wordpress主题模板文件下载windows优化大师官方网站
08-jsp详解
- 1、什么是 jsp,它有什么用?
- 2、jsp 的本质是什么
- 3、jsp 的三种语法
- a)jsp 头部的 page 指令
- b)jsp 中的常用脚本
- c)jsp 中的三种注释
- 4、jsp 九大内置对象
- 5、jsp 四大域对象
- 6、jsp 中的 out 输出和 response.getWriter 输出的区 别
- 7、jsp 的常用标签
- 8、jsp 的练习题
- 9、什么是 Listener 监听器?
1、什么是 jsp,它有什么用?
jsp 的全换是 java server pages。Java 的服务器页面。
jsp 的主要作用是代替 Servlet 程序回传 html 页面的数据。
因为 Servlet 程序回传 html 页面数据是一件非常繁锁的事情。开发成本和维护成本都极高。
Servlet 回传 html 页面数据的代码:
public class PringHtml extends HttpServlet {@Overrideprotected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {// 通过响应的回传流回传html页面数据resp.setContentType("text/html; charset=UTF-8");PrintWriter writer = resp.getWriter();writer.write("<!DOCTYPE html>\r\n");writer.write(" <html lang=\"en\">\r\n");writer.write(" <head>\r\n");writer.write(" <meta charset=\"UTF-8\">\r\n");writer.write(" <title>Title</title>\r\n");writer.write(" </head>\r\n");writer.write(" <body>\r\n");writer.write(" 这是html页面数据 \r\n");writer.write(" </body>\r\n");writer.write("</html>\r\n");writer.write("\r\n");}
}
jsp 回传一个简单 html 页面的代码:
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html><head><title>jsp</title></head><body>这是jsp页面</body>
</html>
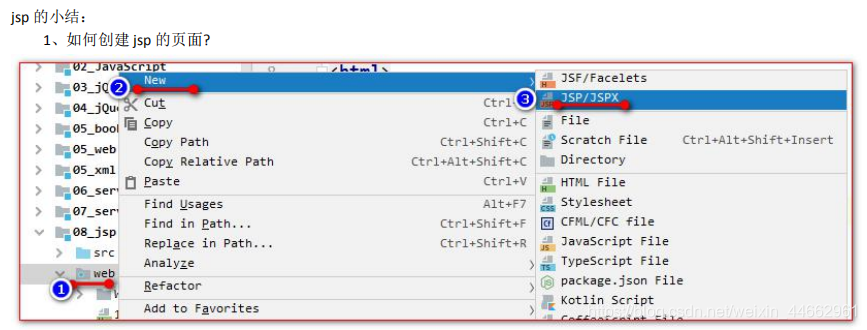

2、jsp 的本质是什么
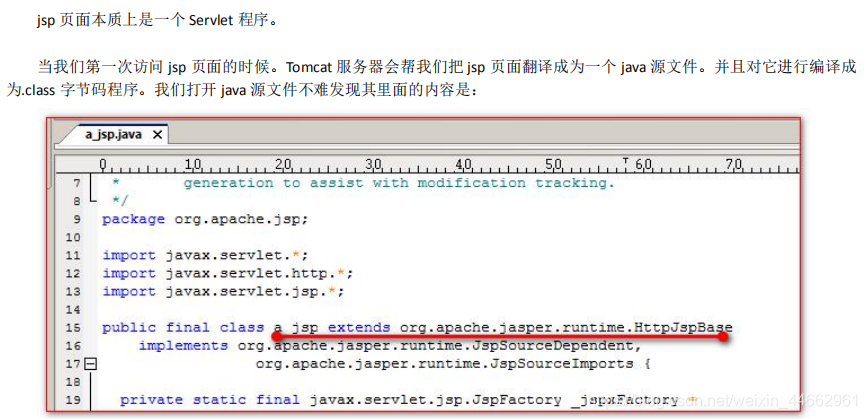
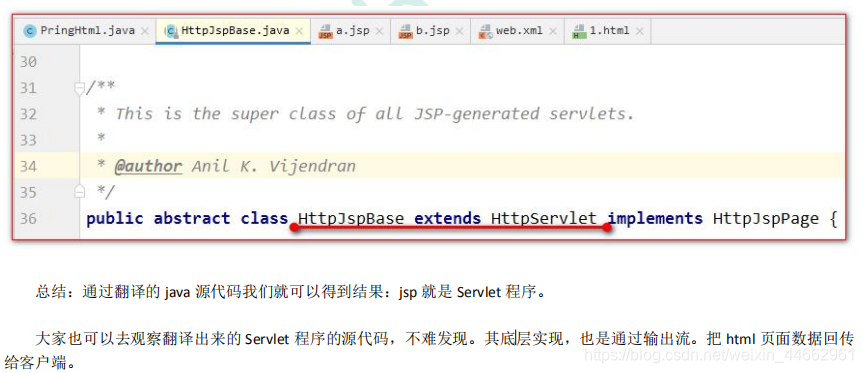
我们跟踪原代码发现,HttpJspBase 类。它直接地继承了 HttpServlet 类。也就是说。jsp 翻译出来的 java 类,它间接了继 承了 HttpServlet 类。也就是说,翻译出来的是一个 Servlet 程序
/** Generated by the Jasper component of Apache Tomcat* Version: Apache Tomcat/8.5.43* Generated at: 2020-07-13 14:43:09 UTC* Note: The last modified time of this file was set to* the last modified time of the source file after* generation to assist with modification tracking.*/
package org.apache.jsp;import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.*;
import javax.servlet.jsp.*;public final class index_jsp extends org.apache.jasper.runtime.HttpJspBaseimplements org.apache.jasper.runtime.JspSourceDependent,org.apache.jasper.runtime.JspSourceImports {private static final javax.servlet.jsp.JspFactory _jspxFactory =javax.servlet.jsp.JspFactory.getDefaultFactory();private static java.util.Map<java.lang.String,java.lang.Long> _jspx_dependants;private static final java.util.Set<java.lang.String> _jspx_imports_packages;private static final java.util.Set<java.lang.String> _jspx_imports_classes;static {_jspx_imports_packages = new java.util.HashSet<>();_jspx_imports_packages.add("javax.servlet");_jspx_imports_packages.add("javax.servlet.http");_jspx_imports_packages.add("javax.servlet.jsp");_jspx_imports_classes = null;}private volatile javax.el.ExpressionFactory _el_expressionfactory;private volatile org.apache.tomcat.InstanceManager _jsp_instancemanager;public java.util.Map<java.lang.String,java.lang.Long> getDependants() {return _jspx_dependants;}public java.util.Set<java.lang.String> getPackageImports() {return _jspx_imports_packages;}public java.util.Set<java.lang.String> getClassImports() {return _jspx_imports_classes;}public javax.el.ExpressionFactory _jsp_getExpressionFactory() {if (_el_expressionfactory == null) {synchronized (this) {if (_el_expressionfactory == null) {_el_expressionfactory = _jspxFactory.getJspApplicationContext(getServletConfig().getServletContext()).getExpressionFactory();}}}return _el_expressionfactory;}public org.apache.tomcat.InstanceManager _jsp_getInstanceManager() {if (_jsp_instancemanager == null) {synchronized (this) {if (_jsp_instancemanager == null) {_jsp_instancemanager = org.apache.jasper.runtime.InstanceManagerFactory.getInstanceManager(getServletConfig());}}}return _jsp_instancemanager;}public void _jspInit() {}public void _jspDestroy() {}public void _jspService(final javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest request, final javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse response)throws java.io.IOException, javax.servlet.ServletException {final java.lang.String _jspx_method = request.getMethod();if (!"GET".equals(_jspx_method) && !"POST".equals(_jspx_method) && !"HEAD".equals(_jspx_method) && !javax.servlet.DispatcherType.ERROR.equals(request.getDispatcherType())) {response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED, "JSPs only permit GET POST or HEAD");return;}final javax.servlet.jsp.PageContext pageContext;javax.servlet.http.HttpSession session = null;final javax.servlet.ServletContext application;final javax.servlet.ServletConfig config;javax.servlet.jsp.JspWriter out = null;final java.lang.Object page = this;javax.servlet.jsp.JspWriter _jspx_out = null;javax.servlet.jsp.PageContext _jspx_page_context = null;try {response.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8");pageContext = _jspxFactory.getPageContext(this, request, response,null, true, 8192, true);_jspx_page_context = pageContext;application = pageContext.getServletContext();config = pageContext.getServletConfig();session = pageContext.getSession();out = pageContext.getOut();_jspx_out = out;out.write("\n");out.write("\n");out.write("<html>\n");out.write(" <head>\n");out.write(" <title>jsp</title>\n");out.write(" </head>\n");out.write(" <body>\n");out.write(" 这是jsp页面\n");out.write(" </body>\n");out.write("</html>\n");} catch (java.lang.Throwable t) {if (!(t instanceof javax.servlet.jsp.SkipPageException)){out = _jspx_out;if (out != null && out.getBufferSize() != 0)try {if (response.isCommitted()) {out.flush();} else {out.clearBuffer();}} catch (java.io.IOException e) {}if (_jspx_page_context != null) _jspx_page_context.handlePageException(t);else throw new ServletException(t);}} finally {_jspxFactory.releasePageContext(_jspx_page_context);}}
}3、jsp 的三种语法
a)jsp 头部的 page 指令
jsp 的 page 指令可以修改 jsp 页面中一些重要的属性,或者行为。
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
i. language 属性 表示 jsp 翻译后是什么语言文件。暂时只支持 java。
ii. contentType 属性 表示 jsp 返回的数据类型是什么。也是源码中 response.setContentType()参数值
iii. pageEncoding 属性 表示当前 jsp 页面文件本身的字符集。
iv. import 属性 跟 java 源代码中一样。用于导包,导类。========================两个属性是给 out 输出流使用=============================
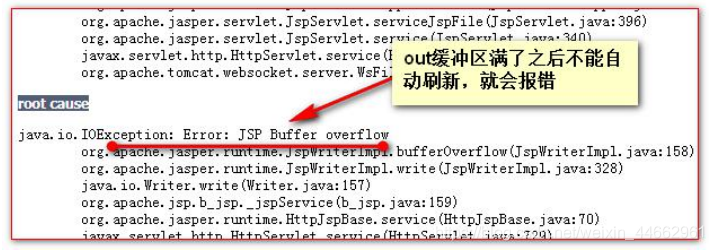
v. autoFlush 属性 设置当 out 输出流缓冲区满了之后,是否自动刷新冲级区。默认值是 true。
vi. buffer 属性 设置 out 缓冲区的大小。默认是 8kb
vii. errorPage 属性 设置当 jsp 页面运行时出错,自动跳转去的错误页面路径。 <!-- errorPage 表示错误后自动跳转去的路径 <br/> 这个路径一般都是以斜杠打头,它表示请求地址为 http://ip:port/工程路径/
映射到代码的 Web 目录 -->
viii. isErrorPage 属性 设置当前 jsp 页面是否是错误信息页面。默认是 false。如果是 true 可以 获取异常信息。
ix. session 属性 设置访问当前 jsp 页面,是否会创建 HttpSession 对象。默认是 true。
x. extends 属性 设置 jsp 翻译出来的 java 类默认继承谁。
缓冲区溢出错误:
b)jsp 中的常用脚本
i. 声明脚本(极少使用)
声明脚本的格式是: <%! 声明 java 代码 %>
作用:可以给 jsp 翻译出来的 java 类定义属性和方法甚至是静态代码块。内部类等。
练习
1、声明类属性
2、声明 static 静态代码块
3、声明类方法
4、声明内部类
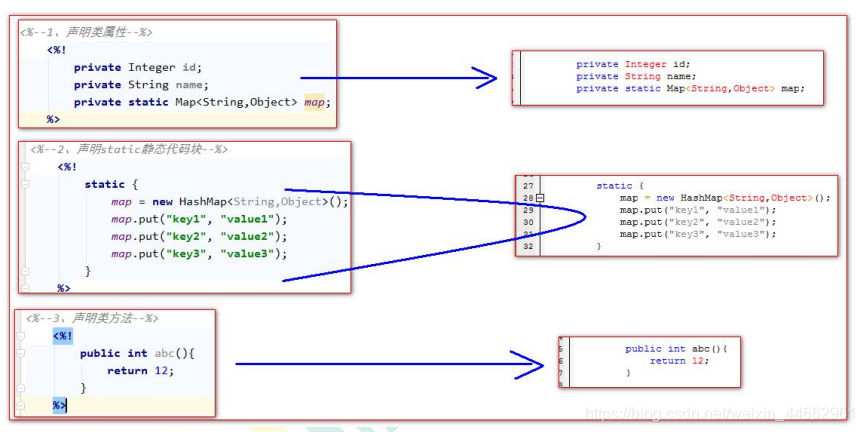
<%--1、声明类属性--%><%!private Integer id;private String name;private static Map<String,Object> map;%>
<%--2、声明static静态代码块--%><%!static {map = new HashMap<String,Object>();map.put("key1", "value1");map.put("key2", "value2");map.put("key3", "value3");}%>
<%--3、声明类方法--%><%!public int abc(){return 12;}%>
<%--4、声明内部类--%><%!public static class A {private Integer id = 12;private String abc = "abc";}%>
声明脚本代码翻译对照:
ii. 表达式脚本(常用)

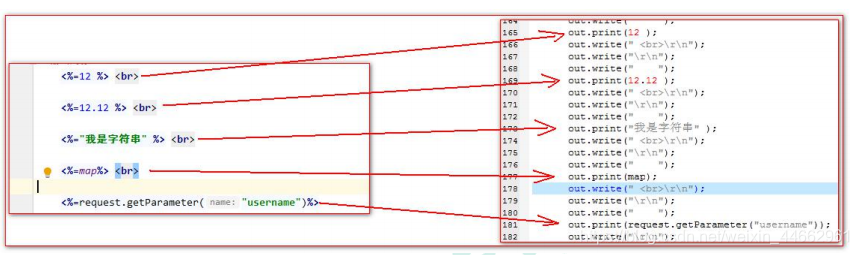
<%=12 %> <br><%=12.12 %> <br><%="我是字符串" %> <br><%=map%> <br><%=request.getParameter("username")%>
翻译对照:
iii. 代码脚本
代码脚本的格式是: <% java 语句 %>
代码脚本的作用是:可以在 jsp 页面中,编写我们自己需要的功能(写的是 java 语句)。
- 代码脚本的特点是:
1、代码脚本翻译之后都在_jspService 方法中
2、代码脚本由于翻译到_jspService()方法中,所以在_jspService()方法中的现有对象都可以直接使用。
3、还可以由多个代码脚本块组合完成一个完整的 java 语句。
4、代码脚本还可以和表达式脚本一起组合使用,在 jsp 页面上输出数据
练习:
- 代码脚本----if 语句
- 代码脚本----for 循环语句
- 翻译后 java 文件中_jspService 方法内的代码都可以写
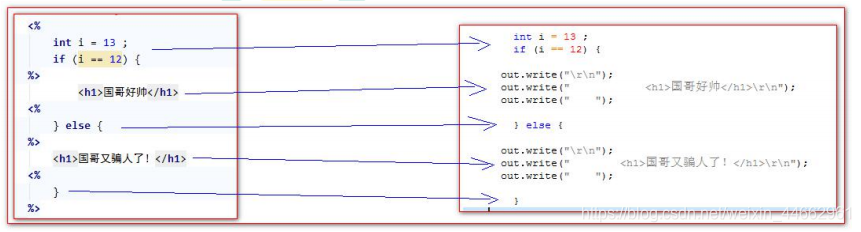
<%--1.代码脚本----if 语句--%><%int i = 13 ;if (i == 12) {%><h1>人无远虑</h1><%} else {%><h1>必有近忧</h1><%}%>
<br>
<%--2.代码脚本----for 循环语句--%><table border="1" cellspacing="0"><%for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) {%><tr><td>第 <%=j + 1%>行</td></tr><%}%></table>
<%--3.翻译后java文件中_jspService方法内的代码都可以写--%><%String username = request.getParameter("username");System.out.println("用户名的请求参数值是:" + username);%>
c)jsp 中的三种注释
i. html 注释 <!-- 这是 html 注释 -->
html 注释会被翻译到 java 源代码中。在_jspService 方法里,以 out.writer 输出到客户端。 ii. java 注释 <% // 单行 java 注释
/* 多行 java 注释 */ %>
java 注释会被翻译到 java 源代码中。 iii. jsp 注释
<%-- 这是 jsp 注释 --%>
jsp 注释可以注掉,jsp 页面中所有代码。
4、jsp 九大内置对象
jsp 中的内置对象,是指 Tomcat 在翻译 jsp 页面成为 Servlet 源代码后,内部提供的九大对象,叫内置对象。
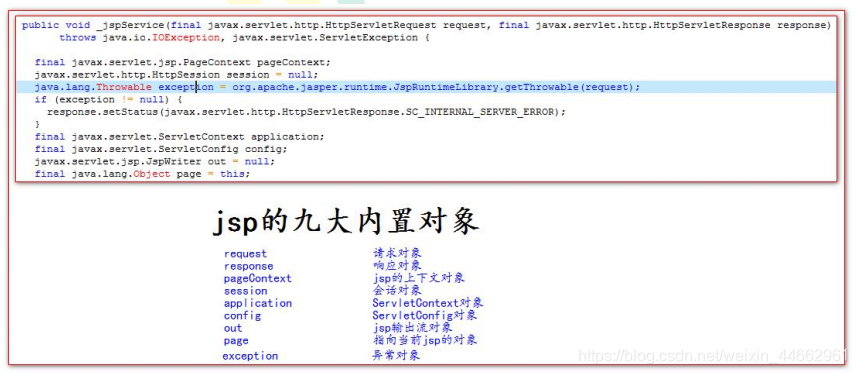
5、jsp 四大域对象

pageContext ====>>> request ====>>> session ====>>> application
scope.jsp 页面
<body><h1>scope.jsp页面</h1><%// 往四个域中都分别保存了数据pageContext.setAttribute("key", "pageContext");request.setAttribute("key", "request");session.setAttribute("key", "session");application.setAttribute("key", "application");%>pageContext域是否有值:<%=pageContext.getAttribute("key")%> <br>request域是否有值:<%=request.getAttribute("key")%> <br>session域是否有值:<%=session.getAttribute("key")%> <br>application域是否有值:<%=application.getAttribute("key")%> <br><%
// request.getRequestDispatcher("/scope2.jsp").forward(request,response);%><%--<jsp:forward page=""></jsp:forward> 是请求转发标签,它的功能就是请求转发page 属性设置请求转发的路径--%><jsp:forward page="/scope2.jsp"></jsp:forward>
</body>
scope2.jsp 页面
<body><h1>scope2.jsp页面</h1>pageContext域是否有值:<%=pageContext.getAttribute("key")%> <br>request域是否有值:<%=request.getAttribute("key")%> <br>session域是否有值:<%=session.getAttribute("key")%> <br>application域是否有值:<%=application.getAttribute("key")%> <br>
</body>
6、jsp 中的 out 输出和 response.getWriter 输出的区 别
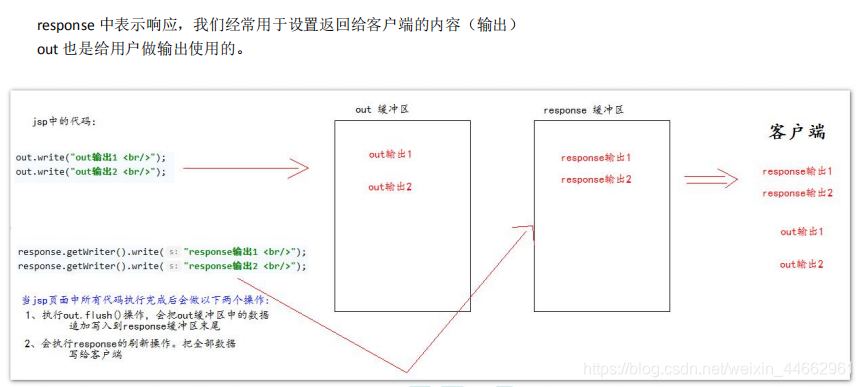
由于 jsp 翻译之后,底层源代码都是使用 out 来进行输出,所以一般情况下。我们在 jsp 页面中统一使用 out 来进行输出。避 免打乱页面输出内容的顺序。 out.write() 输出字符串没有问题 out.print() 输出任意数据都没有问题(都转换成为字符串后调用的 write 输出)
深入源码,浅出结论:在 jsp 页面中,可以统一使用 out.print()来进行输出
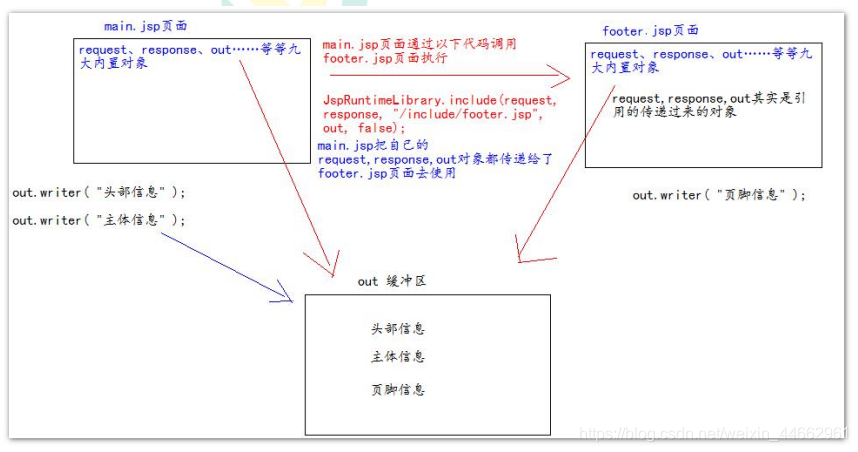
7、jsp 的常用标签

<%@ include file="/include/footer.jsp"%>

<jsp:include page="/include/footer.jsp"><jsp:param name="username" value="bbj"/><jsp:param name="password" value="root"/>
</jsp:include>
动态包含的底层原理:

8、jsp 的练习题
练习一:在 jsp 页面中输出九九乘法口诀表
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head><title>Title</title><style type="text/css">table{width: 650px;}</style>
</head>
<body><%-- 练习一:在jsp页面中输出九九乘法口诀表 --%><h1 align="center">九九乘法口诀表</h1><table align="center"><% for (int i = 1; i <= 9; i++) { %><tr><% for (int j = 1; j <= i ; j++) { %><td><%=j + "x" + i + "=" + (i*j)%></td><% } %></tr><% } %></table>
</body>
</html>练习二:jsp 输出一个表格,里面有 10 个学生信息。

Student 类:
public class Student {private Integer id;private String name;private Integer age;private String phone;
SearchStudentServlet 程序:
public class SearchStudentServlet extends HttpServlet {@Overrideprotected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {// 获取请求的参数// 发sql语句查询学生的信息// 使用for循环生成查询到的数据做模拟List<Student> studentList = new ArrayList<Student>();for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {int t = i + 1;studentList.add(new Student(t,"name"+t, 18+t,"phone"+t));}// 保存查询到的结果(学生信息)到request域中req.setAttribute("stuList", studentList);// 请求转发到showStudent.jsp页面req.getRequestDispatcher("/test/showStudent.jsp").forward(req,resp);}
}
showStudent.jsp 页面
<%@ page import="com.atiguigu.pojo.Student" %>
<%@ page import="java.util.List" %><%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head><title>Title</title><style>table{border: 1px blue solid;width: 600px;border-collapse: collapse;}td,th{border: 1px blue solid;}</style>
</head>
<body>
<%--练习二:jsp输出一个表格,里面有10个学生信息。--%><%List<Student> studentList = (List<Student>) request.getAttribute("stuList");%><table><tr><td>编号</td><td>姓名</td><td>年龄</td><td>电话</td><td>操作</td></tr><% for (Student student : studentList) { %><tr><td><%=student.getId()%></td><td><%=student.getName()%></td><td><%=student.getAge()%></td><td><%=student.getPhone()%></td><td>删除、修改</td></tr><% } %></table></body>
</html>9、什么是 Listener 监听器?

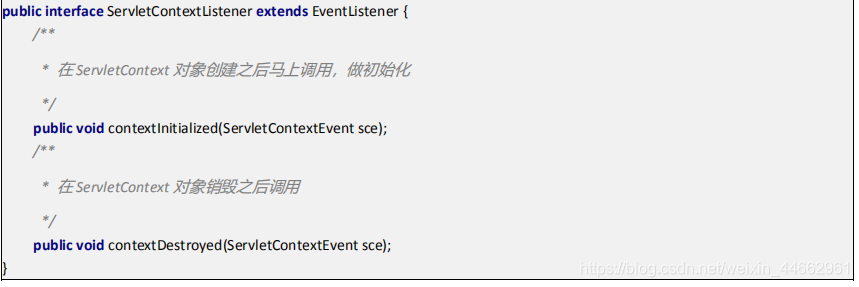
ServletContextListener 监听器
ServletContextListener 它可以监听 ServletContext 对象的创建和销毁。 ServletContext 对象在 web 工程启动的时候创建,在 web 工程停止的时候销毁。 监听到创建和销毁之后都会分别调用 ServletContextListener 监听器的方法反馈。
两个方法分别是:

监听器实现类:
public class MyServletContextListenerImpl implements ServletContextListener {@Overridepublic void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) {System.out.println("ServletContext对象被创建了");}@Overridepublic void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent sce) {System.out.println("ServletContext对象被销毁了");}
}
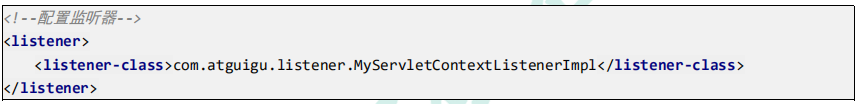
web.xml 中的配置:
以上就是关于jsp的介绍,如果有不当之处或者遇到什么问题,欢迎在文章下面留言~
如果你想了解更多关于JavaWeb的内容,可以查看:JavaWeb学习目录(超详细)
