免费拥有自己的网站成都网络营销推广公司
文章目录
- 序言
- TODO : 每个框架10个题默写3遍
- 背包问题
- 排序
- 堆排序
- 多线程
- 数据结构设计(LRU.LFU要求熟练背诵并默认)
- LRU
- LFU
- 红黑树
- 跳表
- 练习题
- labuldong 的刷题笔记目录
- 第⼀章、基础数据结构
- 数组双指针
- ⼆分搜索
- 34.在排序数组中查找元素的第⼀个和最后⼀个位置
- 704. ⼆分查找
- 35. 搜索插⼊位置
- 354. 俄罗斯套娃信封问题
- 392. 判断⼦序列
- 793. 阶乘函数后 K 个零
- 875. 爱吃⾹蕉的珂珂
- 1011. 在 D 天内送达包裹的能⼒
- 滑动窗⼝
- 3. ⽆重复字符的最⻓⼦串
- 76. 最⼩覆盖⼦串
- 438. 找到字符串中所有字⺟异位词
- 567. 字符串的排列
- 239. 滑动窗⼝最⼤值
- 其他题⽬
- 26. 删除有序数组中的重复项
- 27. 移除元素
- 283. 移动零
- 259. 较⼩的三数之和
- 11. 盛最多⽔的容器
- 42. 接⾬⽔
- 15. 三数之和
- 18. 四数之和
- 1099. ⼩于 K 的两数之和
- 16. 最接近的三数之和
- 870. 优势洗牌
- 986. 区间列表的交集
- 链表双指针
- 2. 两数相加
- 19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
- 21. 合并两个有序链表
- 23. 合并 K 个升序链表
- 141. 环形链表
- 142. 环形链表 II
- 160. 相交链表
- 876. 链表的中间结点
- 25. K 个⼀组翻转链表
- 83. 删除排序链表中的重复元素
- 92. 反转链表 II
- 234. 回⽂链表
- 前缀和
- 303. 区域和检索 - 数组不可变
- 304. ⼆维区域和检索 - 矩阵不可变
- 327. 区间和的个数
- 1352. 最后 K 个数的乘积
- 差分数组
- 370. 区间加法
- 1094. 拼⻋
- 1109. 航班预订统计
- 队列/栈算法
- 20. 有效的括号
- 921. 使括号有效的最少添加
- 1541. 平衡括号字符串的最少插⼊次数
- 32. 最⻓有效括号
- 71. 简化路径
- 150. 逆波兰表达式求值
- 225. ⽤队列实现栈
- 232. ⽤栈实现队列
- 239. 滑动窗⼝最⼤值
- ⼆叉堆
- 23. 合并 K 个升序链表
- 215. 数组中的第 K 个最⼤元素
- 295. 数据流的中位数
- 703. 数据流中的第 K ⼤元素
- 1834. 单线程 CPU
- 1845. 座位预约管理系统
- 数据结构设计
- 146. LRU 缓存机制
- 341. 扁平化嵌套列表迭代器
- 380. O(1) 时间插⼊、删除和获取随机元素
- 460. LFU 缓存
- 895. 最⼤频率栈
- 1845. 座位预约管理系统
- 第⼆章、进阶数据结构
- ⼆叉树
- 94. ⼆叉树的中序遍历
- 100. 相同的树
- 102. ⼆叉树的层序遍历
- 103. ⼆叉树的锯⻮形层序遍历
- 104. ⼆叉树的最⼤深度
- 144. ⼆叉树的前序遍历
- 543. ⼆叉树的直径
- 105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造⼆叉树
- 106. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造⼆叉树
- 654. 最⼤⼆叉树
- 107. ⼆叉树的层序遍历 II
- 111. ⼆叉树的最⼩深度
- 114. ⼆叉树展开为链表
- 116. 填充每个节点的下⼀个右侧节点指针
- 226. 翻转⼆叉树
- 145. ⼆叉树的后序遍历
- 222. 完全⼆叉树的节点个数
- 236. ⼆叉树的最近公共祖先
- 297. ⼆叉树的序列化与反序列化
- 341. 扁平化嵌套列表迭代器
- 501. ⼆叉搜索树中的众数
- 559. N 叉树的最⼤深度
- 589. N 叉树的前序遍历
- 590. N 叉树的后序遍历
- 652. 寻找重复的⼦树
- 965. 单值⼆叉树
- ⼆叉搜索树
- 95. 不同的⼆叉搜索树 II
- 96. 不同的⼆叉搜索树
- 98. 验证⼆叉搜索树
- 450. 删除⼆叉搜索树中的节点
- 700. ⼆叉搜索树中的搜索
- 701. ⼆叉搜索树中的插⼊操作
- 230. ⼆叉搜索树中第 K ⼩的元素
- 538. 把⼆叉搜索树转换为累加树
- 1038. 把⼆叉搜索树转换为累加树
- 501. ⼆叉搜索树中的众数
- 530. ⼆叉搜索树的最⼩绝对差
- 783. ⼆叉搜索树节点最⼩距离
- 1373. ⼆叉搜索⼦树的最⼤键值和 图论算法
- 图论算法
- 图的遍历
- 797. 所有可能的路径
- ⼆分图
- 785. 判断⼆分图
- 886. 可能的⼆分法
- 环检测/拓扑排序
- 207. 课程表
- 210. 课程表 II 并查集算法
- 765. 情侣牵⼿
- 130. 被围绕的区域
- 990. 等式⽅程的可满⾜性
- 最⼩⽣成树
- 261. 以图判树
- 1135. 最低成本联通所有城市
- 1584. 连接所有点的最⼩费⽤
- 最短路径
- 743. ⽹络延迟时间
- 1514. 概率最⼤的路径
- 1631. 最⼩体⼒消耗路径
- 第三章、暴⼒搜索算法
- 回溯算法
- 17. 电话号码的字⺟组合
- 22. 括号⽣成
- 37. 解数独
- 39. 组合总和
- 46. 全排列
- 77. 组合
- 78. ⼦集
- 51. N 皇后
- 104. ⼆叉树的最⼤深度
- 494. ⽬标和
- 698. 划分为 k 个相等的⼦集
- DFS 算法
- 130. 被围绕的区域
- 200. 岛屿数量
- 694. 不同的岛屿数量
- 695. 岛屿的最⼤⾯积
- 1020. ⻜地的数量
- 1254. 统计封闭岛屿的数⽬
- 1905. 统计⼦岛屿
- BFS 算法
- 102. ⼆叉树的层序遍历
- 103. ⼆叉树的锯⻮形层序遍历
- 107. ⼆叉树的层序遍历 II
- 111. ⼆叉树的最⼩深度
- 752. 打开转盘锁
- 773. 滑动谜题
- 第四章、动态规划算法
- ⼀维 DP
- 45. 跳跃游戏 II
- 55. 跳跃游戏
- 53. 最⼤⼦序和
- 70. 爬楼梯
- 198. 打家劫舍
- 213. 打家劫舍 II
- 337. 打家劫舍 III
- 300. 最⻓递增⼦序列
- 354. 俄罗斯套娃信封问题
- 322. 零钱兑换
- ⼆维 DP
- 10. 正则表达式匹配
- 62. 不同路径
- 64. 最⼩路径和
- 72. 编辑距离
- 121. 买卖股票的最佳时机
- 122. 买卖股票的最佳时机 II
- 123. 买卖股票的最佳时机 III
- 188. 买卖股票的最佳时机 IV
- 309. 最佳买卖股票时机含冷冻期
- 714. 买卖股票的最佳时机含⼿续费
- 174. 地下城游戏
- 312. 戳⽓球
- 416. 分割等和⼦集
- 494. ⽬标和
- 514. ⾃由之路
- 518. 零钱兑换 II
- 583. 两个字符串的删除操作
- 712. 两个字符串的最⼩ ASCII 删除和
- 1143. 最⻓公共⼦序列
- 787. K 站中转内最便宜的航班
- 887. 鸡蛋掉落
- 931. 下降路径最⼩和
- 背包问题
- 416. 分割等和⼦集
- 494. ⽬标和
- 518. 零钱兑换 II
- 第五章、其他经典算法
- 数学算法
- 17. 电话号码的字⺟组合
- 77. 组合
- 78. ⼦集
- 134. 加油站
- 136. 只出现⼀次的数字
- 191. 位 1 的个数
- 231. 2 的幂
- 268. 丢失的数字
- 172. 阶乘后的零
- 793. 阶乘函数后 K 个零
- 204. 计数质数
- 292. Nim 游戏
- 319. 灯泡开关
- 877. ⽯⼦游戏
- 295. 数据流的中位数
- 372. 超级次⽅
- 382. 链表随机节点
- 398. 随机数索引
- 391. 完美矩形
- 509. 斐波那契数
- 645. 错误的集合
- 710. ⿊名单中的随机数
- 区间问题
- 56. 合并区间
- 986. 区间列表的交集
- 1288. 删除被覆盖区间
- 435. ⽆重叠区间
- 452. ⽤最少数量的箭引爆⽓球
- 1024. 视频拼接
- 1834. 单线程 CPU
序言
解答以下的几个困惑:
- 不知道整么想
- 不知道整么做
- 不知道要注意些什么
稍微整理了一下,发现要搞懂的题目特别多,就收缩边界,不要展开,刷完leedcode前300道题,剩下的听天由命。
像 背单词⼀样背算法,对于各种算法技巧,如果没事⼉就看,哪有记不住的道理。
如果看了题 ⽬不能迅速想到解题思路,或者看了思路写不出代码,那就说明这块知识点掌握的不太好,需要重新复习巩固。
TODO : 每个框架10个题默写3遍
背包问题
背包问题专辑
排序
堆排序
//先写出一个节点的堆化操作,再遍历每个节点实现堆化,输出的话就是用最后一个节点替换第一个节点,再堆化。这需要一个过程
func SortArray() []int {arr := []int{6, 3, 5, 4, 1, 2, 7}build(arr)var res []intfor len(arr) != 0 {res = append(res, arr[0])arr[0] = arr[len(arr)-1]arr = arr[:len(arr)-1]build(arr)}fmt.Println(res)return res
}func build(arr []int) {for i := len(arr) - 1; i >= 0; i-- {heapfy(arr, i)}
}func heapfy(nums []int, index int) {if index == len(nums) || (2*index+1) >= len(nums) {return}if (2*index + 2) >= len(nums) {if nums[2*index+1] < nums[index] {swap(nums, 2*index+1, index)}return}root := indexleft := 2*index + 1right := 2*index + 2rootV := nums[root]leftV := nums[left]rightV := nums[right]minV := rootVif leftV < minV {minV = leftVswap(nums, left, root)if left < len(nums) {heapfy(nums, left)}}if rightV < minV {minV = rightVswap(nums, right, root)if right < len(nums) {heapfy(nums, right)}}return
}func swap(nums []int, x, y int) {temp := nums[x]nums[x] = nums[y]nums[y] = temp
}
堆排序:
力扣上能过
func sortArray(nums []int) []int {// 堆排序-大根堆,升序排序,基于比较交换的不稳定算法,时间O(nlogn),空间O(1)-迭代建堆// 遍历元素时间O(n),堆化时间O(logn),开始建堆次数多些,后面次数少 // 主要思路:// 1.建堆,从非叶子节点开始依次堆化,注意逆序,从下往上堆化// 建堆流程:父节点与子节点比较,子节点大则交换父子节点,父节点索引更新为子节点,循环操作// 2.尾部遍历操作,弹出元素,再次堆化// 弹出元素排序流程:从最后节点开始,交换头尾元素,由于弹出,end--,再次对剩余数组元素建堆,循环操作// 建堆函数,堆化var heapify func(nums []int, root, end int)heapify = func(nums []int, root, end int) {// 大顶堆堆化,堆顶值小一直下沉for {// 左孩子节点索引child := root*2 + 1// 越界跳出if child > end {return}// 比较左右孩子,取大值,否则child不用++if child < end && nums[child] <= nums[child+1] {child++}// 如果父节点已经大于左右孩子大值,已堆化if nums[root] > nums[child] {return}// 孩子节点大值上冒nums[root], nums[child] = nums[child], nums[root]// 更新父节点到子节点,继续往下比较,不断下沉root = child}}end := len(nums)-1// 从最后一个非叶子节点开始堆化for i:=end/2;i>=0;i-- {heapify(nums, i, end)}// 依次弹出元素,然后再堆化,相当于依次把最大值放入尾部for i:=end;i>=0;i-- {nums[0], nums[i] = nums[i], nums[0]end--heapify(nums, 0, end)}return nums
}
力扣上超时了
package sortimport "fmt"//堆排序
func main() {arr := []int{1, 9, 10, 30, 2, 5, 45, 8, 63, 234, 12}fmt.Println(HeapSort(arr))
}
func HeapSortMax(arr []int, length int) []int {// length := len(arr)if length <= 1 {return arr}depth := length/2 - 1 //二叉树深度for i := depth; i >= 0; i-- {topmax := i //假定最大的位置就在i的位置leftchild := 2*i + 1rightchild := 2*i + 2if leftchild <= length-1 && arr[leftchild] > arr[topmax] { //防止越过界限topmax = leftchild}if rightchild <= length-1 && arr[rightchild] > arr[topmax] { //防止越过界限topmax = rightchild}if topmax != i {arr[i], arr[topmax] = arr[topmax], arr[i]}}return arr
}
func HeapSort(arr []int) []int {length := len(arr)for i := 0; i < length; i++ {lastlen := length - iHeapSortMax(arr, lastlen)if i < length {arr[0], arr[lastlen-1] = arr[lastlen-1], arr[0]}}return arr
}
多线程
leedcode多线程9道题
- 实现1到100的累加求和
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger();for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {int finalI = i;Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {for (int j = (finalI - 1) * 10 + 1; j <= finalI * 10; j++) {count.addAndGet(j);}});thread.start();thread.join();//join必须在start后⾯;join将两个交替执⾏的线程强制为按顺序执⾏。可以说将并⾏的改 成了串⾏}//结果正确5050}System.out.println(count.get());}
数据结构设计(LRU.LFU要求熟练背诵并默认)
LRU
LRU是从时间维度进行淘汰
// 错误设计1:list是拿不到当前节点的引用的
package mainimport ("container/list""fmt"
)func main() {obj := Constructor(2)obj.Put(1, 1)obj.Put(2, 2)fmt.Println(obj.Get(1)) //2obj.Put(3, 3)fmt.Println(obj.Get(2)) //3obj.Put(4, 4)fmt.Println(obj.Get(1)) //4fmt.Println(obj.Get(3)) //4fmt.Println(obj.Get(4)) //4}type LRUCache struct {capacity intsize intcache map[int]*list.Listque *list.List
}type node struct {key, value int
}func Constructor(capacity int) LRUCache {return LRUCache{capacity: capacity,cache: make(map[int]*list.List),que: list.New(),}
}func (this *LRUCache) Get(key int) int {if v, ok := this.cache[key]; ok {this.que.MoveBefore(v.Front(), this.que.Front())return (v.Front().Value).(node).value}return -1
}func (this *LRUCache) Put(key int, value int) {if v, ok := this.cache[key]; ok {this.que.MoveBefore(v.Front(), this.que.Front())} else {if this.size+1 > this.capacity {//满了this.que.Remove(this.que.Back())delete(this.cache, key)nd := node{key: key,value: value,}this.que.PushFront(nd)this.cache[key] = this.que} else {nd := node{key: key,value: value,}this.que.PushFront(nd)this.cache[key] = this.que/**我依次put了1,2,3我希望的this.cache[key] = this.que是1-2-3 实际 1-2-32-3 实际 1-2-33 实际 1-2-3*/this.size++}}
}
修正后的正确设计–基于golang的list.List双链表,它的remove是O(1),不像linkednode是O(n)
type LRUCache struct {size intcapacity intque *list.Listcache map[int]*list.Element
}type Node struct {key intvalue int
}func Constructor(capacity int) LRUCache {cache := LRUCache{size: 0,capacity: capacity,cache: make(map[int]*list.Element),que: list.New(),}return cache
}func (this *LRUCache) Get(key int) int {if v, ok := this.cache[key]; ok {/**this.que.Remove(v)node := v.Value.(Node)push进去的是Node,那么下文取出来时Value.(*Node)就会报错,必须推进去是list.Elementthis.que.PushFront(node) */this.que.MoveToFront(v)return v.Value.(*Node).value}return -1
}func (this *LRUCache) Put(key int, value int) {if v, ok := this.cache[key]; ok {v.Value.(*Node).value = valuethis.que.MoveToFront(v)} else {if this.size == this.capacity {//满了back := this.que.Back()delete(this.cache, back.Value.(*Node).key)this.que.Remove(back)this.size--}front := this.que.PushFront(&Node{key: key,value: value,})this.cache[key] = frontthis.size++}
}
不符合时间复杂度的设计-java lineknode
// 不符合时间复杂度的设计2:lineknode的remove在改场景该用法的使用下时间复杂度是O(n)
class LRUCache {private int capacity;private Map<Integer, Integer> cache;private LinkedList<Integer> link;public LRUCache(int capacity) {this.capacity = capacity;cache = new HashMap<>();link = new LinkedList<>();}public int get(int key) {if (!cache.containsKey(key)) return -1;else {int value = cache.get(key);link.remove(Integer.valueOf(key));link.addFirst(key);return value;}}public void put(int key, int value) {if (capacity == 0) return;if (cache.containsKey(key)) { //k存在,更新缓存kvcache.put(key, value);link.remove(Integer.valueOf(key));link.addFirst(key);} else {if (link.size() == capacity) {cache.remove(Integer.valueOf(link.pollLast()));}link.addFirst(key);cache.put(key, value);}}
}
自定义双链表的正确的LRU实现
type LRUCache struct {size intcapacity intcache map[int]*DLinkedNode//双链表的经典实现,记录头节点和尾节点,并且头节点和尾节点都是虚拟哑结点(能极大简化链表的操作)//双链表用空间换时间,可实现删除是O(1)head, tail *DLinkedNode
}type DLinkedNode struct {key intvalue intprev, next *DLinkedNode
}func initDLinkedNode(key, value int) *DLinkedNode {return &DLinkedNode{key: key,value: value,}
}
func Constructor(capacity int) LRUCache {cache := LRUCache{size: 0,capacity: capacity,cache: make(map[int]*DLinkedNode),// 双链表的构造非常巧妙,初始化首尾2个哑结点head: initDLinkedNode(0, 0),tail: initDLinkedNode(0, 0),}cache.head.next = cache.tailcache.tail.prev = cache.headreturn cache
}func (this *LRUCache) Get(key int) int {if v, ok := this.cache[key]; ok {val := v.valuethis.moveToHead(v)return val}return -1
}func (this *LRUCache) Put(key int, value int) {if v, ok := this.cache[key]; ok {//this.moveToHead(v) //假设已有3,1,现在用户更新成了3,5,所以这个不能省v.value = valuev.value = valuethis.moveToHead(v)} else {if this.size == this.capacity {//满了tail := this.removeTail()//删除的是key,不是value,不要写成tail.value,这里非常容易不动脑子的写成valuedelete(this.cache, tail.key) this.size--}node := initDLinkedNode(key, value)this.addToHead(node)this.cache[key] = nodethis.size++}
}func (this *LRUCache) addToHead(node *DLinkedNode) {/**this.head.next = nodenode.prev = this.headthis.head.next.prev = node//this.tail.prev = node //写错了,正确写法见上node.next = this.head.next//node.next = this.tail //写错了,正确写法见上*/node.prev = this.headnode.next = this.head.nextthis.head.next.prev = nodethis.head.next = node}func (this *LRUCache) removeNode(node *DLinkedNode) {/**错误写法p := node.prevn := node.nextn.next = pp.next = n*/node.prev.next = node.nextnode.next.prev = node.prev
}func (this *LRUCache) moveToHead(node *DLinkedNode) {//先移除节点,在添加到头部,非常妙,简化了移动指针的很复杂的操作this.removeNode(node)this.addToHead(node)
}func (this *LRUCache) removeTail() *DLinkedNode {prev := this.tail.prevthis.removeNode(prev)return prev
}
LFU
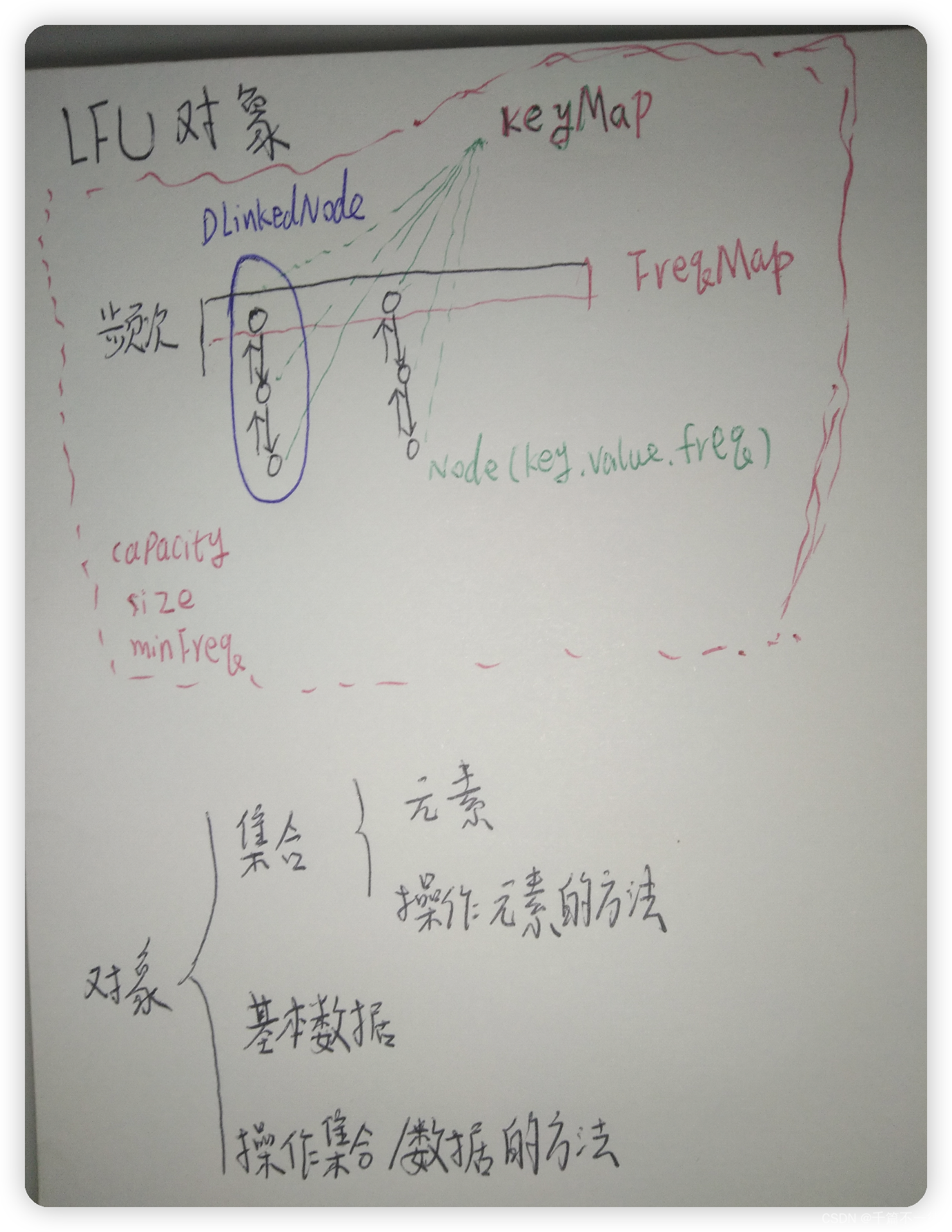
LFU根据使用频次进行淘汰-同频再根据时间淘汰
type LFUCache struct {minFreq intsize intcapacity intfreqTable map[int]*DLinkedNodekeyTable map[int]*Node
}func Constructor(capacity int) LFUCache {cache := LFUCache{size: 0,capacity: capacity,freqTable: make(map[int]*DLinkedNode),keyTable: make(map[int]*Node),minFreq: 0,}return cache
}func (this *LFUCache) Get(key int) int {if val, ok := this.keyTable[key]; ok {value := val.valuefreq := val.freqlnode := this.freqTable[freq]lnode.remove(val)delete(this.keyTable,key)aa := this.freqTable[this.minFreq]if aa.head.next == aa.tail {this.minFreq++}if mv, ok := this.freqTable[freq+1]; ok {n :=initNode(key, value, freq+1)mv.addFirst(n)this.keyTable[key]=n} else {lnode := initDLinkedNode()node := initNode(key, value, freq+1)this.keyTable[key] = nodelnode.addFirst(node)this.freqTable[freq+1] = lnode}return value} else {return -1}
}func (this *LFUCache) Put(key int, value int) {if val, ok := this.keyTable[key]; ok {//升级频率freq := val.freqlnode := this.freqTable[freq]lnode.remove(val)aa := this.freqTable[this.minFreq]if aa.head.next == aa.tail {this.minFreq++}if mv, ok := this.freqTable[freq+1]; ok {n := initNode(key, value, freq+1)mv.addFirst(n)this.keyTable[key] = n} else {lnode := initDLinkedNode()node := initNode(key, value, freq+1)this.keyTable[key] = nodelnode.addFirst(node)this.freqTable[freq+1] = lnode}} else {if this.size == this.capacity {if this.capacity == 0 {return} else {prev := this.freqTable[this.minFreq].tail.prevthis.freqTable[this.minFreq].remove(prev)delete(this.keyTable, prev.key)//delete(this.freqTable, this.minFreq) capity容量表示能放多少个key,而不是频次分类的key数量this.size--}}if val, ok := this.freqTable[1]; ok {n := initNode(key, value, 1)val.addFirst(n)this.keyTable[key] = n} else {lnode := initDLinkedNode()node := initNode(key, value, 1)this.keyTable[key] = nodelnode.addFirst(node)this.freqTable[1] = lnode}this.size++this.minFreq = 1}
}type Node struct {key intvalue intfreq intprev, next *Node
}type DLinkedNode struct {head, tail *Node
}func (n DLinkedNode) addFirst(node *Node) {node.next = n.head.nextn.head.next.prev = noden.head.next = nodenode.prev = n.head
}func (n DLinkedNode) remove(val *Node) {nt := val.nextp := val.prevp.next = ntnt.prev = p
}func initDLinkedNode() *DLinkedNode {head := initNode(0, 0, 0)tail := initNode(0, 0, 0)head.next = tailtail.prev = headreturn &DLinkedNode{head: head,tail: tail,}
}func initNode(key, value, freq int) *Node {return &Node{key: key,value: value,freq: freq,}
}红黑树
跳表
练习题
labuldong 的刷题笔记目录
labuldong 的刷题笔记目录
