做本地网站能赚钱么/沪深300指数
有时候,我们需要把对象A的所有值复制给对象B(B = A),但是这样用等号给赋值你会发现,当B中的某个对象值改变时,同时也会修改到A中相应对象的值!
也许你会说,用clone()不就行了?!你的想法只对了一半,因为用clone()时,除了基础数据和String类型的不受影响外,其他复杂类型(如集 合、对象等)还是会受到影响的!
例子如下:
package com.test;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;public class StudentClone implements Cloneable
{ String name; int age; List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>(){{add("A");add("B");add("C");}};StudentClone(String name,int age) { this.name=name; this.age=age; } public Object clone() { Object o=null; try { o=(StudentClone)super.clone();//Object 中的clone()识别出你要复制的是哪一个对象。 } catch(CloneNotSupportedException e) { System.out.println(e.toString()); } return o; } public static void main(String[] args) { StudentClone s1= new StudentClone("zhangsan",50); StudentClone s2=(StudentClone)s1.clone(); s2.list.add("D");s2.name="lisi"; s2.age=20; System.out.println("name="+s1.name+","+"age="+s1.age);//修改学生2后,不影响学生1的值。 System.out.println("name="+s2.name+","+"age="+s2.age);System.out.println("name="+s1.name+","+"age="+s1.age);System.out.println(s1.list.size()+"hhhhhhh");System.out.println(s2.list.size()+"uuuuuuu");} }
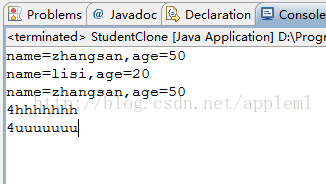
运行的结果如下:
浅层赋值只对基本类型起作用,对集合没用