文昌网站建设网页设计网站
原文地址:Tree Traversals
不像线性数据结构(数组,列表,队列,堆栈等),它们在逻辑上只有一种遍历方式,树可以有不同的遍历方式。下面就是遍历树的一般所用的方法:
Algorithm Inorder(tree)1. Traverse the left subtree, i.e., call Inorder(left-subtree)2. Visit the root.3. Traverse the right subtree, i.e., call Inorder(right-subtree)中序遍历应用:
在二叉查询树(BST)中,中序遍历是非递减遍历已知节点。可以通过中序遍历的一个变量得到BST的非递减顺序。
例如:上图的中序遍历是:4 2 5 1 3。
先序遍历:
Algorithm Preorder(tree)1. Visit the root.2. Traverse the left subtree, i.e., call Preorder(left-subtree)3. Traverse the right subtree, i.e., call Preorder(right-subtree) 先序遍历的应用:
先序遍历可以用于建立一个树的拷贝。先序遍历也可以用于在表达式树中获取前缀表达式。请看http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polish_notation就知道为啥前缀表达式是有用的了。
例如:上图的先序遍历是:1 2 4 5 3。
后续遍历:
Algorithm Postorder(tree)1. Traverse the left subtree, i.e., call Postorder(left-subtree)2. Traverse the right subtree, i.e., call Postorder(right-subtree)3. Visit the root.后序遍历的应用:
后续遍历可以用于删除树。请看树的删除问题的详细描述。在一个表达式树中,后序遍历也可以用于获取后缀表达式。请看http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Reverse_Polish_notation,后缀表达式的用法。
例如:上图的后序遍历为:4 5 2 3 1。
C语言实现
// C program for different tree traversals
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left childand a pointer to right child */
struct node
{int data;struct node* left;struct node* right;
};/* Helper function that allocates a new node with thegiven data and NULL left and right pointers. */
struct node* newNode(int data)
{struct node* node = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));node->data = data;node->left = NULL;node->right = NULL;return(node);
}/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes according to the"bottom-up" postorder traversal. */
void printPostorder(struct node* node)
{if (node == NULL)return;// first recur on left subtreeprintPostorder(node->left);// then recur on right subtreeprintPostorder(node->right);// now deal with the nodeprintf("%d ", node->data);
}/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes in inorder*/
void printInorder(struct node* node)
{if (node == NULL)return;/* first recur on left child */printInorder(node->left);/* then print the data of node */printf("%d ", node->data); /* now recur on right child */printInorder(node->right);
}/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes in preorder*/
void printPreorder(struct node* node)
{if (node == NULL)return;/* first print data of node */printf("%d ", node->data); /* then recur on left sutree */printPreorder(node->left); /* now recur on right subtree */printPreorder(node->right);
} /* Driver program to test above functions*/
int main()
{struct node *root = newNode(1);root->left = newNode(2);root->right = newNode(3);root->left->left = newNode(4);root->left->right = newNode(5); printf("\nPreorder traversal of binary tree is \n");printPreorder(root);printf("\nInorder traversal of binary tree is \n");printInorder(root); printf("\nPostorder traversal of binary tree is \n");printPostorder(root);getchar();return 0;
}Java语言实现
// Java program for different tree traversals/* Class containing left and right child of currentnode and key value*/
class Node
{int key;Node left, right;public Node(int item){key = item;left = right = null;}
}class BinaryTree
{// Root of Binary TreeNode root;BinaryTree(){root = null;}/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes according to the"bottom-up" postorder traversal. */void printPostorder(Node node){if (node == null)return;// first recur on left subtreeprintPostorder(node.left);// then recur on right subtreeprintPostorder(node.right);// now deal with the nodeSystem.out.print(node.key + " ");}/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes in inorder*/void printInorder(Node node){if (node == null)return;/* first recur on left child */printInorder(node.left);/* then print the data of node */System.out.print(node.key + " ");/* now recur on right child */printInorder(node.right);}/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes in preorder*/void printPreorder(Node node){if (node == null)return;/* first print data of node */System.out.print(node.key + " ");/* then recur on left sutree */printPreorder(node.left);/* now recur on right subtree */printPreorder(node.right);}// Wrappers over above recursive functionsvoid printPostorder() { printPostorder(root); }void printInorder() { printInorder(root); }void printPreorder() { printPreorder(root); }// Driver methodpublic static void main(String[] args){BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();tree.root = new Node(1);tree.root.left = new Node(2);tree.root.right = new Node(3);tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);System.out.println("Preorder traversal of binary tree is ");tree.printPreorder();System.out.println("\nInorder traversal of binary tree is ");tree.printInorder();System.out.println("\nPostorder traversal of binary tree is ");tree.printPostorder();}
}输出:
Preorder traversal of binary tree is
1 2 4 5 3
Inorder traversal of binary tree is
4 2 5 1 3
Postorder traversal of binary tree is
4 5 2 3 1另外一个例子:
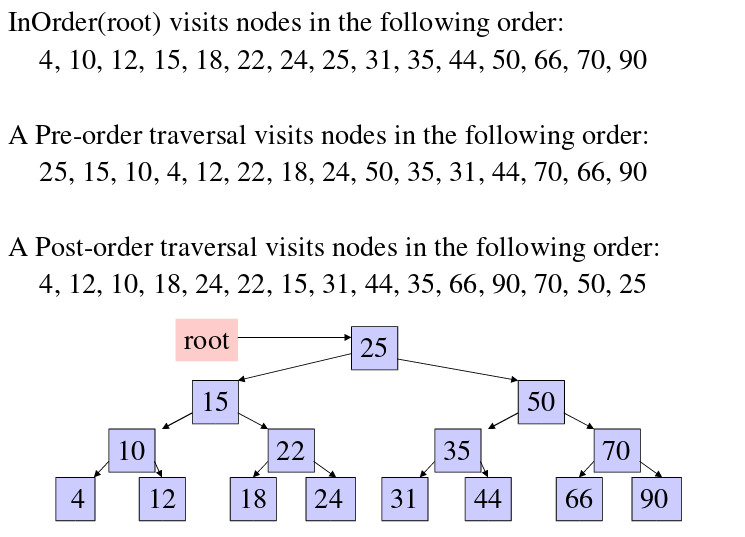
图片地址:https://www.cs.swarthmore.edu/~newhall/unixhelp/Java_bst.pdf
时间复杂度:O(n)
我们看下不同的边界情况。
函数复杂度 T(n) ——对于遍历说涉及到的所有问题——可以定义为:
T(n) = T(k) + T(n – k – 1) + c
这里根一边的节点的数目,n-k-1是另一边的节点数。
我们分析一下边界条件:
情况1:偏树(Skewed tree)(其中的一个子树为空,而另一边的子树不为空)。
这种情况下k等于0。
T(n)=T(0)+T(n−1)+c
T(n)=2T(0)+T(n−2)+2c
T(n)=3T(0)+T(n−3)+3c
T(n)=4T(0)+T(n−4)+4c
…………………………………………
………………………………………….
T(n)=(n−1)T(0)+T(1)+(n−1)c
T(n)=nT(0)+(n)c
T(0)的值将是一个常数,比如d。(遍历一个空树的时间就是花费常量的时间)
T(n)=n(c+d)
T(n)=Θ(n)(Thetaofn)
情况2:左右子树的节点数目是相同的
T(n)=2T(⌊n/2⌋)+c
这个递归函数对于大师级的方法( http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Master_theorem)是标准形式(T(n)=aT(n/b)+(−)(n))。如果我们用大师方法解决,那么会得到(-)(n)。
空间复杂度:如果我们不考虑栈的大小,那么函数调用是O(1) 否则是O(n)。
