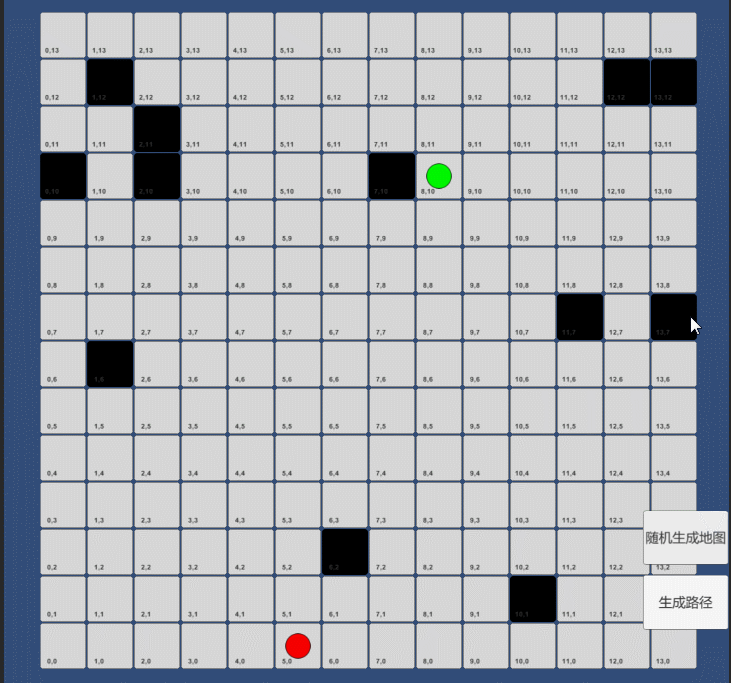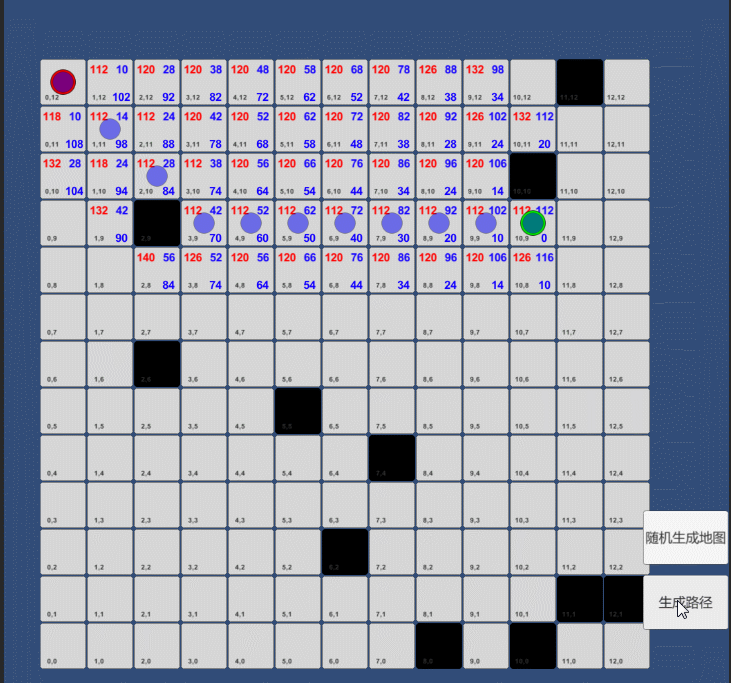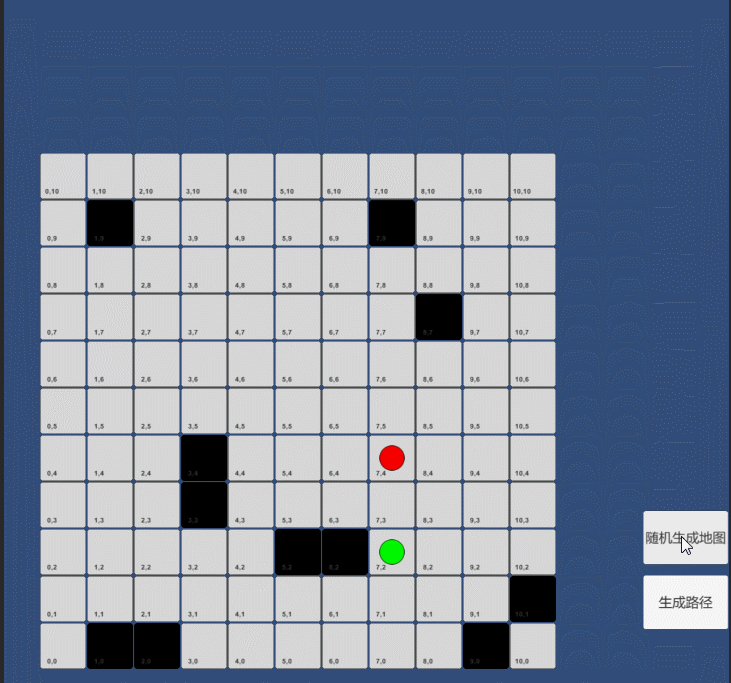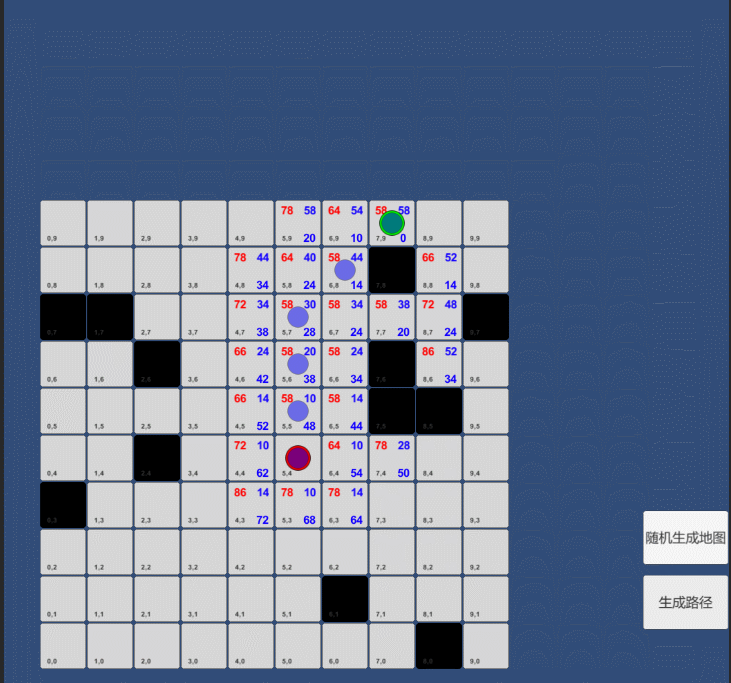
二:路径排序
// 与起点的移动代价public int gCost;// 与目标点的评估移动代价//这种方式通常称作试探法,有点让人混乱。因为这是一个猜测,所以得到这个称谓。在找到路径之前,我们真的不知道实际的距离,因为途中有各种东西(墙,水,等等)public int hCost;// 总的移动代价//我们需要的路径是这样生成的:反复的遍历开放列表,选择具有最小F值的方块。public int fCost{get { return gCost + hCost; }}
找到形成路径的方块的关键是下面的等式:F = G + H
G = 从开始 起点到格子中当前计算点的移动代价,沿着到达该方块而生成的那个路径。
H = 从当前计算点到最终目标 绿点的评估移动代价。这种方式通常称作试探法,有点让人混乱。因为这是一个猜测,所以得到这个称谓。在找到路径之前,我们真的不知道实际的距离,因为途中有各种东西(墙,水,等等)。在本教程里给出了一种计算H的方法,但在网上你能找到很多其他的文章。
F=G+H 就是表示从起点到终点的总位移代价
1.在本例中,我们为每个水平/垂直的移动指定代价为10,而斜角的移动代价为14。我们使用这些值,因为斜角移动的实际距离是2的平方根(别害怕),或者大概1.414倍的水平/垂直的移动代价。出于简化的目的使用了10和14。比例大致是正确的,而我们却避免了方根和小数的计算。倒不是我们没有能力做或者不喜欢数学。使用这些数字也能让计算更快一些。以后你就会发现,如果不使用这些技巧,寻路的计算非常慢。
2.既然我们沿着到达给定方块的路径来计算G的值,找出那个方块的G值的方法就是找到其关联节点的G值,再加上10或者14而得,这依赖于他处于其关联节点的斜角或者直角(非斜角)而定。这在本例后面会更加清晰,随着我们从开始点离开而得到更多的方块。
3.H能通过多种方法估算。我们这里用到的方法叫做Manhattan方法,计算从当前方块经过水平/垂直移动而到达目标方块的方块总数。然后将总数乘以 10。这种方法之所以叫做Manhattan方法,因为他很象计算从一个地点到达另一个地点的城市街区数量计算,此时你不能斜向的穿越街区。重要的是,当计算H的时候,要忽略任何路径中的障碍。这是一个对剩余距离的 估算值,而不是实际值,这就是试探法的称谓由来。
4.G和H相加就算出了F。F,G,和H值都写入了每个方块。如开始方块相邻右边的方块,F显示在左上方,G显示在右上方,而 H显示在右下方。
5.持续搜索,把当前目标点从开放列表取出,并加入封闭列表。然后把所有的相邻点添加进开放表里面(如果不在开放表里面就加进去,如果这些点有障碍物就忽略掉),将选定方块作为这些新加入方块的关联节点。
6.如果一个相邻方块已经存在于开放列表,检查到达那个方块的路径是否更优。换句话说,检查经由当前方块到达那里是否具有更小的G 值。如果没有,不做任何事。
相反,如果新路径的G值更小,把这个相邻方块的关联节点改为当前选定的方块。最后,重新计算那个方块的F和G值。
//如果是墙或者在关闭列表中则跳过if (cell.isWall || closeLs.Contains(cell))continue;int cost = cur.gCost + GetDistanceCost(cell, cur);//检查经由当前方块到达那里是否具有更小的G 值,则更新该点信息if (cost < cell.gCost || !openLs.Contains(cell)){cell.gCost = cost;cell.hCost = GetDistanceCost(cell, endCell);cell.parent = cur;Debug.Log("cell:" + cell.ToString() + " parent:" + cur.ToString() + " " + cell.PrintCost());//如果点不在开启列表中则添加if (!openLs.Contains(cell)){openLs.Add(cell);//显示在界面,和A*算法无关cell.obj.transform.Find("FCost").GetComponent<Text>().text = cell.fCost.ToString();cell.obj.transform.Find("GCost").GetComponent<Text>().text = cell.gCost.ToString();cell.obj.transform.Find("HCost").GetComponent<Text>().text = cell.hCost.ToString();}}三:源代码:源工程:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_37310110/article/details/113336900
#region 模块信息
// **********************************************************************
// Copyright (C) 2021
// Please contact me if you have any questions
// File Name: AssetBundleManager
// Author: 幻世界
// QQ: 853394528
// **********************************************************************
#endregion
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEngine.UI;/// <summary>
/// 单独的格子
/// </summary>
public class Cell
{public int x;public int y;public bool isWall;// 与起点的移动代价public int gCost;// 与目标点的评估移动代价//这种方式通常称作试探法,有点让人混乱。因为这是一个猜测,所以得到这个称谓。在找到路径之前,我们真的不知道实际的距离,因为途中有各种东西(墙,水,等等)public int hCost;// 总的移动代价//我们需要的路径是这样生成的:反复的遍历开放列表,选择具有最小F值的方块。public int fCost{get { return gCost + hCost; }}// 父节点public Cell parent=null;public GameObject obj;public Cell(int x,int y,bool isWall,GameObject obj){this.x = x;this.y = y;this.isWall = isWall;this.obj = obj;}public override string ToString(){return "("+x+","+y+")";}public string PrintCost(){return "{ fCost:" + fCost + ",hCost:" + hCost + "}";}
}public class AstarGrid : MonoBehaviour {public GameObject CellAsset;public GameObject PointAsset;public int gridSize = 10;int cellSize = 70;List<string> wallList = new List<string>();public List<Cell> cells = new List<Cell>();public Vector2 startPos = new Vector2 (3,6);public Vector2 endPos = new Vector2 (7,6);public void FindPath(){FindPath(startPos, endPos);}public void CreateGridMap(){if (cells.Count != 0){foreach (var item in transform.GetComponentsInChildren<Image>()){Destroy(item.gameObject);}cells.Clear();}gridSize = Random.Range(10, 15);UpDateGridMap();}public void UpDateGridMap(){//墙if (wallList.Count!=0){wallList.Clear();}for (int i = 0; i < Random.Range(10, 15); i++){wallList.Add(Random.Range(0, gridSize).ToString() + '_' + Random.Range(0, gridSize));}//起止点startPos = new Vector2(Random.Range(0, gridSize), Random.Range(0, gridSize));endPos = new Vector2(Random.Range(0, gridSize), Random.Range(0, gridSize));while (wallList.Contains(startPos.x + "_" + startPos.y) || wallList.Contains(endPos.x + "_" + endPos.y)){startPos = new Vector2(Random.Range(0, gridSize), Random.Range(0, gridSize));endPos = new Vector2(Random.Range(0, gridSize), Random.Range(0, gridSize));}//创建格子for (int i = 0; i < gridSize; i++){for (int j = 0; j < gridSize; j++){GameObject obj= GameObject.Instantiate<GameObject>(CellAsset, transform);RectTransform trans = obj.transform as RectTransform;trans.anchoredPosition = new Vector2(i,j) * cellSize;bool isWall=false;trans.Find("Pos").GetComponent<Text>().text = i + "," + j;if(wallList.Contains( i+"_"+j)){isWall = true;obj.GetComponent<Image>().color=Color.black;}Cell cell = new Cell(i, j, isWall, obj);cells.Add(cell);}}//创建起点GameObject obj1 = GameObject.Instantiate<GameObject>(PointAsset, transform);RectTransform trans1 = obj1.transform as RectTransform;trans1.anchoredPosition = startPos * cellSize;obj1.GetComponent<Image>().color = Color.red;trans1.localScale = Vector3.one * 1.2f;obj1.name = "start";//创建终点GameObject obj2 = Instantiate<GameObject>(PointAsset, transform);RectTransform trans2 = obj2.transform as RectTransform;trans2.anchoredPosition = endPos * cellSize;obj2.GetComponent<Image>().color = Color.green;trans2.localScale = Vector3.one * 1.2f;obj2.name = "end";}public Cell GetCell(Vector2 pos){return cells.Find((c) => { return c.x == (int)pos.x && c.y == (int)pos.y; });}public void CreatePath(Cell endPos){Cell cell = endPos;while(cell!=null){GameObject obj1 = GameObject.Instantiate<GameObject>(PointAsset, transform);RectTransform trans1 = obj1.transform as RectTransform;trans1.anchoredPosition = cellSize*new Vector2(cell.x,cell.y);obj1.GetComponent<Image>().color = new Color(Color.blue.r, Color.blue.g, Color.blue.b,0.5f);cell = cell.parent;}}/// <summary>/// 使用A*算法寻路/// </summary>/// <param name="start"></param>/// <param name="end"></param>void FindPath(Vector2 start, Vector2 end){//开启列表List<Cell> openLs = new List<Cell>();//关闭列表List<Cell> closeLs = new List<Cell>();//起点Cell startCell = GetCell(start);//终点Cell endCell = GetCell(end);Debug.LogFormat("寻路开始,start({0}),end({1})!", start, end);//将起点作为待处理的点放入开启列表,openLs.Add(startCell);//如果开启列表没有待处理点表示寻路失败,此路不通while (openLs.Count > 0){//遍历开启列表,找到消费最小的点作为检查点Cell cur = openLs[0];for (int i = 0; i < openLs.Count; i++){if (openLs[i].fCost < cur.fCost && openLs[i].hCost < cur.hCost){cur = openLs[i]; }}Debug.Log("当前检查点:" + cur.ToString() +" open列表节点数量:" + openLs.Count);//从开启列表中删除检查点,把它加入到一个“关闭列表”,列表中保存所有不需要再次检查的方格。openLs.Remove(cur);closeLs.Add(cur);//检查是否找到终点if (cur == endCell){Debug.Log("寻路结束!");CreatePath(cur);return;}//根据检查点来找到周围可行走的点List<Cell> aroundCells = GetAllAroundCells(cur);foreach (var cell in aroundCells){//如果是墙或者在关闭列表中则跳过if (cell.isWall || closeLs.Contains(cell))continue;int cost = cur.gCost + GetDistanceCost(cell, cur);//检查经由当前方块到达那里是否具有更小的G 值,则更新该点信息if (cost < cell.gCost || !openLs.Contains(cell)){cell.gCost = cost;cell.hCost = GetDistanceCost(cell, endCell);cell.parent = cur;Debug.Log("cell:" + cell.ToString() + " parent:" + cur.ToString() + " " + cell.PrintCost());//如果点不在开启列表中则添加if (!openLs.Contains(cell)){openLs.Add(cell);//显示在界面,和A*算法无关cell.obj.transform.Find("FCost").GetComponent<Text>().text = cell.fCost.ToString();cell.obj.transform.Find("GCost").GetComponent<Text>().text = cell.gCost.ToString();cell.obj.transform.Find("HCost").GetComponent<Text>().text = cell.hCost.ToString();}}}}Debug.Log("寻路失败!");}// 取得周围的节点public List<Cell> GetAllAroundCells(Cell cell){List<Cell> list = new List<Cell>();for (int i = -1; i <= 1; i++){for (int j = -1; j <= 1; j++){// 如果是自己,则跳过if (i == 0 && j == 0)continue;int x = cell.x + i;int y = cell.y + j;// 判断是否越界,如果没有,加到列表中if (x < gridSize && x >= 0 && y < gridSize && y >= 0){list.Add(GetCell(new Vector2(x, y)));}}}return list;}/// <summary>/// 估价函数,试探函数/// </summary>/// <param name="a"></param>/// <param name="b"></param>/// <returns></returns>/// 在本例中,我们为每个水平/垂直的移动指定代价为10,而斜角的移动代价为14。/// 我们使用这些值,因为斜角移动的实际距离是2的平方根(别害怕),或者大概1.414倍的水平/垂直的移动代价。/// 出于简化的目的使用了10和14int GetDistanceCost(Cell a, Cell b){int cntX = Mathf.Abs(a.x - b.x);int cntY = Mathf.Abs(a.y - b.y);// 判断到底是那个轴相差的距离更远if (cntX > cntY){return 14 * cntY + 10 * (cntX - cntY);}else{return 14 * cntX + 10 * (cntY - cntX);}}}