打开网站后直接做跳转页面吗/推广联系方式
Runtime
2015.01.19By 970655147
这个类主要适用于添加jvm关闭时的钩子函数, 运行进程[使用ProcessBuilder], 获取jvm可使用的cpu个数, 内存的使用情况, 运行gc, 关闭jvm, 加载本地库等等
start ->
声明
, 大家可以看看注释
/*** Every Java application has a single instance of class* <code>Runtime</code> that allows the application to interface with* the environment in which the application is running. The current* runtime can be obtained from the <code>getRuntime</code> method.* <p>* An application cannot create its own instance of this class.** @author unascribed* @see java.lang.Runtime#getRuntime()* @since JDK1.0*/public class Runtime
Runtime. 属性
// 可以通过getRuntime获取runtimeprivate static Runtime currentRuntime = new Runtime();
Runtime. Runtime()
// 构造方法私有化 构造单例/** Don't let anyone else instantiate this class */private Runtime() {}
Runtime. getRuntime()
// 获取Runtimepublic static Runtime getRuntime() {return currentRuntime;}
Runtime. exit(int status)
// System.ext(exitCode ) 也是调用了Runtime.exit(exitCode )
public void exit(int status) {// security checkSecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager();if (security != null) {security.checkExit(status);}// exitShutdown.exit(status);}Shutdown. exit(int status)/* Invoked by Runtime.exit, which does all the security checks.* Also invoked by handlers for system-provided termination events,* which should pass a nonzero status code.*/
static void exit(int status) {// 如果status不为0, 更新runFinalizersOnExit为false// 检测状态, 如果state为RUNNING, 更新state为HOOKS// 如果状态为FINALIZERS[sequences方法中得到该状态], 则判断status如果其不为0, 直接中断jvm// 否则 设置需要运行所有未调用的终结方法。// 如果状态为FINALIZERS 并且status为0, 则运行所有未调用的终结方法 并中断jvm// 如果状态为RUNNING 或者HOOKS, 先运行所有的关闭虚拟机的钩子函数, 然后如果runFinalizersOnExit为true [Shutdown. setRunFinalizersOnExit(boolean)] 的话, 运行所有未调用的终结方法 并中断jvmboolean runMoreFinalizers = false;synchronized (lock) {if (status != 0) runFinalizersOnExit = false;switch (state) {case RUNNING: /* Initiate shutdown */state = HOOKS;break;case HOOKS: /* Stall and halt */break;case FINALIZERS:if (status != 0) {/* Halt immediately on nonzero status */halt(status);} else {/* Compatibility with old behavior:* Run more finalizers and then halt*/runMoreFinalizers = runFinalizersOnExit;}break;}}if (runMoreFinalizers) {runAllFinalizers();halt(status);}synchronized (Shutdown.class) {/* Synchronize on the class object, causing any other thread* that attempts to initiate shutdown to stall indefinitely*/sequence();halt(status);}}Shutdown. halt (int status)/* The halt method is synchronized on the halt lock* to avoid corruption of the delete-on-shutdown file list.* It invokes the true native halt method.*/static void halt(int status) {synchronized (haltLock) {halt0(status);}}Shutdown. halt0 (int status)static native void halt0(int status);Shutdown. runAllFinalizers ( )/* Wormhole for invoking java.lang.ref.Finalizer.runAllFinalizers */private static native void runAllFinalizers();Shutdown. sequence()/* The actual shutdown sequence is defined here.** If it weren't for runFinalizersOnExit, this would be simple -- we'd just* run the hooks and then halt. Instead we need to keep track of whether* we're running hooks or finalizers. In the latter case a finalizer could* invoke exit(1) to cause immediate termination, while in the former case* any further invocations of exit(n), for any n, simply stall. Note that* if on-exit finalizers are enabled they're run iff the shutdown is* initiated by an exit(0); they're never run on exit(n) for n != 0 or in* response to SIGINT, SIGTERM, etc.*/
private static void sequence() {
// 确保状态为HOOKS, [必需保证是从exit方法 或者shutdown方法调用]
// 先运行所有的关闭虚拟机的钩子函数, 并更新state为FINALIZERS
// 如果runFinalizersOnExit为true [Shutdown. setRunFinalizersOnExit(boolean)] 的话, 运行所有未调用的终结方法 并中断jvm
// 这里我们先到这里, 待会儿再来详细分析Shutdown.javasynchronized (lock) {/* Guard against the possibility of a daemon thread invoking exit* after DestroyJavaVM initiates the shutdown sequence*/if (state != HOOKS) return;}runHooks();boolean rfoe;synchronized (lock) {state = FINALIZERS;rfoe = runFinalizersOnExit;}if (rfoe) runAllFinalizers();}
Runtime. addShutdownHook(Thread hook)
public void addShutdownHook(Thread hook) {SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager();if (sm != null) {sm.checkPermission(new RuntimePermission("shutdownHooks"));}// 添加hook[Callback]方法ApplicationShutdownHooks.add(hook);}ApplicationShutdownHooks. add(Thread hook)static synchronized void add(Thread hook) {if(hooks == null)throw new IllegalStateException("Shutdown in progress");if (hook.isAlive())throw new IllegalArgumentException("Hook already running");if (hooks.containsKey(hook))throw new IllegalArgumentException("Hook previously registered");hooks.put(hook, hook);}/* The set of registered hooks */private static IdentityHashMap<Thread, Thread> hooks;
那么ApplicationShutdown又是怎么和Shutdown关联起来的呢?, 请看下面
ApplicationShutdown. staticBlock
static {try {// 其实就是为Shutdown在slot[1]处添加了一个钩子, 来运行applicationShutdown收集的所有shutdownHooks
// 这里我们先到这里, 待会儿再来详细分析ApplicationShutdown.javaShutdown.add(1 /* shutdown hook invocation order */,false /* not registered if shutdown in progress */,new Runnable() {public void run() {runHooks();}});hooks = new IdentityHashMap<>();} catch (IllegalStateException e) {// application shutdown hooks cannot be added if// shutdown is in progress.hooks = null;}}
Runtime. remove(Thread hook)
static synchronized boolean remove(Thread hook) {if(hooks == null)throw new IllegalStateException("Shutdown in progress");if (hook == null)throw new NullPointerException();// 移除hook方法return hooks.remove(hook) != null;}
Runtime. halt(int status)
public void halt(int status) {SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager();if (sm != null) {sm.checkExit(status);}// 中断Shutdown.halt(status);}
Runtime. runFinalizersOnExit(boolean value)
@Deprecatedpublic static void runFinalizersOnExit(boolean value) {SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager();if (security != null) {try {security.checkExit(0);} catch (SecurityException e) {throw new SecurityException("runFinalizersOnExit");}}// 在exit之前是否运行finalizer// 设置Shutdown. runFinalizersOnExit, 但是由于不安全, 以过时Shutdown.setRunFinalizersOnExit(value);}
Runtime. exec(String command)
public Process exec(String command) throws IOException {return exec(command, null, null);}Runtime. exec(String command, String[] envp) throws IOExceptionpublic Process exec(String command, String[] envp) throws IOException {return exec(command, envp, null);}Runtime. exec(String command, String[] envp, File dir) throws IOExceptionpublic Process exec(String command, String[] envp, File dir)throws IOException {if (command.length() == 0)throw new IllegalArgumentException("Empty command");// 将command构建成command数组 之后利用ProcessBuilder.startStringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(command);String[] cmdarray = new String[st.countTokens()];for (int i = 0; st.hasMoreTokens(); i++)cmdarray[i] = st.nextToken();return exec(cmdarray, envp, dir);}Runtime exec(String[] cmdarray, String[] envp, File dir) throws IOExceptionpublic Process exec(String[] cmdarray, String[] envp, File dir)throws IOException {// 利用ProcessBuilder创建一个进程return new ProcessBuilder(cmdarray).environment(envp).directory(dir).start();}
Runtime.availableProcessors()[native]
public native int availableProcessors();Runtime.freeMemory()[native]
public native long freeMemory();Runtime.totalMemory()[native]
public native long totalMemory();Runtime.maxMemory()[native]
public native long maxMemory();Runtime.gc()[native]
// System.gc() 就是调用的这个gc方法public native void gc();Runtime. runFinalization()
public void runFinalization() {runFinalization0();}Runtime. runFinalization0() [native]/* Wormhole for calling java.lang.ref.Finalizer.runFinalization */
private static native void runFinalization0();
Runtime. traceInstructions(boolean on)[native]
public native void traceInstructions(boolean on);Runtime. traceMethodCalls(boolean on)
public native void traceMethodCalls(boolean on);Runtime.load(String filename)
@CallerSensitivepublic void load(String filename) {load0(Reflection.getCallerClass(), filename);}Runtime. load0(Class fromClass, String filename)synchronized void load0(Class fromClass, String filename) {SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager();if (security != null) {security.checkLink(filename);}if (!(new File(filename).isAbsolute())) {throw new UnsatisfiedLinkError("Expecting an absolute path of the library: " + filename);}// ..类加载器加载指定的dynamic library 第三个参数应该是是否是绝对路径吧 看不懂..ClassLoader.loadLibrary(fromClass, filename, true);}
Runtime. loadLibrary(String libname)
@CallerSensitivepublic void loadLibrary(String libname) {loadLibrary0(Reflection.getCallerClass(), libname);}Runtime. loadLibrary0(Class fromClass, String libname)synchronized void loadLibrary0(Class fromClass, String libname) {SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager();if (security != null) {security.checkLink(libname);}if (libname.indexOf((int)File.separatorChar) != -1) {throw new UnsatisfiedLinkError("Directory separator should not appear in library name: " + libname);}// 类加载器加载指定的dynamic libraryClassLoader.loadLibrary(fromClass, libname, false);}ClassLoader. loadLibrary(Class fromClass, String name, boolean isAbsolute)// Invoked in the java.lang.Runtime class to implement load and loadLibrary.static void loadLibrary(Class fromClass, String name,boolean isAbsolute) {ClassLoader loader =(fromClass == null) ? null : fromClass.getClassLoader();// 初始化系统环境变量if (sys_paths == null) {usr_paths = initializePath("java.library.path");sys_paths = initializePath("sun.boot.library.path");}// 如果用户给定的是绝对路径 直接加载if (isAbsolute) {if (loadLibrary0(fromClass, new File(name))) {return;}throw new UnsatisfiedLinkError("Can't load library: " + name);}// 在当前目录寻找指定libraryif (loader != null) {String libfilename = loader.findLibrary(name);if (libfilename != null) {File libfile = new File(libfilename);if (!libfile.isAbsolute()) {throw new UnsatisfiedLinkError("ClassLoader.findLibrary failed to return an absolute path: " + libfilename);}if (loadLibrary0(fromClass, libfile)) {return;}throw new UnsatisfiedLinkError("Can't load " + libfilename);}}// 在系统环境变量所在路径查找指定libraryfor (int i = 0 ; i < sys_paths.length ; i++) {File libfile = new File(sys_paths[i], System.mapLibraryName(name));if (loadLibrary0(fromClass, libfile)) {return;}}// 在用户环境变量所在路径查找指定libraryif (loader != null) {for (int i = 0 ; i < usr_paths.length ; i++) {File libfile = new File(usr_paths[i],System.mapLibraryName(name));if (loadLibrary0(fromClass, libfile)) {return;}}}// 没找到指定的library// Oops, it failedthrow new UnsatisfiedLinkError("no " + name + " in java.library.path");}
Runtime. getLocalizedInputStream(InputStream in)
@Deprecatedpublic InputStream getLocalizedInputStream(InputStream in) {return in;}
Runtime. getLocalizedOutputStream(OutputStream out)
@Deprecatedpublic OutputStream getLocalizedOutputStream(OutputStream out) {return out;}
ApplicationShutdownHooks [class]
class ApplicationShutdownHooks {/* The set of registered hooks */
private static IdentityHashMap<Thread, Thread> hooks;// 其实就是为Shutdown在slot[1]处添加了一个钩子, 来运行applicationShutdown收集的所有shutdownHooks// 整个类实际上就是为Shutdown.java 服务的, 将Runtime.addShutdownHook(Thread), removeShutdownHook(Thread), 注册的所有钩子, 作为Shutdown的1号钩子static {try {Shutdown.add(1 /* shutdown hook invocation order */,false /* not registered if shutdown in progress */,new Runnable() {public void run() {runHooks();}});hooks = new IdentityHashMap<>();} catch (IllegalStateException e) {// application shutdown hooks cannot be added if// shutdown is in progress.hooks = null;}}// 初始化构造方法, 不存在实例private ApplicationShutdownHooks() {}/* Add a new shutdown hook. Checks the shutdown state and the hook itself,* but does not do any security checks.*/// 添加一个关闭虚拟机 时需要执行钩子函数static synchronized void add(Thread hook) {if(hooks == null)throw new IllegalStateException("Shutdown in progress");if (hook.isAlive())throw new IllegalArgumentException("Hook already running");if (hooks.containsKey(hook))throw new IllegalArgumentException("Hook previously registered");hooks.put(hook, hook);}/* Remove a previously-registered hook. Like the add method, this method* does not do any security checks.*/// 移除一个关闭虚拟机 时需要执行钩子函数static synchronized boolean remove(Thread hook) {if(hooks == null)throw new IllegalStateException("Shutdown in progress");if (hook == null)throw new NullPointerException();return hooks.remove(hook) != null;}/* Iterates over all application hooks creating a new thread for each* to run in. Hooks are run concurrently and this method waits for* them to finish.*/// 依次执行每一个钩子函数, 并等待所有的钩子函数对应的线程执行完毕static void runHooks() {Collection<Thread> threads;synchronized(ApplicationShutdownHooks.class) {threads = hooks.keySet();hooks = null;}for (Thread hook : threads) {hook.start();}for (Thread hook : threads) {try {hook.join();} catch (InterruptedException x) { }}}
}
Shutdown [class]
class Shutdown {/* Shutdown state */
// 三种状态, 初始化当前的状态为RUNNING
// 是否需要在虚拟机关闭的时候, 运行所有未调用的终结方法
// 最大的系统钩子的个数, 以及所有的钩子private static final int RUNNING = 0;private static final int HOOKS = 1;private static final int FINALIZERS = 2;private static int state = RUNNING;/* Should we run all finalizers upon exit? */private static boolean runFinalizersOnExit = false;// The system shutdown hooks are registered with a predefined slot.// The list of shutdown hooks is as follows:// (0) Console restore hook// (1) Application hooks// (2) DeleteOnExit hookprivate static final int MAX_SYSTEM_HOOKS = 10;private static final Runnable[] hooks = new Runnable[MAX_SYSTEM_HOOKS];// the index of the currently running shutdown hook to the hooks array
// 当前正在运行的钩子的索引
// 用于线程安全维护的锁, 用于中断处理的锁private static int currentRunningHook = 0;/* The preceding static fields are protected by this lock */private static class Lock { };private static Object lock = new Lock();/* Lock object for the native halt method */private static Object haltLock = new Lock();/* Invoked by Runtime.runFinalizersOnExit */// 设置 是否jvm关闭的时候运行所有未调用的终结方法static void setRunFinalizersOnExit(boolean run) {synchronized (lock) {runFinalizersOnExit = run;}}/*** Add a new shutdown hook. Checks the shutdown state and the hook itself,* but does not do any security checks.** The registerShutdownInProgress parameter should be false except* registering the DeleteOnExitHook since the first file may* be added to the delete on exit list by the application shutdown* hooks.** @params slot the slot in the shutdown hook array, whose element* will be invoked in order during shutdown* @params registerShutdownInProgress true to allow the hook* to be registered even if the shutdown is in progress.* @params hook the hook to be registered** @throw IllegalStateException* if registerShutdownInProgress is false and shutdown is in progress; or* if registerShutdownInProgress is true and the shutdown process* already passes the given slot*/
static void add(int slot, boolean registerShutdownInProgress, Runnable hook) {//做一些校验, 添加一个系统钩子synchronized (lock) {if (hooks[slot] != null)throw new InternalError("Shutdown hook at slot " + slot + " already registered");if (!registerShutdownInProgress) {if (state > RUNNING)throw new IllegalStateException("Shutdown in progress");} else {if (state > HOOKS || (state == HOOKS && slot <= currentRunningHook))throw new IllegalStateException("Shutdown in progress");}hooks[slot] = hook;}}/* Run all registered shutdown hooks*/
private static void runHooks() {// 执行所有的钩子函数, 单线程执行for (int i=0; i < MAX_SYSTEM_HOOKS; i++) {try {Runnable hook;synchronized (lock) {// acquire the lock to make sure the hook registered during// shutdown is visible here.currentRunningHook = i;hook = hooks[i];}if (hook != null) hook.run();} catch(Throwable t) {if (t instanceof ThreadDeath) {ThreadDeath td = (ThreadDeath)t;throw td;}}}}/* The halt method is synchronized on the halt lock* to avoid corruption of the delete-on-shutdown file list.* It invokes the true native halt method.*/
static void halt(int status) {// 中断jvm虚拟机synchronized (haltLock) {halt0(status);}}// 中断jvmstatic native void halt0(int status);/* Wormhole for invoking java.lang.ref.Finalizer.runAllFinalizers */
// jvm关闭的时候运行所有未调用的终结方法private static native void runAllFinalizers();/* The actual shutdown sequence is defined here.** If it weren't for runFinalizersOnExit, this would be simple -- we'd just* run the hooks and then halt. Instead we need to keep track of whether* we're running hooks or finalizers. In the latter case a finalizer could* invoke exit(1) to cause immediate termination, while in the former case* any further invocations of exit(n), for any n, simply stall. Note that* if on-exit finalizers are enabled they're run iff the shutdown is* initiated by an exit(0); they're never run on exit(n) for n != 0 or in* response to SIGINT, SIGTERM, etc.*/
private static void sequence() {// 确保状态为HOOKS, [必需保证是从exit方法 或者shutdown方法调用]
// 先运行所有的关闭虚拟机的钩子函数, 并更新state为FINALIZERS
// 如果runFinalizersOnExit为true [Shutdown. setRunFinalizersOnExit(boolean)] 的话, 运行所有未调用的终结方法 并中断jvmsynchronized (lock) {/* Guard against the possibility of a daemon thread invoking exit* after DestroyJavaVM initiates the shutdown sequence*/if (state != HOOKS) return;}runHooks();boolean rfoe;synchronized (lock) {state = FINALIZERS;rfoe = runFinalizersOnExit;}if (rfoe) runAllFinalizers();}/* Invoked by Runtime.exit, which does all the security checks.* Also invoked by handlers for system-provided termination events,* which should pass a nonzero status code.*/
static void exit(int status) {// 如果status不为0, 更新runFinalizersOnExit为false// 检测状态, 如果state为RUNNING, 更新state为HOOKS// 如果状态为FINALIZERS[sequences方法中得到该状态], 则判断status如果其不为0, 直接中断jvm// 否则 设置需要运行所有未调用的终结方法。// 如果状态为FINALIZERS 并且status为0, 则运行所有未调用的终结方法 并中断jvm// 如果状态为RUNNING 或者HOOKS, 先运行所有的关闭虚拟机的钩子函数, 然后如果runFinalizersOnExit为true [Shutdown. setRunFinalizersOnExit(boolean)] 的话, 运行所有未调用的终结方法 并中断jvmboolean runMoreFinalizers = false;synchronized (lock) {if (status != 0) runFinalizersOnExit = false;switch (state) {case RUNNING: /* Initiate shutdown */state = HOOKS;break;case HOOKS: /* Stall and halt */break;case FINALIZERS:if (status != 0) {/* Halt immediately on nonzero status */halt(status);} else {/* Compatibility with old behavior:* Run more finalizers and then halt*/runMoreFinalizers = runFinalizersOnExit;}break;}}if (runMoreFinalizers) {runAllFinalizers();halt(status);}synchronized (Shutdown.class) {/* Synchronize on the class object, causing any other thread* that attempts to initiate shutdown to stall indefinitely*/sequence();halt(status);}}/* Invoked by the JNI DestroyJavaVM procedure when the last non-daemon* thread has finished. Unlike the exit method, this method does not* actually halt the VM.*/
static void shutdown() {// 检测状态, 如果state为RUNNING, 更新state为HOOKS// 先运行所有的关闭虚拟机的钩子函数, 然后如果runFinalizersOnExit为true [Shutdown. setRunFinalizersOnExit(boolean)] 的话, 运行所有未调用的终结方法 并中断jvm// 这里与上面的exit方法的区别存在两处, 一处在于对于FINALIZERS状态的处理, 另一处在于, 这里不会中断jvm虚拟机synchronized (lock) {switch (state) {case RUNNING: /* Initiate shutdown */state = HOOKS;break;case HOOKS: /* Stall and then return */case FINALIZERS:break;}}synchronized (Shutdown.class) {sequence();}}}
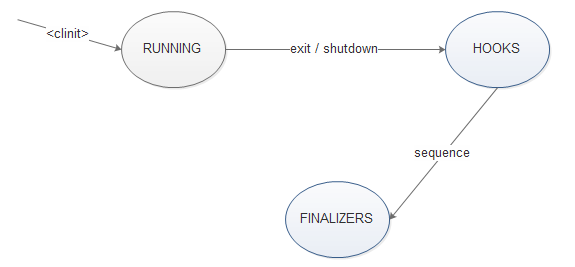
附上Shutdown状态切换图 :
->
ok, Runtime 到此结束了, 这个类主要涉及其他的两个ApplicationShutdown.java, 和Shutdown.java 两个包级别的类
资源下载 : http://download.csdn.net/detail/u011039332/9102743
注 : 因为作者的水平有限,必然可能出现一些bug, 所以请大家指出!