网站测试页面怎么做/软文有哪些
指标监控
- 1、SpringBoot Actuator
- 1、简介
- 2、1.x与2.x的不同
- 3、如何使用
- 2、Actuator Endpoint
- 1、最常使用的端点
- 最常用的Endpoint
- 2、Health Endpoint
- 3、Metrics Endpoint
- 4、管理Endpoints
- 1、开启与禁用Endpoints
- 2、暴露Endpoints (监控端点)
- 定制 Endpoint
- 1、定制一个组件的Health信息(自定义的Health类名必须叫xxxHealthIndicator.xxx则是组件名字)
- 这里定制监控端点有两种方式,一种是实现HealthIndicator 接口,一种是继承 AbstractHealthIndicator抽象类
- 方法一: 继承接口
- 方法二:实现抽象类
- 设置为总是显示详细信息
- 2、定制info信息---用于展示当前应用详细信息
- 方式一: 编写配置文件
- 方式二: 编写InfoContributor
- 3、定制Metrics信息 (运行时指标)
- 1、SpringBoot支持自动适配的Metrics
- 2.增加定制Metrics
- 定制Endpoint(端点)
- @Selector
- 可视化
- 1.导入依赖
- 2.并在yaml中配置:
- 3.创建另一个服务器作为监控者,监控客户端数据
- 测试
- 详细使用还可以看下面这篇文章
1、SpringBoot Actuator
1、简介
未来每一个微服务在云上部署以后,我们都需要对其进行监控、追踪、审计、控制等。SpringBoot就抽取了Actuator场景,使得我们每个微服务快速引用即可获得生产级别的应用监控、审计等功能。
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId></dependency>
2、1.x与2.x的不同

3、如何使用
- 引入场景
- 访问 http://localhost:8080/actuator/** (监控端点,有很多)
- 暴露所有监控信息为HTTP
management:endpoints:enabled-by-default: true #暴露所有端点信息web:exposure:include: '*' #以web方式暴露
测试
http://localhost:8080/actuator/beans
http://localhost:8080/actuator/configprops
http://localhost:8080/actuator/metrics
http://localhost:8080/actuator/metrics/jvm.gc.pause
http://localhost:8080/actuator/endpointName/detailPath
。。。。。。
2、Actuator Endpoint
1、最常使用的端点



最常用的Endpoint
Health:监控状况
Metrics:运行时指标
Loggers:日志记录
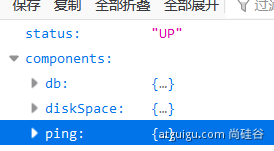
2、Health Endpoint
健康检查端点,我们一般用于在云平台,平台会定时的检查应用的健康状况,我们就需要Health Endpoint可以为平台返回当前应用的一系列组件健康状况的集合。
开启health的显示详细endpoint.health.show-details=always
重要的几点:
- health endpoint返回的结果,应该是一系列健康检查后的一个汇总报告 (有任何一个应用是宕机状态,整个就是宕机状态)
- 很多的健康检查默认已经自动配置好了,比如:数据库、redis等
- 可以很容易的添加自定义的健康检查机制
3、Metrics Endpoint
提供详细的、层级的、空间指标信息,这些信息可以被pull(主动推送)或者push(被动获取)方式得到;
- 通过Metrics对接多种监控系统
- 简化核心Metrics开发
- 添加自定义Metrics或者扩展已有Metrics

4、管理Endpoints
1、开启与禁用Endpoints
- 默认所有的Endpoint除过shutdown都是开启的。
- 需要开启或者禁用某个Endpoint。配置模式为 management.endpoint..enabled = true
management:endpoint:beans:enabled: true
- 或者禁用所有的Endpoint然后手动开启指定的Endpoint (management.endpoints.enabled-by-default默认是true)
management:endpoints:enabled-by-default: falseendpoint:beans:enabled: truehealth:enabled: true
2、暴露Endpoints (监控端点)
支持的暴露方式
HTTP:默认只暴露health和info Endpoint
JMX:默认暴露所有Endpoint (例如Jconsole)
除过health和info,剩下的Endpoint都应该进行保护访问。如果引入SpringSecurity,则会默认配置安全访问规则


定制 Endpoint
1、定制一个组件的Health信息(自定义的Health类名必须叫xxxHealthIndicator.xxx则是组件名字)
这里定制监控端点有两种方式,一种是实现HealthIndicator 接口,一种是继承 AbstractHealthIndicator抽象类
方法一: 继承接口
import org.springframework.boot.actuate.health.Health;
import org.springframework.boot.actuate.health.HealthIndicator;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Component
public class MyHealthIndicator implements HealthIndicator {@Overridepublic Health health() {int errorCode = check(); // perform some specific health checkif (errorCode != 0) {return Health.down().withDetail("Error Code", errorCode).build();}return Health.up().build();}}构建Health
Health build = Health.down().withDetail("msg", "error service").withDetail("code", "500").withException(new RuntimeException()).build();
management:health:enabled: trueshow-details: always #总是显示详细信息。可显示每个模块的状态信息
方法二:实现抽象类
@Component
public class MyConHealthIndicator extends AbstractHealthIndicator {//这里可以通过获取容器中某个我们要监测的组件,判断其健康情况,来决定是up还是down/*** 真实的检查方法** @param builder* @throws Exception*/@Overrideprotected void doHealthCheck(Health.Builder builder) throws Exception {//mongodb。 获取连接进行测试Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();// 检查完成if (1 == 2) {
// builder.up(); //健康builder.status(Status.UP);map.put("count", 1);map.put("ms", 100);} else {
// builder.down();builder.status(Status.OUT_OF_SERVICE);map.put("err", "连接超时");map.put("ms", 3000);}builder.withDetail("code", 100).withDetails(map);}
}

设置为总是显示详细信息
management:endpoints:enabled-by-default: true #暴露所有端点信息web:exposure:include: '*' #以web方式暴露endpoint:health:show-details: always #总是显示详细信息。可显示每个模块的状态信息

2、定制info信息—用于展示当前应用详细信息
方式一: 编写配置文件
management:endpoints:enabled-by-default: true #暴露所有端点信息web:exposure:include: '*' #以web方式暴露endpoint:health:show-details: always #总是显示详细信息。可显示每个模块的状态信息
info:appName: boot-adminversion: 2.0.1mavenProjectName: @project.artifactId@ #使用@@可以获取maven的pom文件值mavenProjectVersion: @project.version@
方式二: 编写InfoContributor
@Component
public class ExampleInfoContributor implements InfoContributor {@Overridepublic void contribute(Info.Builder builder) {builder.withDetail("example",Collections.singletonMap("key", "value"));}
}
会输出以上方式返回的所有info信息,即配置文件和代码迭代的所有info信息
3、定制Metrics信息 (运行时指标)
1、SpringBoot支持自动适配的Metrics

2.增加定制Metrics
@RestController
public class TestController
{Counter counter;public TestController(MeterRegistry meterRegistry){counter = meterRegistry.counter("myservice.method.running.counter");}@GetMapping("/test")public String test(){//该请求每发一次,就会增加一次记录数,来记录当前请求被调用的次数counter.increment();return "hhhhh";}
}//也可以使用下面的方式
@Bean
MeterBinder queueSize(Queue queue) {return (registry) -> Gauge.builder("queueSize", queue::size).register(registry);
}


定制Endpoint(端点)
@Component
@Endpoint(id = "container")
public class DockerEndpoint {@ReadOperationpublic Map getDockerInfo() {//创建一个单实例的map对象//端点的读操作return Collections.singletonMap("info", "docker started...");}@WriteOperationprivate void restartDocker() {System.out.println("docker restarted....");}
}
-
@EndPoint中的id不能使用驼峰法,需要以-分割 - @Spring Boot会去扫描@EndPoint注解下的@ReadOperation, @WriteOperation,@DeleteOperation注解,分别对应生成Get/Post/Delete的Mapping。注解中有个produces参数,可以指定mediatype, 如:application/json等。
@Selector
@Endpoint(id = "customPoint")
@Component
public class StatusEndPoint {@ReadOperationpublic String getCustom(@Selector String name) {return "MyName is ." + name;}}

看到红色mapped就说明可以成功了
访问http://127.0.0.1:8080/actuator/customPoint/156
结果

可视化
1.导入依赖
让当前项目数据被监控端的服务器收集,表明当前项目是被监控的客户端
<dependency><groupId>de.codecentric</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-admin-starter-client</artifactId><version>2.3.1</version></dependency>
2.并在yaml中配置:
spring:boot:admin:client:url: http://localhost:8888 #我们这个客户端要把数据汇报给哪一个监控端的服务器instance:prefer-ip: true #使用ip注册进来application:name: 大忽悠 #当前应用的名字
3.创建另一个服务器作为监控者,监控客户端数据
表明当前项目作为检测端
<dependency><groupId>de.codecentric</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-admin-starter-server</artifactId><version>2.3.1</version></dependency>
在主配置类上加上对应开启服务监控功能的注解
@EnableAdminServer //开启服务监控功能
@SpringBootApplication
public class HealthDemo1Application {public static void main(String[] args) {SpringApplication.run(HealthDemo1Application.class, args);}}
最好修改当前项目端口号,防止端口号冲突
server.port=8888

测试
现在启动两个项目,访问http://localhost:8888/即可看到下面的界面:



详细使用还可以看下面这篇文章
链接
