南昌网站建设信息/宁波seo优化服务

/*
写在完成后,查找了很多资料,看到了很多方法,也看了部分top的源码,最终选择了这几种混合的方式来写,可能有更优解,不过目前这样应该够用。
--2020/12/15-- Simon
*/需求:定期获取CPU,内存,硬盘的使用率。
- [x] CPU利用率:top /proc/stat
- [x] 内存使用率:top -- sysinfo
- [x] 硬盘占用率:df (disk free) 还要想想 -- fstatfs/statfs 系统调用
先从 CPU 利用率着手,这三项数据都已经封装了现有的指令中,如果自己写一个应该怎么着手?会有什么差异
从用户态,系统态,空闲态。
平时所说CPU利用率是指:CPU执行非系统空闲进程的时间/CPU总的执行时间即 1-CPU空闲运行时间/总运行时间。
但是这个计算方式并不具备参考意义,因为总CPU时间是机器开机以来的,事实上,为了计算CPU使用率,性能工具都会取间隔一段时间(比如5秒)的两次值,做差后,再计算这段时间的平均CPU使用率。即: $$ text { 平均CPU使用率 }=1-frac{text { 空闲时间 }{text {new }}-text { 空闲时间 }{text {old }}}{text { 总 } C P U text { 时间 }{text {new }}-text { 总CPU 时间 }{text {old }}} $$ top参数详解
思考原理,IPbench的cpu_target_lukem插件参照,给程序设置一个极低的优先级,如果有任何计算任务都会打断它,如果没有计算任务,我们的程序就会占用部分CPU时间,程序运行时间上来推算CPU的空闲时间。
还有一种思路就是直接调用本地文件中的信息。
/proc/stat
linux系统的/proc目录是一种伪文件系统(虚拟文件系统),存储的是当前内核运行状态的一系列特殊文件,用户可以查看有关系统硬件及当前运行进程的信息。可以使用cat指令查看。
想要计算CPU使用率,首先要了解文件 /proc/stat中的内容
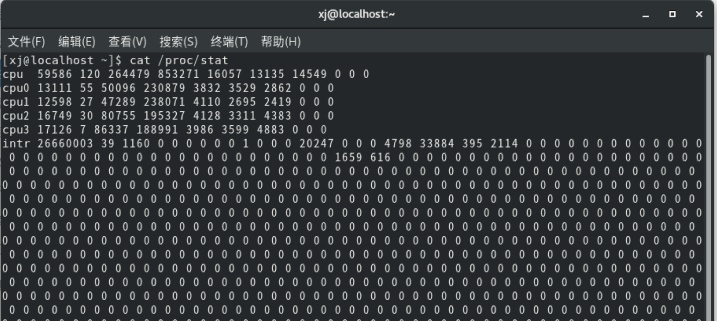
cpu以及0123中每行的每个参数意思解释:(以cpu为例)
user(59586):从系统启动开始累积到当前时刻,用户态的CPU时间(单位:jiffies),不包含nice值为负进程。 1jiffies=0.01秒。
nice(120):从系统启动开始累计到当前时刻,nice值为负的进程所占用的CPU时间(单位:jiffies)。
system(264479):从系统启动开始累计到当前时刻,核心时间。(单位:jiffies)。
idle(853271):从系统启动开始累积到当前时刻,除硬盘IO等待时间意外其他等待时间。(单位:jiffies)。
iowait(16057):从系统启动开始累积到当前时刻,硬盘IO等待时间。(单位:jiffies)。
irq(13135):从系统启动开始累积到当前时刻,硬中断时间。(单位:jiffies)。
softirq(14549):从系统启动开始累积到当前时刻,软中断时间。(单位:jiffies)。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>typedef struct CPU_PACKED //定义一个cpu occupy的结构体
{char name[20]; unsigned int user;unsigned int nice;unsigned int system;unsigned int idle;
}CPU_OCCUPY;int cal_cpuoccupy(CPU_OCCUPY *O,CPU_OCCUPY *n)
{unsigned long od, nd;unsigned long id, sd;int cpu_use = 0;od = (unsigned long)(o->user + o->nice + o->system + o->idle); //第一次(用户+优先级+系统+空闲)的时间再赋给odnd = (unsigned long)(n->user + n->nice + n->system + n->idle); //第二次(用户+优先级+系统+空闲)的时间再赋给ndid = (unsigned long)(n->user - o->user); //用户第一次和第二次的时间之差再赋给idsd = (unsigned long)(n->system - o->system); //系统第一次和第二次的时间之差再赋给sdif((nd-od) != 0)cpu_use = (int)((sd+id)*100)/(nd-od); //((用户+系统)乘100)除(第一次和第二次的时间差)再赋给g_cpu_usedelse cpu_use = 0;return cpu_use;
}void get_cpuoccupy (CPU_OCCUPY *cpust) //对无类型get函数含有一个形参结构体类弄的指针o
{FILE *fd;int n;char buff[256];CPU_OCCUPY *cpu_occupy;cpu_occupy = cpust;fd = fopen("/proc/stat","r");fgets(buff,sizeof(buff),fd);sscanf(buff,"%s %u %u %u %u",cpu_occupy->name,&cpu_occupy->user,&cpu_occupy->nice,&cpu_occupy->system,&cpu_occupy->idle);fclose(fd);
}
int main()
{CPU_OCCUPY cpu_stat1;CPU_OCCUPY cpu_stat2;int cpu;//第一次获取cpu使用情况get_cpuoccupy((CPU_OCCUPY *)&cpu_stat1);slepp(1);//第二次获取cpu使用情况get_cpuoccupy((CPU_OCCUPY *)&cpu_stat2);//计算cpu使用率cpu = cal_cpuoccupy((CPU_OCCUPY *)&cpu_stat1,(CPU_OCCUPY *)&cpu_stat2);printf("cpu usage:%d n",cpu);return 0;
}sysinfo
sysinfo函数的帮助页面如下 (通过这个我们很轻松的解决了内存使用情况部分)
wbyq@wbyq:/mnt/hgfs/linux-share-dir/linux_c$ man sysinfo
SYSINFO(2) Linux Programmer's Manual SYSINFO(2)
NAMEsysinfo - return system information
SYNOPSIS#include <sys/sysinfo.h>int sysinfo(struct sysinfo *info);DESCRIPTIONsysinfo() returns certain statistics on memory and swap usage, as well as the load average.Until Linux 2.3.16, sysinfo() returned information in the following structure:struct sysinfo {long uptime; /* Seconds since boot */unsigned long loads[3]; /* 1, 5, and 15 minute load averages */unsigned long totalram; /* Total usable main memory size */unsigned long freeram; /* Available memory size */unsigned long sharedram; /* Amount of shared memory */unsigned long bufferram; /* Memory used by buffers */unsigned long totalswap; /* Total swap space size */unsigned long freeswap; /* Swap space still available */unsigned short procs; /* Number of current processes */char _f[22]; /* Pads structure to 64 bytes */};In the above structure, the sizes of the memory and swap fields are given in bytes.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/sysinfo.h>int main(int argc,char **argv)
{/*2. 获取当前系统内存使用情况*/struct sysinfo s_info;char info_buff[100];while(1){if(sysinfo(&s_info)==0){sprintf(info_buff,"总内存: %.ld M",s_info.totalram/1024/1024);printf("%sn",info_buff);sprintf(info_buff,"未使用内存: %.ld M",s_info.freeram/1024/1024);printf("%sn",info_buff);sprintf(info_buff,"交换区总内存: %.ld M",s_info.totalswap/1024/1024);printf("%sn",info_buff);sprintf(info_buff,"交换区未使用内存: %.ld M",s_info.freeswap/1024/1024);printf("%sn",info_buff);sprintf(info_buff,"系统运行时间: %.ld 分钟",s_info.uptime/60);printf("%sn",info_buff);printf("nn");}sleep(1);}return 0;
}fstatfs/statfs 系统调用
用法: #include <sys/vfs.h> /*或者 <sys/statfs.h>*/
int statfs (const char path, struct statfs buf);
int fstatfs(int fd, struct statfs *buf);
参数:
- path -- 位于需要查询信息的文件描述的文件路径名。
- fd -- 位于需要查询信息的文件系统的文件描述词。
- buf -- 以下结构体的指针变量,用于存储文件系统相关的信息。
struct statfs{long f_type; /*文件系统类型*/long f_bsize; /* 经过优化的传输块大小 */long f_blocks; /* 文件系统数据块总数 */long f_bfree; /* 可用块数 */long f_bavail; /* 非超级用户可获取的块数 */long f_files; /* 文件结点总数 */long f_ffree; /* 可用文件结点数 */fsid_t f_fsid; /* 文件系统标识 */long f_namelen; /* 文件名的最大长度 */
}A simple sample :
#include <sys/vfs.h>
#include <stdio.h>int main()
{struct statfs diskInfo;statfs("/",&diskInfo);unsigned long blocksize = diskInfo.f_bsize;// 每个block里面包含的字节数unsigned long totalsize = blocksize * diskInfo.f_blocks;//总的字节数printf("TOTAL_SIZE == %lu MB/n",totalsize>>20); // 1024*1024 =1MB 换算成MB单位unsigned long freeDisk = diskInfo.f_bfree*blocksize; //再计算下剩余的空间大小printf("DISK_FREE == %ld MB/n",freeDisk>>20);return 0;
}一个简单的测试:
#include <sys/statfs.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>#define KB 1024.0 // 2^10
#define MB 1048576.0 // 2^20
#define GB 1073741824.0 // 2^30 int main(void)
{struct statfs diskInfo;statfs("/", &diskInfo);unsigned long blocksize = diskInfo.f_bsize; // 每个block里包含的字节数unsigned long totalsize = blocksize * diskInfo.f_blocks; // 总的字节数,f_blocks为block的数目printf("块数:%lld",diskInfo.f_blocks);printf("Total_size = %lld B = %f KB = %f MB = %f GBn",totalsize,totalsize / KB,totalsize / MB,totalsize / GB);unsigned long freeDisk = diskInfo.f_bfree * blocksize; // 剩余空间的大小unsigned long availableDisk = diskInfo.f_bavail * blocksize; // 可用空间大小printf("Disk_free = %f MB = %f GBn""Disk_available = %f MB = %f GBn",freeDisk / MB,freeDisk / GB,availableDisk / MB,availableDisk / GB);return 0;
}相关的文件系统类型有: ADFS_SUPER_MAGIC 0xadf5 AFFS_SUPER_MAGIC 0xADFF BEFS_SUPER_MAGIC 0x42465331 BFS_MAGIC 0x1BADFACE CIFS_MAGIC_NUMBER 0xFF534D42 CODA_SUPER_MAGIC 0x73757245 COH_SUPER_MAGIC 0x012FF7B7 CRAMFS_MAGIC 0x28cd3d45 DEVFS_SUPER_MAGIC 0x1373 EFS_SUPER_MAGIC 0x00414A53 EXT_SUPER_MAGIC 0x137D EXT2_OLD_SUPER_MAGIC 0xEF51 EXT2_SUPER_MAGIC 0xEF53 EXT3_SUPER_MAGIC 0xEF53 HFS_SUPER_MAGIC 0x4244 HPFS_SUPER_MAGIC 0xF995E849 HUGETLBFS_MAGIC 0x958458f6 ISOFS_SUPER_MAGIC 0x9660 JFFS2_SUPER_MAGIC 0x72b6 JFS_SUPER_MAGIC 0x3153464a MINIX_SUPER_MAGIC 0x137F / orig. minix / MINIX_SUPER_MAGIC2 0x138F / 30 char minix / MINIX2_SUPER_MAGIC 0x2468 / minix V2 / MINIX2_SUPER_MAGIC2 0x2478 / minix V2, 30 char names / MSDOS_SUPER_MAGIC 0x4d44 NCP_SUPER_MAGIC 0x564c NFS_SUPER_MAGIC 0x6969 NTFS_SB_MAGIC 0x5346544e OPENPROM_SUPER_MAGIC 0x9fa1 PROC_SUPER_MAGIC 0x9fa0 QNX4_SUPER_MAGIC 0x002f REISERFS_SUPER_MAGIC 0x52654973 ROMFS_MAGIC 0x7275 SMB_SUPER_MAGIC 0x517B SYSV2_SUPER_MAGIC 0x012FF7B6 SYSV4_SUPER_MAGIC 0x012FF7B5 TMPFS_MAGIC 0x01021994 UDF_SUPER_MAGIC 0x15013346 UFS_MAGIC 0x00011954 USBDEVICE_SUPER_MAGIC 0x9fa2 VXFS_SUPER_MAGIC 0xa501FCF5 XENIX_SUPER_MAGIC 0x012FF7B4 XFS_SUPER_MAGIC 0x58465342 _XIAFS_SUPER_MAGIC 0x012FD16D
返回说明:
成功执行时候,返回0。失败返回-1,error被设定为一下的某个值
EACCES: (statfs())文件或路径名中包含的目录不可访问 EBADF : (fstatfs()) 文件描述词无效 EFAULT: 内存地址无效 EINTR : 操作由信号中断 EIO : 读写出错 ELOOP : (statfs())解释路径名过程中存在太多的符号连接 ENAMETOOLONG:(statfs()) 路径名太长 ENOENT:(statfs()) 文件不存在 ENOMEM: 核心内存不足 ENOSYS: 文件系统不支持调用 ENOTDIR:(statfs())路径名中当作目录的组件并非目录 EOVERFLOW:信息溢出
总:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/sysinfo.h>
#include <sys/statfs.h>
#define Mb 1048576
#define Min 60
#define gap_t 1
#define gap_c 1
typedef struct CPU_PACKED //定义一个cpu occupy的结构体
{char name[20]; unsigned int user;unsigned int nice;unsigned int system;unsigned int idle;
}CPU_OCCUPY;void get_cpuoccupy (CPU_OCCUPY *cpust) //对无类型get函数含有一个形参结构体类弄的指针o
{FILE *fd;int n;char buff[256];CPU_OCCUPY *cpu_occupy;cpu_occupy = cpust;fd = fopen("/proc/stat","r");fgets(buff,sizeof(buff),fd);sscanf(buff,"%s %u %u %u %u",cpu_occupy->name,&cpu_occupy->user,&cpu_occupy->nice,&cpu_occupy->system,&cpu_occupy->idle);fclose(fd);
}int cal_cpuoccupy(CPU_OCCUPY *o,CPU_OCCUPY *n)
{unsigned long od, nd;unsigned long id, sd;int cpu_use = 0;od = (unsigned long)(o->user + o->nice + o->system + o->idle); //第一次(用户+优先级+系统+空闲)的时间再赋给odnd = (unsigned long)(n->user + n->nice + n->system + n->idle); //第二次(用户+优先级+系统+空闲)的时间再赋给ndid = (unsigned long)(n->user - o->user); //用户第一次和第二次的时间之差再赋给idsd = (unsigned long)(n->system - o->system); //系统第一次和第二次的时间之差再赋给sdif((nd-od) != 0)cpu_use = (int)((sd+id)*100)/(nd-od); //((用户+系统)乘100)除(第一次和第二次的时间差)再赋给g_cpu_usedelse cpu_use = 0;return cpu_use;
}int main(int argc,char **argv)
{struct sysinfo s_info;struct statfs sfs;char info_buff[100];while(1){
//cpu
CPU_OCCUPY cpu_stat1;CPU_OCCUPY cpu_stat2;int cpu;//第一次获取cpu使用情况get_cpuoccupy((CPU_OCCUPY *)&cpu_stat1);
sleep(gap_c);//第二次获取cpu使用情况get_cpuoccupy((CPU_OCCUPY *)&cpu_stat2);//计算cpu使用率cpu = cal_cpuoccupy((CPU_OCCUPY *)&cpu_stat1,(CPU_OCCUPY *)&cpu_stat2);//diskint disk_have = 0;int ret = statfs("/", &sfs);disk_have = (sfs.f_blocks - sfs.f_bfree ) * 100 / (sfs.f_blocks - sfs.f_bfree + sfs.f_bavail) + 1;//mem
//从sysinfo系统调用if(sysinfo(&s_info)==0){sprintf(info_buff,"总内存: %.ld M",s_info.totalram/Mb);printf("%sn",info_buff);sprintf(info_buff,"未使用内存: %.ld M",s_info.freeram/Mb);printf("%sn",info_buff);sprintf(info_buff,"交换区总内存: %.ld M",s_info.totalswap/Mb);printf("%sn",info_buff);sprintf(info_buff,"交换区未使用内存: %.ld M",s_info.freeswap/Mb);printf("%sn",info_buff);}
// disk
// 从fstatfs/statfs系统调用
printf("disk:%d%%n",disk_have);//cpu
printf("cpu usage:%d%%n",cpu);//time
sprintf(info_buff,"系统运行时间: %.ld 分钟",s_info.uptime/Min);printf("%sn",info_buff);printf("nn");sleep(gap_t);}return 0;
}