内容营销的重要性内蒙古seo优化
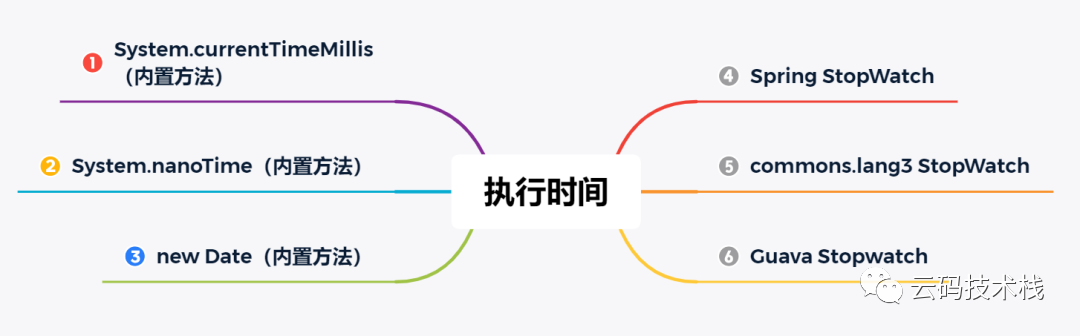
一些代码的执行时间,但是又不想使用Java Microbenchmark Harness,Java 对于微基准测试套件,因为这个测试框架有点重。所以以下就记录了关于 Java 中比较常用的6种执行时间统计方法,如下图所示:
01
方法一:System.currentTimeMillis
Java内置方法之一,是System的自带时间方法,使用 System#currentTimeMillis来统计执行的时间(统计单位:毫秒),下面是案例代码:
import java.util.Date;public class TimeIntervalTest {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { // 开始时间Date sdate = new Date();// 执行时间(1s)Thread.sleep(1000);// 结束时间Date edate = new Date();// 统计执行时间(毫秒) System.out.printf("执行时长:%d 毫秒." , (etime - stime));
}
}
执行结果为:
//执行时长:1000 毫秒.
02
方法二:System.nanoTime
Java 内置的方法之二,使用 System#nanoTime方法,但是它还有一个缺点,就是不能重用代码,每次都需要重新写一个 start 的时间起点。这个是统计执行时间(统计单位:纳秒),它的执行方法和 System#currentTimeMillis 方法是差不多的,代码如下:
public classTimeIntervalTest {public static voidmain(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { // 开始时间long stime = System.nanoTime();// 执行时间(1s)Thread.sleep(1000); // 结束时间longetime = System.nanoTime(); // 计算执行时间System.out.printf("执行时长:%d 纳秒.", (etime - stime));
}
}
执行结果:
//执行时长:1000769200 纳秒.
//小贴士:1 毫秒 = 100 万纳秒。
03
方法三:new Date
new Date也是 java 的内置方法,在开始执行前 new Date() 创建一个当前时间对象,在执行结束之后 new Date() 一个当前执行时间,再统计两个 Date 的时间间隔,示例如下:
importjava.util.Date;public class TimeIntervalTest {public static void main(String[] args)throws InterruptedException { // 开始时间 Date sdate = new Date(); // 执行时间(1s)Thread.sleep(1000); // 结束时间Date edate = new Date(); // 统计执行时间(毫秒)System.out.printf("执行时长:%d 毫秒." , (edate.getTime() - sdate.getTime()));
}
}
执行结果为:
//执行时长:1000 毫秒.
04
方法四:Spring StopWatch
还有我们可以使用的是 Spring 或 Spring Boot 项目,可以在项目中直接使用 StopWatch 对象和 org.apache.commons.lang.time.StopWatch 的用法类似。来获取值,代码如下:
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();// 开始时间
stopWatch.start();// 执行时间(1s)Thread.sleep(1000);// 结束时间stopWatch.stop();// 统计执行时间(秒)System.out.printf("执行时长:%d 秒.%n", stopWatch.getTotalTimeSeconds());
// %n 为换行// 统计执行时间(毫秒)System.out.printf("执行时长:%d 毫秒.%n", stopWatch.getTotalTimeMillis()); // 统计执行时间(纳秒)System.out.printf("执行时长:%d 纳秒.%n", stopWatch.getTotalTimeNanos());
执行结果为:
//执行时长:0.9996313 秒. 执行时长:999 毫秒. 执行时长:999631300 纳秒.
//小贴士:Thread#sleep 方法的执行时间稍有偏差,在 1s 左右都是正常的。
05
方法五:commons-lang3 StopWatch
在这里普通项目就可以使用这个方法,非常好用的计算耗时的工具类,那我们可以用 Apache commons-lang3 中的 StopWatch 对象来实现时间统计,首先先添加 commons-lang3 的依赖:
<dependency><groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId> <artifactId>commons-lang3</artifactId> <version>3.10</version>
</dependency>
时间统计代码:
importorg.apache.commons.lang3.time.StopWatch;importjava.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;public classTimeIntervalTest public static voidmain(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch(); // 开始时间 stopWatch.start(); // 执行时间(1s)Thread.sleep(1000);// 结束时间 stopWatch.stop(); // 统计执行时间(秒)System.out.println("执行时长:" + stopWatch.getTime(TimeUnit.SECONDS) + " 秒.");// 统计执行时间(毫秒)System.out.println("执行时长:" + stopWatch.getTime(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS) +" 毫秒."); // 统计执行时间(纳秒)System.out.println("执行时长:"+ stopWatch.getTime(TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS) +" 纳秒.");
}
}
执行结果为:
//执行时长:1 秒. 执行时长:1000 毫秒.
//执行时长:1000555100 纳秒.
06
方法六:Guava Stopwatch
除了 Apache 的 commons-lang3 外,还有一个常用的 Java 工具包,那就是 Google 的 Guava,Guava 中也包含了 Stopwatch 统计类。先添加 Guava 的依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.guava</groupId>>guava</artifactId>
<version>29.0-jre</version>
</dependency>
编写时间统计代码:
importcom.google.common.base.Stopwatch;importjava.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;public classTimeIntervalTest {public static voidmain(String[] args)throwsInterruptedException { // 创建并启动计时器Stopwatch stopwatch = Stopwatch.createStarted(); // 执行时间(1s)Thread.sleep(1000);// 停止计时器stopwatch.stop();// 执行时间(单位:秒)System.out.printf("执行时长:%d 秒. %n", stopwatch.elapsed().getSeconds()); // %n 为换行
// 执行时间(单位:毫秒)System.out.printf("执行时长:%d 豪秒.", stopwatch.elapsed(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS));
}
}
执行结果为:
//执行时长:1 秒.
//执行时长:1000 豪秒.
原理分析·
可以设置布尔变量,用来在程序运行时对一些逻辑进行标记。其中false和true需要自己定义其含义。因此在设置flag的时,需要注意false以及true对应的含义。否则这些逻辑上的错误就很难被检查出来。
1.Spring StopWatch 原理分析
StopWatch 的核心源码:
packageorg.springframework.util;importjava.text.NumberFormat;import java.util.LinkedList;importjava.util.List;import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;public class StopWatch {private final String id;private booleankeepTaskList; private final List taskList;private long startTimeNanos;@Nullableprivate String currentTaskName; @Nullableprivate StopWatch.TaskInfo lastTaskInfo;private int taskCount;private longtotalTimeNanos; public StopWatch() {this("");
} publicStopWatch(String id) {this.keepTaskList = true; this.taskList = new LinkedList(); this.id = id;
} public String getId() { return this.id;
}public void setKeepTaskList(boolean keepTaskList) { this.keepTaskList = keepTaskList;
}public void start() throws IllegalStateException { this.start("");
}public void start(String taskName) throws IllegalStateException { if (this.currentTaskName != null) {throw new IllegalStateException("Can't start StopWatch: it's already running");
} else {this.currentTaskName = taskName;this.startTimeNanos = System.nanoTime();
}
} public void stop() throws IllegalStateException {if (this.currentTaskName == null) { throw new IllegalStateException("Can't stop StopWatch: it's not running");
} else { long lastTime = System.nanoTime() - this.startTimeNanos; this.totalTimeNanos += lastTime; this.lastTaskInfo = new StopWatch.TaskInfo(this.currentTaskName, lastTime); if (this.keepTaskList) {this.taskList.add(this.lastTaskInfo);
}
++this.taskCount; this.currentTaskName = null;
}
}// .... 忽略其他代码
}
我们可以从上述 start() 和 stop() 的源码中可以看出,Spring 实现时间统计的使用了 System.nanoTime() 的内置方法来实现的。
2.Google Stopwatch 原理分析
Stopwatch 实现源码如下:
public final class Stopwatch {private final Ticker ticker; private boolean isRunning;private long elapsedNanos;private long startTick;@CanIgnoreReturnValue public Stopwatch start() {
Preconditions.checkState(!this.isRunning, "This stopwatch is already running."); this.isRunning = true; this.startTick = this.ticker.read(); return this;
} @CanIgnoreReturnValue public Stopwatch stop() { long tick = this.ticker.read();
Preconditions.checkState(this.isRunning, "This stopwatch is already stopped.");this.isRunning = false; this.elapsedNanos += tick - this.startTick; return this;
}// 忽略其他源码...
}
以下是关于 Stopwatch 对象中调用了 ticker 类来实现时间统计的源码:
public abstract classTicker {private static final Ticker SYSTEM_TICKER = new Ticker() {public long read() {return Platform.systemNanoTime();
}
};protected Ticker() {
}public abstract long read(); public static Ticker systemTicker() { return SYSTEM_TICKER;
}
}final class Platform {private static final Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(Platform.class.getName());private static final PatternCompiler patternCompiler = loadPatternCompiler();private Platform() {
} static long systemNanoTime() {return System.nanoTime();
} // 忽略其他源码...
}
对于所有框架的 StopWatch 来说,其底层都是通过调用 Java 内置的 System.nanoTime() 得到两个时间来实现的,开始时间和结束时间,然后再通过结束时间减去开始时间来统计执行时间的。
总结
我们在这里介绍了 6 种实现代码统计的方法,其中 3 种是 Java 内置的方法:
01.
System.currentTimeMillis()
02.
System.nanoTime()
03.
new Date()
另外 3 种常用框架 spring、commons-langs3、guava 的时间统计器 StopWatch。
在一般情况在不使用到 spring、commons-langs3、guava 这三种框架的前提下,建议使用 System.currentTimeMillis() 或 System.nanoTime() 来实现代码统计,还有就是直接使用 StopWatch 对象来统计执行时间也是可以的。
● 扩展—Stopwatch 知识让统计更方便
其中StopWatch 存在的意义就是让代码统计更简单,
import com.google.common.base.Stopwatch;import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;public classTimeIntervalTest {public static voidmain(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { // 创建并启动计时器
Stopwatch stopwatch = Stopwatch.createStarted(); // 执行时间(1s)
Thread.sleep(1000); // 停止计时器
stopwatch.stop();// 执行统计
System.out.printf("执行时长:%d 毫秒. %n",
stopwatch.elapsed(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)); // 清空计时器
stopwatch.reset(); // 再次启动统计
stopwatch.start(); // 执行时间(2s)
Thread.sleep(2000); // 停止计时器
stopwatch.stop(); // 执行统计
System.out.printf("执行时长:%d 秒. %n",
stopwatch.elapsed(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS));
}
}
我们可以使用一个 Stopwatch 对象统计多段代码的执行时间,也可以通过指定时间类型直接统计出对应的时间间隔,因为我们指定时间的统计单位,一般是_秒、毫秒、纳秒这三种类型。

云码教育
微信号|云码技术栈
新浪微博|云码技术栈
