什么是vue.js
1.vue是目前最火的一个前端框架,react 是最流行的前端框架(react除了开发网站,还可以开发手机APP,vue语法也是可以进行手机app开发的,需要借助于weex)
2.vue.js 是前端的主流框架之一,和angular.js react.js 一起 并成为前端三大主流框架
3.vue.js是一套构建用户界面的框架,值关注视图层,不仅易于上手,还可便于第三方库或既有项目整合.(vue有配套的第三方库,可以整合起来做带向项目的开发)
4.前端的主要工作?主要负责MVC 的v这一层 主要工作就是和界面交道
为什么要学习流行框架
企业为了提高开发效率,在企业中,事件就是效率,效率就是金钱
提高开发的发展历程,原生js -> jquery类的类库 -> 前端模板引擎 -> angular/vue/
在vue中,一个核心的概念,就是让用户不在操作DOM操作元素,解放了用户的双手,让程序员可以更多的时间去关注业务逻辑
增强自己就业时候的竞争力
框架和库 的却别:
框架:是一台完整的解决方案,对项目的侵入性较大,项目如果需要更换框架,则需要重新架构整个项目
node 中的 express
库(插件):提供某一个小功能,对项目的侵入性小,如果某个库完成某些需求,可以很容易切换到其他库的实现要求.
node(后端) 中的MVC 与 前端 MVVM 之间的区别:
MVC (后端概念)
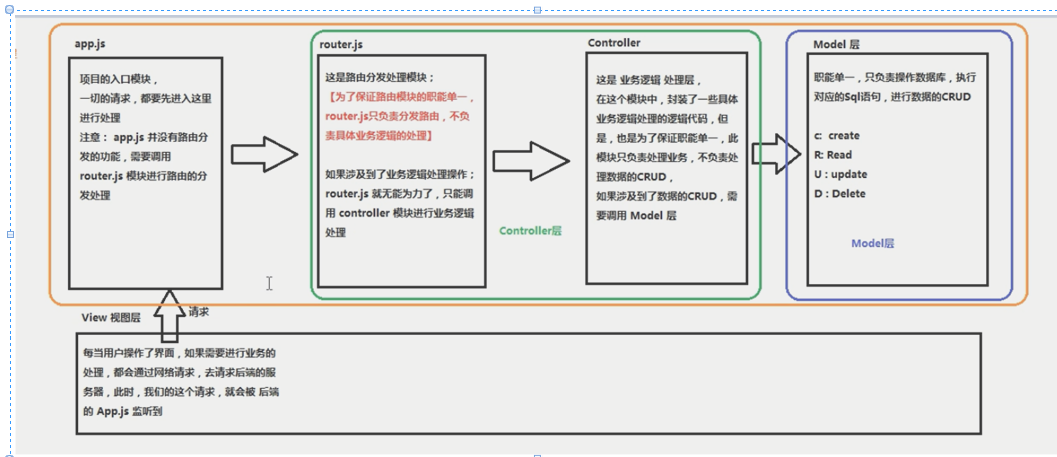
MVVM 前端概念:
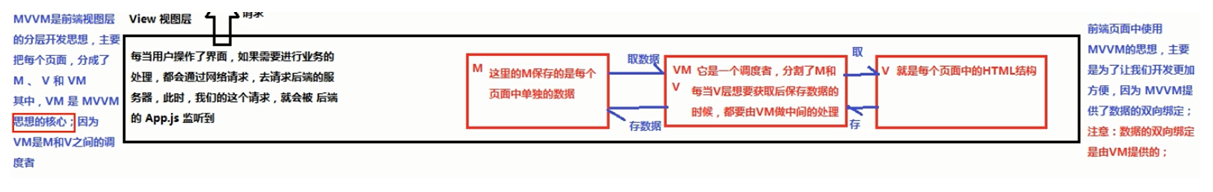
小结:

vue 第一话: 实例化 vue
<!DOCTYPE html> <html><head><meta charset="utf-8"><title>vue firstone</title><script src="vue.js"></script></head><body><div id="app"><p>{{ msg }}</p></div><script>var vm = new Vue({el: '#app',data:{msg:'hello world!',},})</script></body> </html>
需要引入vue.js
vue第二话: v-cloak v-text v-html v-on v-bind
<!DOCTYPE html> <html><head><meta charset="utf-8"><title></title><script src="vue.js"></script><style>[v-cloak]{display: none;}</style></head><body><div id="app"><!-- 文件显示以及解决闪烁问题 cloak/text/html的应用方式 --><p v-cloak>00000{{ msg }}0000</p><h3 v-text="msg">00000000</h3><p v-text="msg"></p><p v-html="msg"></p><!-- -------------------------------- --><!-- 事件绑定 v-bind 绑定js表达式--><p><input type="button" value="按钮" v-bind:title="msg2" /><input type="button" value="按钮" v-bind:title="msg2 + '添加字符'" /><input type="button" value="按钮" :title="msg2 + '简写方式!'" /></p><!-- 事件绑定v-on 绑定methods 事件--><p><input type="button" value="v-on绑定methods" v-on:click="show" /><input type="button" value="v-on绑定methods 简写方式" @click="show" /><input type="button" value="v-on绑定methods 其他事件" v-on:mouseover="show" /></p></div><script>var vm = new Vue({el:'#app',data:{msg:'<h1>hello</h1>',msg2:'(v-bind属性!)this button!'},methods:{show:function(){alert("OK")}, }})</script></body> </html>
vue第三话: 跑马灯练习
<!DOCTYPE html> <html><head><meta charset="utf-8"><title></title><script src="vue.js"></script></head><body><div id="app"><input type="button" value="启动" @click="start" /><input type="button" value="停止"@click="stop" /><input type="text" :value="info" /><h1>{{ info }}</h1></div><script>var vm = new Vue({el:'#app',data:{info:'hello world !',Intervalid:null,},methods:{start(){ // var _this = this // setInterval(function(){ // // console.log(this.info) // var start0 = _this.info.substring(0,1) // var end0 = _this.info.substring(1) // _this.info = end0 + start0 // },400)// => 说明函数体外部的this 参数 传递至函数体内部!if(this.Intervalid != null) return;this.Intervalid = setInterval( () => {// console.log(this.info)var start0 = this.info.substring(0,1)var end0 = this.info.substring(1)this.info = end0 + start0},400)},stop(){clearInterval(this.Intervalid);this.Intervalid = null;},}})</script></body> </html>
vue第四话 v-on 事件修饰符
.stop 阻止冒泡
.prevent 阻止默认时间
.capture 添加时间侦听器使用事件模式
.self 只当前事件在该元素本身(比如不是子元素)触发时触发回调
.once 事件只触发一次
<!DOCTYPE html> <html><head><meta charset="utf-8"><title></title><script></script><script src="vue.js"></script><style>.inner{height: 200px;width: 200px;background-color: aqua;}.inner2{height: 200px;width: 200px;background-color: firebrick;}.inner3{height: 200px;width: 200px;background-color:greenyellow;}.inner4{height: 200px;width: 200px;background-color:gray;}</style></head><body><div id="app"><!-- 此时点击按钮,同时也会触发div的点击事件. --><div class="inner" @click="div0"><input type="button" value="点击" @click="inp0"/><!-- .stop --><input type="button" value="点击(.stop)" @click.stop="inp0"/><!-- .prevent 阻止默认行为 --><p><a href="http://www.baidu.com" @click.prevent="bdclick">百度链接</a></p></div><!-- .capture 捕获机制--><div class="inner2" @click.capture="div0"><input type="button" value="点击" @click="inp0"/></div><!-- .self 点击当前元素时触发--><div class="inner3" @click.self="div0"><input type="button" value="点击" @click.self="inp0"/></div><!-- .once只触发一次 --><div class="inner4" @click.once="div0"><input type="button" value="点击" @click.once="inp0"/></div><!-- 方法之间可以相互叠加调用! --><!-- .self .stop 区别:.self只阻止 自己元素上的冒泡,并不阻止自己外层的元素冒泡.stop阻止除自已以外的其他元素冒泡 --></div><script>var ve = new Vue({el:'#app',data:{ },methods:{div0(){console.log('this div0!')},inp0(){console.log("this inp0!")},bdclick(){console.log('baidu 链接事件!')}},})</script></body> </html>
vue 第五话 双向数据绑定 v-model
<!DOCTYPE html> <html><head><meta charset="utf-8"><title></title><script></script><script src="vue.js"></script></head><body><div id="app"><!-- 使用v-model 可以是先,表单元素和model中数据的双向书绑定但是注意!v-model 只能运用在 表单元素中 --><input type="text" v-model="msg" /><h3>{{ msg }}</h3></div><script>var ve = new Vue({el:'#app',data:{msg:'hello world ! '},methods:{},})</script></body> </html>
vue第6话 简易计算器练习
<!DOCTYPE html> <html><head><meta charset="utf-8"><title></title><script></script><script src="vue.js"></script></head><body><div id="app"><input type="text" v-model="num1" /><select v-model="opt"><option value ="+">+</option><option value ="-">-</option><option value ="*">*</option><option value ="/">/</option></select><input type="text" v-model="num2" /><input type="button" value="=" @click='jisuan' /><input type="text" v-model="result" /></div><script>var ve = new Vue({el:'#app',data:{num1:0,opt:'+',num2:0,result:0,},methods:{jisuan(){ // switch(this.opt){ // case '+': // this.result = parseInt(this.num1) + parseInt(this.num2) // break; // case '-': // this.result = parseInt(this.num1) - parseInt(this.num2) // break; // case '*': // this.result = parseInt(this.num1) * parseInt(this.num2) // break; // case '/': // this.result = parseInt(this.num1) / parseInt(this.num2) // break; // }this.result = eval(this.num1 + this.opt + this.num2)},},})</script></body> </html>
vue 第七话 样式选择
<!DOCTYPE html> <html><head><meta charset="utf-8"><title></title><script src="vue.js"></script><style>.st1{width: 200px;height: 200px;}.st2{background-color: #ADFF2F;}.active{display: none;}</style></head><body><div id="app"><input type="button" value="显示" @click='a'/><input type="button" value="隐藏" @click='b' /><p><h1 :class="['st1','st2']">aaaaaaaaaaaa !!!</h1></p><p><h1 :class="['st1','st2',dis?'active':'']">bbbbbbbbbbbb !!!</h1></p><p><h1 :class="['st1','st2',{'active':dis}]">cccccccccccc !!!</h1></p><p><h1 :class="{st1:true,st2:true,active:dis}">dddddddddd !!!</h1></p><p><h1 :class="sobj">EEEEEEEEEEEEE !!!</h1></p></div><script>var vm = new Vue({el: '#app',data: {dis:false,sobj:{st1:true,st2:true,active:false},},methods: {a(){this.dis = false},b(){this.dis = true},}})</script></body> </html>
vue 第八话 内联样式
<!DOCTYPE html> <html><head><meta charset="utf-8"><title></title><script src="vue.js"></script></head><body><div id="app"><h1 :style="{color:'red','font-weight':200}">asdadsada</h1><h1 :style="sty1">asdadsada</h1> <h1 :style="[sty1 , sty2]">asdadsada</h1> </div><script>var vm = new Vue({el: '#app',data: {sty1:{color:'green','font-weight':100},sty2:{'font-style':'italic'},},methods: {}})</script></body> </html>
vue 第九话 v-for循环
<!DOCTYPE html> <html><head><meta charset="utf-8"><title></title><script src="vue.js"></script></head><body><div id="app"><p>{{ list[0] }}</p><p>{{ list[1] }}</p><p>{{ list }}</p><!-- 循环列表 --><p v-for='i in list'>{{ i }}</p><!-- 循环列表,以及列表索引 --><p v-for='i,index in list'>{{ i }} - {{ index }}</p><!-- 循环列表对象 --><p v-for='i,j in list2'>{{ i.id }} - {{ i.name }} - {{ j }}</p><!-- 循环对象 --><p v-for='i,j,l in user'>{{ i }}- {{ j }} - {{ l }}</p><!-- 循环数据 --><p v-for='count in 15'>{{ count }}</p></div><script>var vm = new Vue({el: '#app',data: {list:[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9],list2:[{id:1,name:'a1'},{id:2,name:'a2'},{id:3,name:'a3'},{id:4,name:'a4'},{id:5,name:'a5'},{id:6,name:'a6'},],user:{id:1,name:'alex',gender:'男',},},methods: {}})</script></body> </html>
vue 第十话 v-for key 值 数据绑定
<!DOCTYPE html> <html><head><meta charset="utf-8"><title></title><script src="vue.js"></script></head><body><div id="app"><p><label>id </label><input type="text" v-model="id"/><label>name</label> <input type="text" v-model="name"/><input type="button" value="add" @click="add" /></p><label>序号</label> - <label>姓名</label><p v-for='i in info' :key='i.id'><input type="checkbox" />{{ i.id }} ------- {{ i.name }}</p><!-- 注意:!!!v-for 循环的时候 key属性只能使用num 或 str 数据类型绑定key在使用的时候,必须要使用v-bind属性绑定的形式,指定key的值在组件中 使用v-for 循环的时候 或者在一些特殊的情况中 如果v-for有问题 必须在使用v-for的是同时指定唯一的字符串/数字 类型:key值 --></div><script>var vm = new Vue({el: '#app',data: {id:'',name:'',info:[{id:1,name:'a1'},{id:2,name:'a2'},{id:3,name:'a3'},{id:4,name:'a4'},{id:5,name:'a5'},{id:6,name:'a6'},],},methods: {add(){// this.info.push({id:this.id,name:this.name})this.info.unshift({id:this.id,name:this.name})},}})</script></body> </html>
vue第十一话 v-if 以及 v-show
<!DOCTYPE html> <html><head><meta charset="utf-8"><title></title><script src="vue.js"></script></head><body><div id="app"><input type="button" value="切换" @click="qiehuan"/><h3 v-if="flag">v-if 语句</h3><h3 v-show="flag">v-show 语句</h3></div><!-- v-if 特点:每次都会重新删除或创建元素有较高的切换性能消耗如果元素设计到频繁的切换,最好不要使用v-if而推荐使用v-showv-show 特点:只是切换了元素的display:none的样式有较高的初始渲染消耗如果元素可能永远也不会被显示出来被用户看到,则推荐使用v-if --><script>var vm = new Vue({el: '#app',data: {flag:true,},methods: {qiehuan(){this.flag = !this.flag}}})</script></body> </html>
