网站的后台怎么做调查问卷同城推广引流平台
1. ByteToMessageDecoder解码器
是一个抽象类,仅提供了一个框架,继承关系如下:
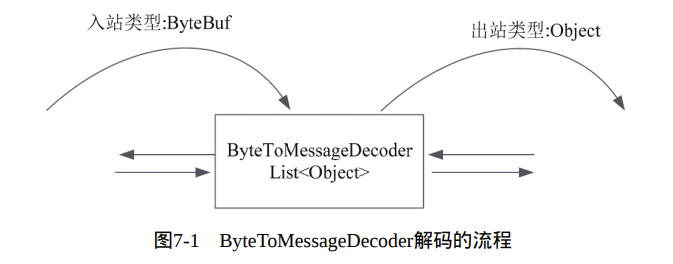
解码流程:
实现一个自己的ByteBuf解码器:
- 继承ByteToMessageDecoder抽象类
- 实现基类的decode抽象方法。将ByteBuf到POJO解码的逻辑写入此方法。将ByteBuf二进制数据,解码成一个个的Java对象。
- 在子类的decode方法中,需要将解码后的Java POJO对象,放入decode的List< Object >实参中,一个个的传递到下一站的Inbound入站处理器。
public class Byte2IntegerDecoder extends ByteToMessageDecoder {@Overrideprotected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in, List<Object> out) throws Exception {while (in.readableBytes() >= 4) {int i = in.readInt();System.out.println("解码出一个整数: " + i);out.add(i);}}
}public class IntegerProcessHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {@Overridepublic void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext context, Object msg) throws Exception {Integer integer = (Integer) msg;System.out.println("打印出一个整数: " + integer);}
}@Test
public void byteDecoderTest() {ChannelInitializer initializer = new ChannelInitializer() {@Overrideprotected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception {// 入站处理器,从前向后的顺序执行ch.pipeline().addLast(new Byte2IntegerDecoder());ch.pipeline().addLast(new IntegerProcessHandler());}};EmbeddedChannel channel = new EmbeddedChannel(initializer);for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {ByteBuf buf = Unpooled.buffer();buf.writeInt(i);channel.writeInbound(buf);}try {Thread.sleep(Integer.MAX_VALUE);} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}
}
2. ReplayingDecoder解码器
上面使用Byte2IntegerDecoder解码器会有一个问题:需要对ByteBuf长度进行检查,如果有足够的字节,才进行整数的读取。
使用ReplayingDecoder解码器可以省去长度的判断。
ReplayingDecoder类是ByteToMessageDecoder的子类。作用如下:
- 在读取ByteBuf缓冲区的数据之前,需要检查缓冲区是否有足够的字节。
- 若BytrBuf中有足够的字节,则会正常读取。否则,会停止解码。
原理如下:
在其内部,定义了一个新的二进制缓冲区类,对ByteBuf缓冲区进行了装饰,类名为ReplayingDecoderByteBuf。特点是:在缓冲区真正读取数据之前,首先进行长度的判断,如果长度合格,则读取数据;否则,抛出ReplayError。ReplayingDecoder捕获到ReplayError后,会留着数据,等待下一次IO事件到来时再获取。
ReplayingDecoderByteBuf继承了ByteBuf,所以该解码器实际上是把ByteBuf里面的数据转换成了ReplayingDecoderByteBuf,增强了对二进制数据的判断,长度不足就抛出异常
可以通过ReplayingDecoder分包ByteBuf,但也有缺点:
当ByteBuf中长度不够时,ReplayingDecoder会捕获异常,这时会把ByteBuf中的读指针还原到之前的读断点指针,然后结束这次解析操作,这需要消耗CPU。
2.1 整数的分包传输
public class IntegerAddDecoder extends ReplayingDecoder<IntegerAddDecoder.Status> {enum Status {PARSE_1, PARSE_2}private Integer first;private Integer second;public IntegerAddDecoder() {//构造函数中,需要初始化父类的state 属性,表示当前阶段super(Status.PARSE_1);}@Overrideprotected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in, List<Object> out) throws Exception {switch (state()) {case PARSE_1:// 从ByteBuf中读取数据first = in.readInt();System.out.println("first = " + first);// 进入第二步,设置读指针断点为当前读取位置checkpoint(Status.PARSE_2);break;case PARSE_2:second = in.readInt();System.out.println("second = " + second);Integer sum = first + second;System.out.println("sum = " + sum);out.add(sum);checkpoint(Status.PARSE_1);break;}}}@Test
public void testIntegerAddDecoder() {ChannelInitializer i = new ChannelInitializer<EmbeddedChannel>() {protected void initChannel(EmbeddedChannel ch) {// 先解码ch.pipeline().addLast(new IntegerAddDecoder());// 再输出ch.pipeline().addLast(new IntegerProcessHandler());}};EmbeddedChannel channel = new EmbeddedChannel(i);for (int j = 0; j < 100; j++) {ByteBuf buf = Unpooled.buffer();buf.writeInt(j);channel.writeInbound(buf);}try {Thread.sleep(Integer.MAX_VALUE);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}
}
// 可以看到,最终输出的只有sum值,输入的数字只有经历一个完整Status才会输出
checkpoint(status)方法的作用:
- 设置state属性的值,更新当前的状态
- 设置读断点指针
读断点指针保存着装饰器内部ReplayingDecoderBuffer成员的起始读指针。当读数据时,如果可读数据不够,ReplayingDecoderBuffer在抛出ReplayError异常之前,还会把读指针的值还原到之前的checkpoint方法设置的读断点指针。所以,在ReplayingDecoder下一次读取时,还会从之前设置的断点位置开始。
所以ReplayingDecoder类型和所有子类都需要保存状态信息,都有状态的,都不适合在不同的通道之间共享。
2.2 字符串的分包传输
public class StringReplayDecoder extends ReplayingDecoder<StringReplayDecoder.Status> {enum Status {PARSE_1, PARSE_2}private int length;private byte[] inBytes;public StringReplayDecoder() {//构造函数中,需要初始化父类的state 属性,表示当前阶段super(Status.PARSE_1);}@Overrideprotected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in,List<Object> out) throws Exception {switch (state()) {case PARSE_1://第一步,从装饰器ByteBuf 中读取长度length = in.readInt();inBytes = new byte[length];// 进入第二步,读取内容// 并且设置“读指针断点”为当前的读取位置checkpoint(Status.PARSE_2);break;case PARSE_2://第二步,从装饰器ByteBuf 中读取内容数组in.readBytes(inBytes, 0, length);out.add(new String(inBytes, StandardCharsets.UTF_8));// 第二步解析成功,// 进入第一步,读取下一个字符串的长度// 并且设置“读指针断点”为当前的读取位置checkpoint(Status.PARSE_1);break;default:break;}}
}public class StringProcessHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {@Overridepublic void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {String s = (String) msg;System.out.println("打印: " + s);}
}@Test
public void testStringReplayDecoder() {ChannelInitializer i = new ChannelInitializer<EmbeddedChannel>() {protected void initChannel(EmbeddedChannel ch) {ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringReplayDecoder());ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringProcessHandler());}};EmbeddedChannel channel = new EmbeddedChannel(i);byte[] bytes = content.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);for (int j = 0; j < 100; j++) {//1-3之间的随机数Random randoms = new Random();// 复制几次int random = Math.abs(randoms.nextInt(3)) + 1;ByteBuf buf = Unpooled.buffer();// 总长度buf.writeInt(bytes.length * random);for (int k = 0; k < random; k++) {buf.writeBytes(bytes);}channel.writeInbound(buf);}try {Thread.sleep(Integer.MAX_VALUE);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}
}
3. MessageToMessageDecoder解码器
作用:可以将一种POJO对象解码成另一种POJO对象。
需要继承MessageToMessageDecoder< T >,明确泛型T,这个实参的作用就是指定入站消息的Java POJO类型。
// 一个简单的实例
public class Integer2StringDecoder extends MessageToMessageDecoder<Integer> {@Overrideprotected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Integer msg, List<Object> out) throws Exception {// 实参为Integer,明确了入站类型为Integer,然后在解码时将Integer转为字符串,发送给下一个入站处理器out.add(String.valueOf(msg));}
}@Test
public void testIntegerToStringDecoder() {ChannelInitializer i = new ChannelInitializer<EmbeddedChannel>() {protected void initChannel(EmbeddedChannel ch) {// 二进制到Integer处理器ch.pipeline().addLast(new Byte2IntegerDecoder());// Integer到String处理器ch.pipeline().addLast(new Integer2StringDecoder());ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringProcessHandler());}};EmbeddedChannel channel = new EmbeddedChannel(i);for (int j = 0; j < 100; j++) {ByteBuf buf = Unpooled.buffer();buf.writeInt(j);channel.writeInbound(buf);}try {Thread.sleep(Integer.MAX_VALUE);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}
}
