济宁住房和城乡建设厅网站首页/下载班级优化大师app
队列的基本实现
- 一、队列的概念
- 二、队列的基本实现
- 1.前期准备
- 2.队列的初始化
- 3.队列的销毁
- 4.入队
- 5.出队
- 6.取队头的数据
- 7.取队尾的数据
- 8.队列数据的个数
- 9.判断队列是否为空
- 10.队列出队顺序
- 11.功能展示
- 12.代码展示
一、队列的概念
队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先进先出, 入队列:进行插入操作的一端称为队尾 ;出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为队头。

● 队列可以使用数组实现也可以使用链表的结构实现,在这里使用链表的结构会更优一点,因为如果使用数组的结构,出队列在数组头上出数据,效率会更低。
二、队列的基本实现
1.前期准备
上面了解了队列的基本概念后,我们开始讲解队列的基本实现了,首先我们准备三个文件:
1.Queue.h :用来对头文件的包含,函数的声明和结构体的创建
2.Queue.c :用来对函数的定义
3. test.c :用来实现函数,整体的逻辑
在Stack.h文件中,定义一个队列的的结构:
typedef int QDataType;typedef struct QueueNode
{QDataType data; //存放数据struct QueueNode* next; //指向结构体的下一个//size_t size;
}QueueNode;typedef struct Queue
{QueueNode* head; //队列的队头QueueNode* tail; //队列的队尾
}Queue;
2.队列的初始化
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);pq->head = NULL;pq->tail = NULL;
}
3.队列的销毁
把队头的位置先给给cur, 然后让队头的下一个位置保存下来,接着把cur释放掉,再让cur指向next,此动作一直循环,直到cur指向空的位置则结束;
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);QueueNode* cur = pq->head;while (cur){QueueNode* next = cur->next;free(cur);cur = next;}pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
4.入队
队列是从队尾入数据,队头出数据的,入队考虑两种情况:一种是队列为空的情况,一种是队列不为空的情况,如果队列为空,则我们把数据放到对头位置也就是队尾,因为当队列为空时,队头和队尾指向同一个位置;当队列不为空时,把结点链接到队尾的下一个位置,然后让原尾结点指向新节点成为新队尾。
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{assert(pq);//开辟新结点QueueNode* newnode = (QueueNode*)malloc(sizeof(QueueNode));newnode->data = x;newnode->next = NULL;if (pq->head == NULL){pq->head = pq->tail = newnode;}else{pq->tail->next = newnode;pq->tail = newnode;}
}
5.出队
因为队列是先进先出,所以我们出数据是从队头开始出的,我们出数据时要考虑到队列里面的数据是否为空,所以我们在出数据前要判断一下队列是否为空,然后把队头的下一个位置保存下来,让队头指向刚刚我们记录下来的位置,这样就完成出数据的动作了;但是如果队里面的数据被我们出队出空了,就意味着对头和队尾指向不再指向那块空间了,所以我们要让队尾也指向空(队列出空了,队头就是NULL),这样程序才算是合格的。
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);//if (pq->head == NULL)//{// return;//}assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));QueueNode* next = pq->head->next;free(pq->head);pq->head = next;//如果队列删完后,tail不做处理的话,tail是一个野指针if (pq->head == NULL){pq->tail = NULL;}
}
6.取队头的数据
队列不为空的清空下,直接返回队头的数据
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));return pq->head->data;
}
7.取队尾的数据
队列不为空的清空下,直接返回队尾的数据
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));return pq->tail->data;
}8.队列数据的个数
定义一个变量n,用了记录队列数据的个数,把队头给给cur,n每次+1后,cur都指向cur的下一个,直到cur为空,循环就结束,最后的n就是队列数据的个数。
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);int n = 0; //记录队列数据的个数QueueNode* cur = pq->head;while (cur){++n;cur = cur->next;}return n;
}
9.判断队列是否为空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);return pq->head == NULL;
}
10.队列出队顺序
首先要判断队列是否为空,队列不为空的情况下,打印队头的数据,然后释放掉队头的数据,直到队列为空。
void QueueAllPop(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));//先进先出printf("出队顺序是:");while (!QueueEmpty(pq)){QDataType front = QueueFront(pq);printf("%d ", front);QueuePop(pq);}printf("\n");
}11.功能展示
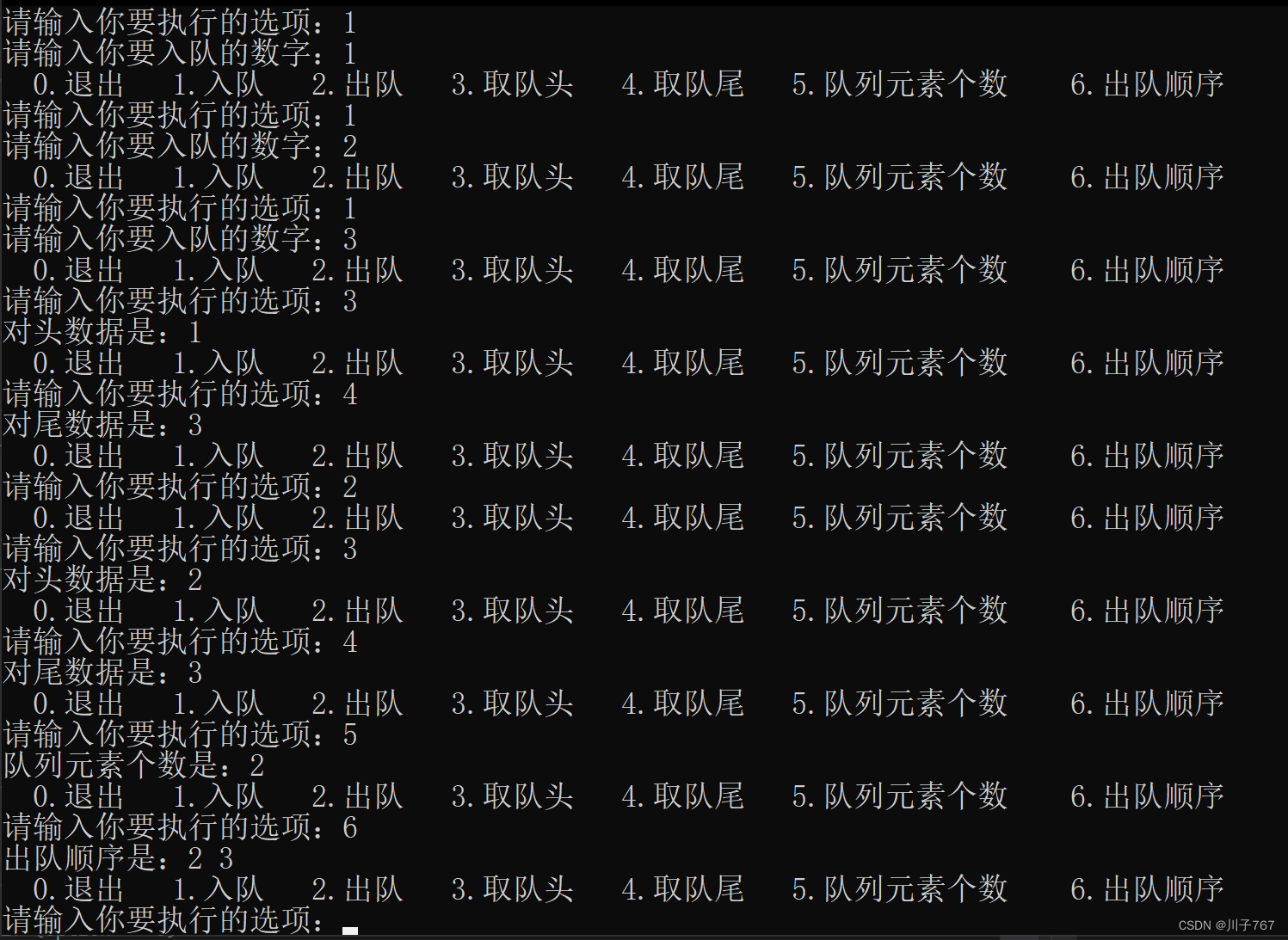
12.代码展示
Queue.h文件
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdbool.h>typedef int QDataType;typedef struct QueueNode
{QDataType data;struct QueueNode* next;//size_t size;
}QueueNode;typedef struct Queue
{QueueNode* head;QueueNode* tail;
}Queue;void QueueInit(Queue* pq);void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq);void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x);void QueuePop(Queue* pq);//取队列的头的数据
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq);//取队列的尾的数据
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq);//队列数据个数
int QueueSize(Queue* pq);
//判断队列是否为空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);
//队列的出栈顺序
void QueueAllPop(Queue* pq);Queue.c文件
#include"Queue.h"void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);pq->head = NULL;pq->tail = NULL;
}
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);QueueNode* cur = pq->head;while (cur){QueueNode* next = cur->next;free(cur);cur = next;}pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{assert(pq);QueueNode* newnode = (QueueNode*)malloc(sizeof(QueueNode));newnode->data = x;newnode->next = NULL;if (pq->head == NULL){pq->head = pq->tail = newnode;}else{pq->tail->next = newnode;pq->tail = newnode;}
}//队尾入,队头出
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);//if (pq->head == NULL)//{// return;//}assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));QueueNode* next = pq->head->next;free(pq->head);pq->head = next;//如果队列删完后,tail不做处理的话,tail是一个野指针if (pq->head == NULL){pq->tail = NULL;}
}//取队列的头的数据
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));return pq->head->data;
}//取队列的尾的数据
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));return pq->tail->data;
}//队列数据个数
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);int n = 0;QueueNode* cur = pq->head;while (cur){++n;cur = cur->next;}return n;
}bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);return pq->head == NULL;
}void QueueAllPop(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));//先进先出printf("出队顺序是:");while (!QueueEmpty(pq)){QDataType front = QueueFront(pq);printf("%d ", front);QueuePop(pq);}printf("\n");
}test.c文件
void menu()
{printf(" 0.退出 1.入队 2.出队 3.取队头 4.取队尾 5.队列元素个数 6.出队顺序 \n");}int main()
{Queue q;QueueInit(&q);int option = -1;while (option){menu();printf("请输入你要执行的选项:");scanf("%d", &option);if (option == 1){int num = 0;printf("请输入你要入队的数字:");scanf("%d", &num);QueuePush(&q, num);}else if (option == 2){QueuePop(&q);}else if (option == 3){printf("对头数据是:%d\n", QueueFront(&q));}else if (option == 4){printf("对尾数据是:%d\n", QueueBack(&q));}else if (option == 5){printf("队列元素个数是:%d\n", QueueSize(&q));}else if (option == 6){QueueAllPop(&q);}else if (option == 0){QueueDestroy(&q);printf("退出\n");}else{printf("无此选项\n");}}return 0;
}
完结!
