做购物网站哪家公司好/北京seo收费
文章目录
- 1 @Conditional注解的作用
- 2 学习dome
- 3 总结
本博客demo源码地址
https://github.com/suchahaerkang/spring-annotation.git
1 @Conditional注解的作用
@Conditional是spring4中的一个注解,作用是在spring容器中注册组件的时候,进行一些条件判断,如果判断成功,那么就可以将组件注册在spring容器中去,否则不注册,@Conditional注解在spring源码中用到了很多,所以这个注解是非常重要的,我们很有必要去掌握。
2 学习dome
为了方便学习,先描述一个小的场景,我们都知道windows之父是bill gates, linux之父是linus,现在我们将这两个人注册都spring容器中
@Bean("bill")public Person person01(){return new Person("bill", 65);}@Bean("linus")public Person person02(){return new Person("linus", 67);}
写个测试用例,看一下容器中是否有这两个实例了
@Testpublic void test04(){//创建容器ApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig2.class);//通过组件类型从容器中获取所有的实例名字String[] beanNames = applicationContext.getBeanNamesForType(Person.class);for (String name :beanNames) {System.out.println(name);}}
运行结果
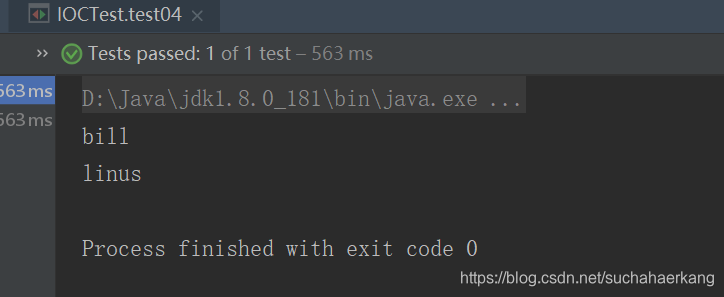
然后现在我们有个需求,希望程序在windows环境下,只能将bill这个实例注册到容器中去,在linux环境下将linus这个实例注册到环境中去,下面我们就通过@Conditional这个注解来解决这个需求
因为@Conditional注解需要一个或则多个条件,所以我们先编写两个条件,条件必须实现Condition 这个接口。这个两个条件分别是:
如果程序在windows操作系统下,那么就返回true
public class WindowsCondition implements Condition {/*** @description:* @param conditionContext 判断条件需要的上下文* @param annotatedTypeMetadata 获取的注解信息* @return: boolean* @author: sukang* @date: 2020/3/5 12:28*/public boolean matches(ConditionContext conditionContext, AnnotatedTypeMetadata annotatedTypeMetadata) {//可以获取ioc容器创建实例的bean工厂ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = conditionContext.getBeanFactory();//可以获取类加载器ClassLoader classLoader = conditionContext.getClassLoader();//可以获取运行时的环境变量和jvm变量Environment environment = conditionContext.getEnvironment();//可以获取注册都容器中的所有实例BeanDefinitionRegistry beanDefinitionRegistry = conditionContext.getRegistry();//这里我们就通过Environment对象获取操作系统的名字String osName = environment.getProperty("os.name");System.out.println("本操作系统为:" + osName);//如果操作系统为windows那么返回成功if(osName.contains("Windows")){return true;}return false;}}
如果操作系统为Linux,那么就返回为true
/*** @description:* @author: sukang* @date: 2020-03-05 12:38*/public class LinuxCondition implements Condition {public boolean matches(ConditionContext conditionContext, AnnotatedTypeMetadata annotatedTypeMetadata) {//可以获取运行时的环境变量和jvm变量Environment environment = conditionContext.getEnvironment();//这里我们就通过Environment对象获取操作系统的名字String osName = environment.getProperty("os.name");System.out.println("本操作系统为:" + osName);//如果操作系统为windows那么返回成功if(osName.contains("Linux")){return true;}return false;}}
配置文件上加上@Conditional的注解
@Conditional(WindowsCondition.class)@Bean("bill")public Person person01(){return new Person("bill", 65);}@Conditional(LinuxCondition.class)@Bean("linus")public Person person02(){return new Person("linus", 67);}
测试用例
@Testpublic void test04(){//创建容器ApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig2.class);//通过组件类型从容器中获取所有的实例名字String[] beanNames = applicationContext.getBeanNamesForType(Person.class);for (String name :beanNames) {System.out.println(name);}}
开始测试,本机为windows环境,所以运行结果为
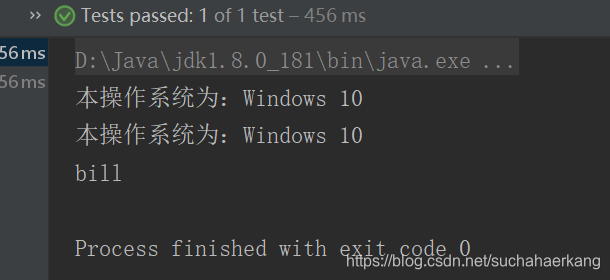
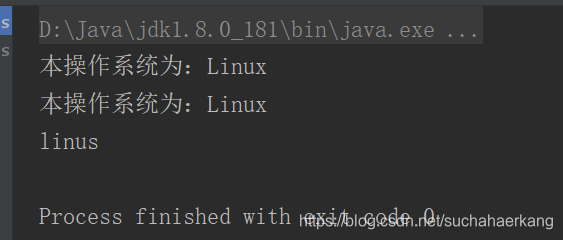
为了模拟程序运行在linux环境下,我们在idea改一下运行环境
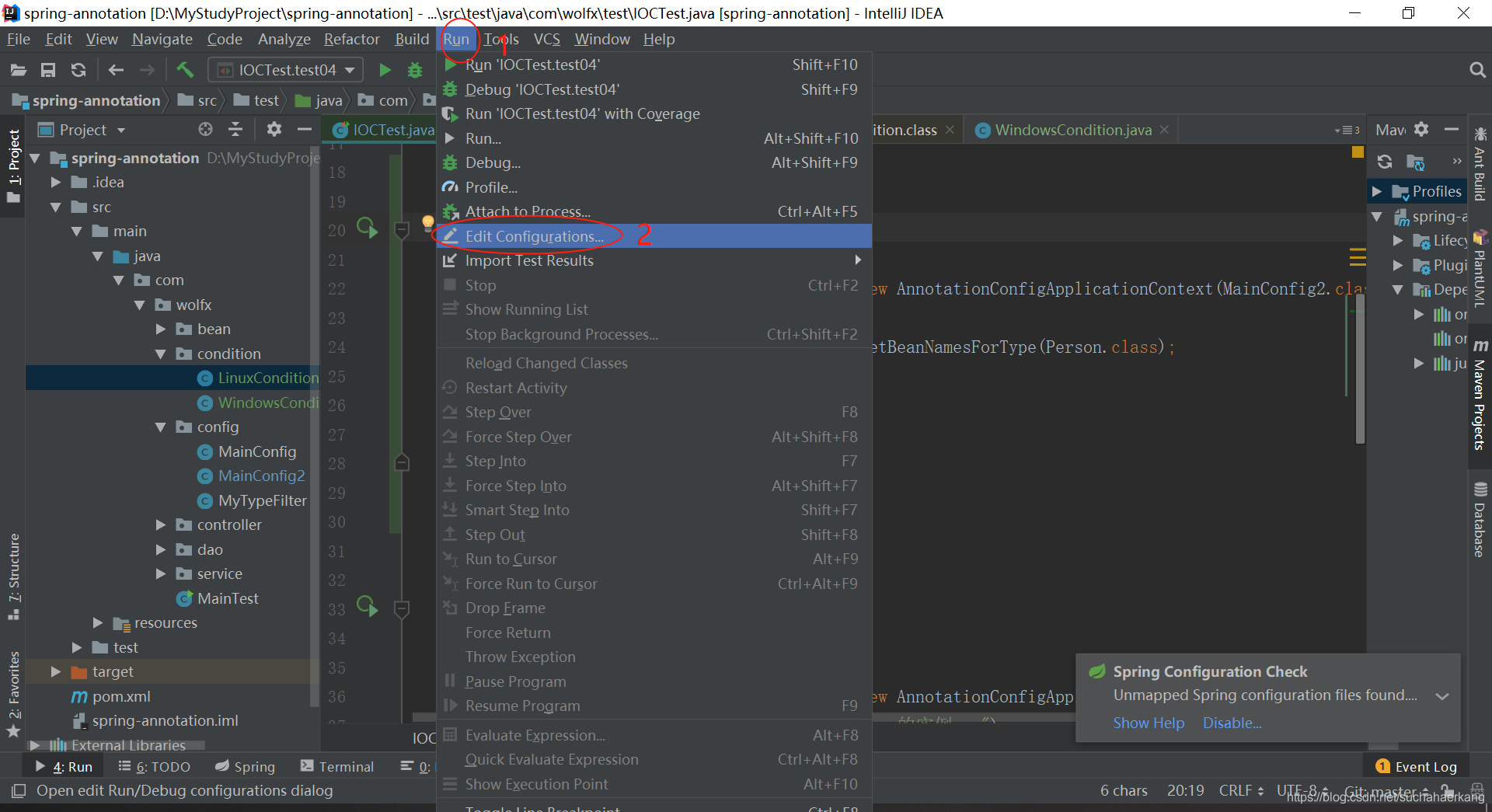
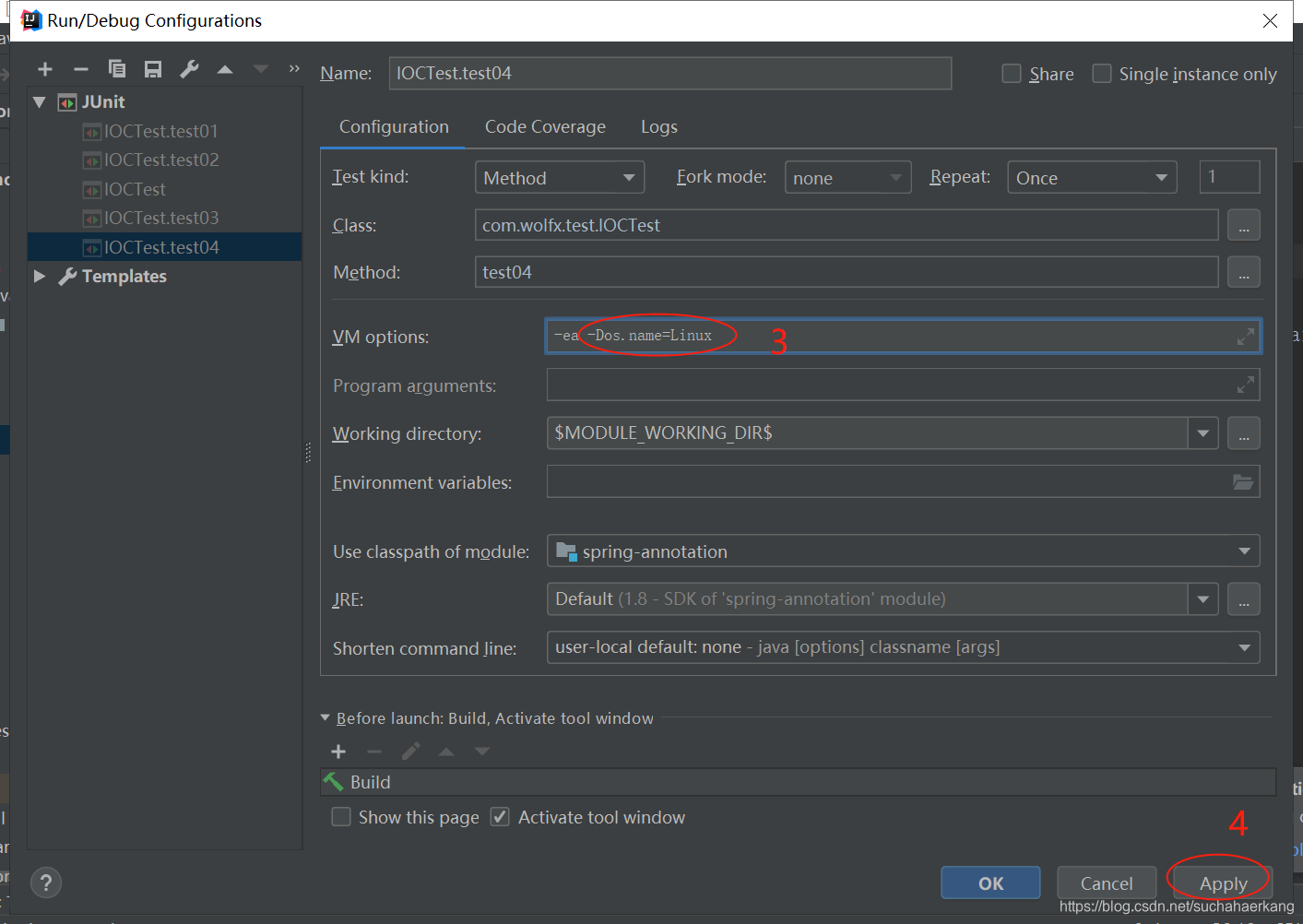
运行结果
3 总结
@Conditional注解可以放在方法或则类上面,如果放在类上表示如果条件不满足,那么配置类里面的组件都不能注册到容器中去
