怎么加入网站做微商城网络推广哪个平台好
1.1 数组的引用传递
1.1.1 传递及返回数组
前面的操作传递和返回的都是基本数据类型,方法中也可用来传递和放回数组。如果要向方法中传递一个数组,则方法的接受参数必须是符合其他类型的数组。而且数组属于引用数据类型,所以在把数组传递进方法之后,如果方法对数组本身做了任何修改,修改结果也将保存下来。
向方法中传递参数:
class ArrayRefDemo01{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int temp[] = {1,3,5};
fun(temp);
for (int i = 0; i < temp.length; i++) {
System.out.print(temp[i] + "、");
}
}
public static void fun(int x[]){
x[0] = 6;
}
}
运算结果:
6、3、5
在程序中讲一个整型数组temp传递到了方法之中,然后在fun()方法中将此整型数组的第一个元素的内容修改为6,因为数组是引用数据类型,所以,即使方法本身没有任何的返回值,修改后的结果也会被保存下来,向方法中传递数组的过程如图:
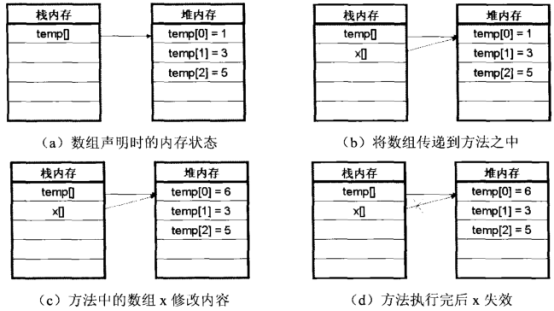
一开始声明的temp数组的内容是“1、3、5”,但是将此数组传递到了方法中,使用了数组x接收,也就是说此时temp实际上是将堆内存空间的使用权传递给了方法,为数组的具体内容起了一个别名x,然后在方法中通过x修改数组中的内容,方法执行完毕之后,数组x因为是局部变量所以就失效了,但是对于数组内容的改变却保留了下来,这就是数组引用传递的过程。
既然方法可以结接受一个数组,那么方法也可以返回一个数组,只需要在返回值类型处声明的写出返回的数组类型即可。
1.1.2 数组排序
class ArrayRefDemo03{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int score[] = {43,54,83,54,76,87,76};
int age[] = {12,23,43,61,53,26};
sort(score);
print(score);
System.out.println("\n\t\t----------------------");
sort(age);
print(age);
}
/**
* 排序
* @param temp
*/
public static void sort(int temp[]){
for (int i = 1; i < temp.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < temp.length; j++) {
if (temp[i] < temp[j]) {
int x = temp[i];
temp[i] = temp[j];
temp[j] = x;
}
}
}
}
/**
* 输出
* @param temp
*/
public static void print(int temp[]){
for (int i = 0; i < temp.length; i++) {
System.out.print(temp[i] + "\t");
}
}
}
运行结果:
43 54 54 76 76 83 87
----------------------
12 23 26 43 53 61
将排序和输出分别定义成一个方法,然后直接调用这两个方法,就可以完成排序或输出功能,在调用sort()或print()方法时将数组的引用传递过去,这样就可以直接对主方法中定义的score和age数组进行排序或输出,如图:
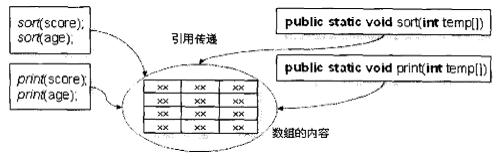
对于排序操作,在Java本身也是有类库支持的,读者可以直接使用“java.util.Arrays.sort(数组名称)”对数组进行排序。
class ArrayRefDemo05{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int score[] = {43,54,83,54,76,87,76};
int age[] = {12,23,43,61,53,26};
java.util.Arrays.sort(score);
print(score);
System.out.println("\n\t\t----------------------");
java.util.Arrays.sort(score);
print(age);
}
/**
* 输出
* @param temp
*/
public static void print(int temp[]){
for (int i = 0; i < temp.length; i++) {
System.out.print(temp[i] + "\t");
}
}
}
运行结果:
43 54 54 76 76 83 87
----------------------
12 23 43 61 53 26
通过一条语句即可完成数组的排序功能。不理解。(书上说:欲知后事如何,且听下回分解。)
1.1.3 数组复制
如果给定两个数组,将其中一个数组指定位置的内容赋值给另外一个数组,可以使用方法来完成,在方法中接受5个参数,分别为“源数组名称”、“源数组开始点”、“目标数组名称”、“目标数组开始点”、“复制长度”,具体代码如下:
//数组的复制
class ArrayCopyDemo01{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i1[] = {12,33,52,65,47,35,68};
int i2[] = {1,4,65,21,6,33,89,34,26,18,43,65};
copy(i1, 3, i2, 1, 3);
for (int i = 0; i < i2.length; i++) {
System.out.print(i2[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void copy(int s[], int s1, int o[], int s2, int len){
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
o[s2 + i] = s[s1 + i];
}
}
}
运行结果:
1 65 47 35 6 33 89 34 26 18 43 65
从程序可以看出,已经完成了数组的复制操作。对于此种代码在java中也同样是存在类库支持的,直接使用System.arraycopy()方法即可,此方法中也要接受参数,参数的接受顺序及意义与上面一样。
class ArrayCopyDemo02{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i1[] = {12,33,52,65,47,35,68};
int i2[] = {1,4,65,21,6,33,89,34,26,18,43,65};
System.arraycopy(i1, 3, i2, 1, 3);
for (int i = 0; i < i2.length; i++) {
System.out.print(i2[i] + " ");
}
}
}
运行结果:
1 65 47 35 6 33 89 34 26 18 43 65
Java中的类库:
在Java中提供了大量的类库,这些类库可以直接从Java doc中查找到。
转载于:https://blog.51cto.com/5838311/986220
