泉州建站费用百度推广客服电话
基本运行功能
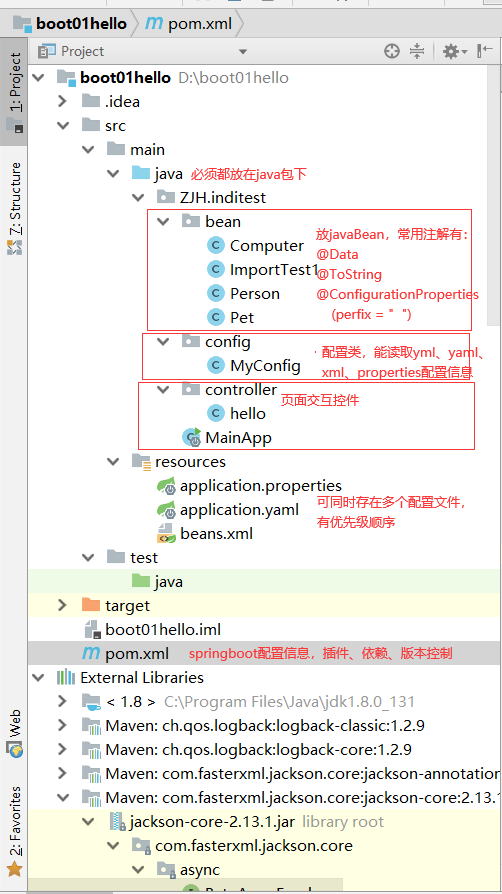
pom.xml
格式
pom.xml配置详解
注意结构,如:dependencies中包括了多个dependency
JavaBean
常用注解
-
@Data:注解在类上;提供类所有属性的 getting 和 setting 方法,此外还提供了equals、canEqual、hashCode、toString 方法
有了@Data提供的get set方法才能顺利的从配置文件中读取信息 -
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = “zjh”)//配置zjh属性,这个注解要结合config中的EnableConfigurationProperties({Person.class,Pet.class})允许配置,还要结合controller中的
@Autowired
Person zjh;//注入到IOC容器才能反应
(@Component以被@EnableConfigurationProperties替代)
示例
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "zjh")//配置zjh属性
@Data
@ToString
public class Person {private String userName;private Boolean boss;private Date birth;private Integer age;private Pet pet;private String[] interests;private List<String> animal;private Map<String, Object> score;private Set<Double> salarys;private Map<String, List<Pet>> allPets;
}
config配置类
常用注解
-
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false或true)
Full(proxyBeanMethods = true)【保证每个@Bean方法被调用多少次返回的组件都是单实例的】
Lite(proxyBeanMethods = false)【每个@Bean方法被调用多少次返回的组件都是新创建的】
组件依赖必须使用Full模式默认。其他默认是否Lite模式 -
@EnableConfigurationProperties({Person.class,Pet.class}){}中的类可以由配置文件配置
-
@Bean 给IOC容器添加组件,@Bean和@Import、@ConfigurationProperties 有冲突,并且@Bean也需要在controller下@Autowired注入
-
@Import 导入某个类,创建默认组件,组件名默认为全类名,和@Bean冲突
-
@ImportResource 解析xml配置
示例
@ImportResource("classpath:beans.xml")
@Import({ImportTest1.class})
//下面两个才是基本运行所必要的注解
@EnableConfigurationProperties({Person.class,Pet.class})
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
public class MyConfig {@Beanpublic ImportTest1 importTest1(){ImportTest1 it1 = new ImportTest1("test");return it1;}//这个Bean组件就唯一添加到了IOC容器中,并且可以被Cotroller或main获取}
controller控制类

常用注解
- @RestController声明,== @ResponseBody+@Controller
- @RequestMapping("/hello"),RUL后缀映射访问请求
- @Autowired,每个要使用的Bean都需要@Autowired注入容器
示例
@RestController
public class hello {//映射请求:浏览器访问请求@RequestMapping("/hello")//收到hello请求public String handle01(){//反应return "world";}// 自动注入,需要Person有空参构造//或Person类直接实现@Data注解@AutowiredPerson zjh;@RequestMapping("/zjh")//zjh必须先//用 @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "zjh")//并且在application.yaml中配置public Person handle02(){return zjh;}@AutowiredPet nn;@RequestMapping("/nn")public Pet handle03(){return nn;}
}
运行主类
- @SpringBootApplication声明为主类
- SpringApplication.run(MainApp.class, args)运行且返回IOC容器
- 该单独的类MainAPP.class和以上三个包同目录
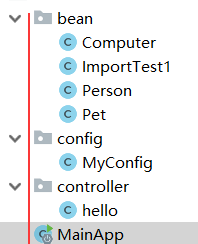
- 该单独的类MainAPP.class和以上三个包同目录
单例、组件依赖:proxyBeanMethods
因为在config类中也遇到了proxyBeanMethods,主类中也有proxyBeanMethods参数
他们分别为:
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = true)
@SpringBootApplication(proxyBeanMethods = true)
Full(proxyBeanMethods = true)【保证每个@Bean方法被调用多少次返回的组件都是单实例的】
Lite(proxyBeanMethods = false)【每个@Bean方法被调用多少次返回的组件都是新创建的】
组件依赖必须使用默认的Full模式,其他则默认使用Lite模式。
示例
@SpringBootApplication
public class MainApp {//这是入口public static void main(String[] args) {//不光可以启动,还可以有返回值IOC容器ConfigurableApplicationContext run = SpringApplication.run(MainApp.class, args);//返回容器run}}
Bean单例的体现
//单例实例的创建不能用new,而是反射机制
//并且在MyConfig中已创建该类的@Bean//或者//具体属性值由yaml配置
//总之,IOC容器中如下getBean得到的是该类的唯一:单例Person person1 = run.getBean(Person.class);Pet pet1 = run.getBean(Pet.class);System.out.println(pet1);System.out.println(person1);
体现2
System.out.println("***************************");String[] beanNamesForType = run.getBeanNamesForType(person1.getClass());//获取所有Person组件的所有名字for(String str : beanNamesForType){System.out.println(str);}//单例下只有一个zjh-ZJH.inditest.bean.Person
结构分析
- 属性设置:Bean声明@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = “zjh”)——>在application.yaml中配置
- 配置组件:声明@Configuration的类就是配置组件——>
@EnableConfigurationProperties({Person.class,Pet.class})
使配置好的Bean生效 - 控制组件:声明@RestController的类就是控制组件——>
结合@Autowired注入,@RequestMapping("/hello")映射请求 - 主类运行:声明@SpringBootApplication的类就是主类,有main方法体——> ConfigurableApplicationContext run = SpringApplication.run(MainApp.class, args);固定用法,运行且返回IOC容器
