网站建设多久可以建成太原做网站哪家好
前言:本文介绍一下 V8 关于 Inspector 的实现,不过不会涉及到具体命令的实现,V8 Inspector 的命令非常多,了解了处理流程后,如果对某个命令感兴趣的话,可以单独去分析。
首先来看一下 V8 Inspector 中几个关键的角色。
1. V8InspectorSession
class V8_EXPORT V8InspectorSession {public:// 收到对端端消息,调用这个方法判断是否可以分发static bool canDispatchMethod(StringView method);// 收到对端端消息,调用这个方法判断分发virtual void dispatchProtocolMessage(StringView message) = 0;
};
V8InspectorSession 是一个基类,本身实现了 canDispatchMethod 方法,由子类实现 dispatchProtocolMessage 方法。看一下 canDispatchMethod 的实现。
bool V8InspectorSession::canDispatchMethod(StringView method) {return stringViewStartsWith(method,protocol::Runtime::Metainfo::commandPrefix) ||stringViewStartsWith(method,protocol::Debugger::Metainfo::commandPrefix) ||stringViewStartsWith(method,protocol::Profiler::Metainfo::commandPrefix) ||stringViewStartsWith(method, protocol::HeapProfiler::Metainfo::commandPrefix) ||stringViewStartsWith(method,protocol::Console::Metainfo::commandPrefix) ||stringViewStartsWith(method,protocol::Schema::Metainfo::commandPrefix);
}
canDispatchMethod 决定了 V8 目前支持哪些命令。接着看一下 V8InspectorSession 子类的实现。
class V8InspectorSessionImpl : public V8InspectorSession,public protocol::FrontendChannel {public:// 静态方法,用于创建 V8InspectorSessionImplstatic std::unique_ptr<V8InspectorSessionImpl> create(V8InspectorImpl*,int contextGroupId,int sessionId,V8Inspector::Channel*,StringView state);// 实现命令的分发void dispatchProtocolMessage(StringView message) override;// 支持哪些命令std::vector<std::unique_ptr<protocol::Schema::API::Domain>> supportedDomains() override;private:// 发送消息给对端void SendProtocolResponse(int callId, std::unique_ptr<protocol::Serializable> message) override;void SendProtocolNotification(std::unique_ptr<protocol::Serializable> message) override;// 会话 idint m_sessionId;// 关联的 V8Inspector 对象V8InspectorImpl* m_inspector;// 关联的 channel,channel 表示会话的两端V8Inspector::Channel* m_channel;// 处理命令分发对象protocol::UberDispatcher m_dispatcher;// 处理某种命令的代理对象std::unique_ptr<V8RuntimeAgentImpl> m_runtimeAgent;std::unique_ptr<V8DebuggerAgentImpl> m_debuggerAgent;std::unique_ptr<V8HeapProfilerAgentImpl> m_heapProfilerAgent;std::unique_ptr<V8ProfilerAgentImpl> m_profilerAgent;std::unique_ptr<V8ConsoleAgentImpl> m_consoleAgent;std::unique_ptr<V8SchemaAgentImpl> m_schemaAgent;
};
下面看一下核心方法的具体实现。
- 创建 V8InspectorSessionImpl
V8InspectorSessionImpl::V8InspectorSessionImpl(V8InspectorImpl* inspector,int contextGroupId,int sessionId,V8Inspector::Channel* channel,StringView savedState): m_contextGroupId(contextGroupId),m_sessionId(sessionId),m_inspector(inspector),m_channel(channel),m_customObjectFormatterEnabled(false),m_dispatcher(this),m_state(ParseState(savedState)),m_runtimeAgent(nullptr),m_debuggerAgent(nullptr),m_heapProfilerAgent(nullptr),m_profilerAgent(nullptr),m_consoleAgent(nullptr),m_schemaAgent(nullptr) {m_runtimeAgent.reset(new V8RuntimeAgentImpl(this, this, agentState(protocol::Runtime::Metainfo::domainName)));protocol::Runtime::Dispatcher::wire(&m_dispatcher, m_runtimeAgent.get());m_debuggerAgent.reset(new V8DebuggerAgentImpl(this, this, agentState(protocol::Debugger::Metainfo::domainName)));protocol::Debugger::Dispatcher::wire(&m_dispatcher, m_debuggerAgent.get());m_profilerAgent.reset(new V8ProfilerAgentImpl(this, this, agentState(protocol::Profiler::Metainfo::domainName)));protocol::Profiler::Dispatcher::wire(&m_dispatcher, m_profilerAgent.get());m_heapProfilerAgent.reset(new V8HeapProfilerAgentImpl(this, this, agentState(protocol::HeapProfiler::Metainfo::domainName)));protocol::HeapProfiler::Dispatcher::wire(&m_dispatcher,m_heapProfilerAgent.get());m_consoleAgent.reset(new V8ConsoleAgentImpl(this, this, agentState(protocol::Console::Metainfo::domainName)));protocol::Console::Dispatcher::wire(&m_dispatcher, m_consoleAgent.get());m_schemaAgent.reset(new V8SchemaAgentImpl(this, this, agentState(protocol::Schema::Metainfo::domainName)));protocol::Schema::Dispatcher::wire(&m_dispatcher, m_schemaAgent.get());
}
V8 支持很多种命令,在创建 V8InspectorSessionImpl 对象时,会注册所有命令和处理该命令的处理器。我们一会单独分析。
2. 接收请求
void V8InspectorSessionImpl::dispatchProtocolMessage(StringView message) {using v8_crdtp::span;using v8_crdtp::SpanFrom;span<uint8_t> cbor;std::vector<uint8_t> converted_cbor;if (IsCBORMessage(message)) {use_binary_protocol_ = true;m_state->setBoolean("use_binary_protocol", true);cbor = span<uint8_t>(message.characters8(), message.length());} else {auto status = ConvertToCBOR(message, &converted_cbor);cbor = SpanFrom(converted_cbor);}v8_crdtp::Dispatchable dispatchable(cbor);// 消息分发m_dispatcher.Dispatch(dispatchable).Run();
}
接收消息后,在内部通过 m_dispatcher.Dispatch 进行分发,这就好比我们在 Node.js 里收到请求后,根据路由分发一样。具体的分发逻辑一会单独分析。
3. 响应请求
void V8InspectorSessionImpl::SendProtocolResponse(int callId, std::unique_ptr<protocol::Serializable> message) {m_channel->sendResponse(callId, serializeForFrontend(std::move(message)));
}
具体的处理逻辑由 channel 实现,channel 由 V8 的使用者实现,比如 Node.js。
4. 数据推送
void V8InspectorSessionImpl::SendProtocolNotification(std::unique_ptr<protocol::Serializable> message) {m_channel->sendNotification(serializeForFrontend(std::move(message)));
}
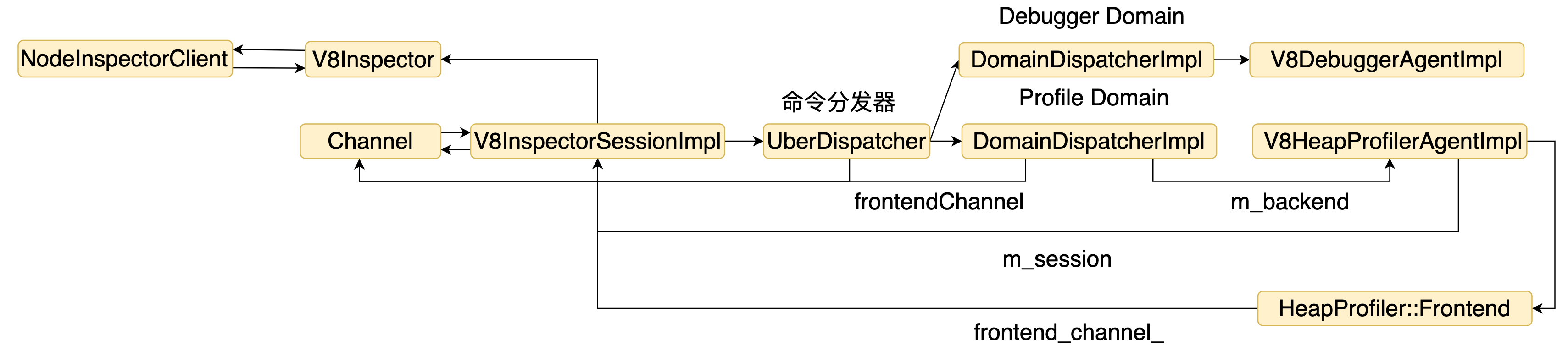
除了一个请求对应一个响应,V8 Inspector 还需要主动推送的能力,具体处理逻辑也是由 channel 实现。从上面点分析可以看到 V8InspectorSessionImpl 的概念相当于一个服务器,在启动的时候注册了一系列路由,当建立一个连接时,就会创建一个 Channel 对象表示。调用方可以通过 Channel 完成请求和接收响应。结构如下图所示。
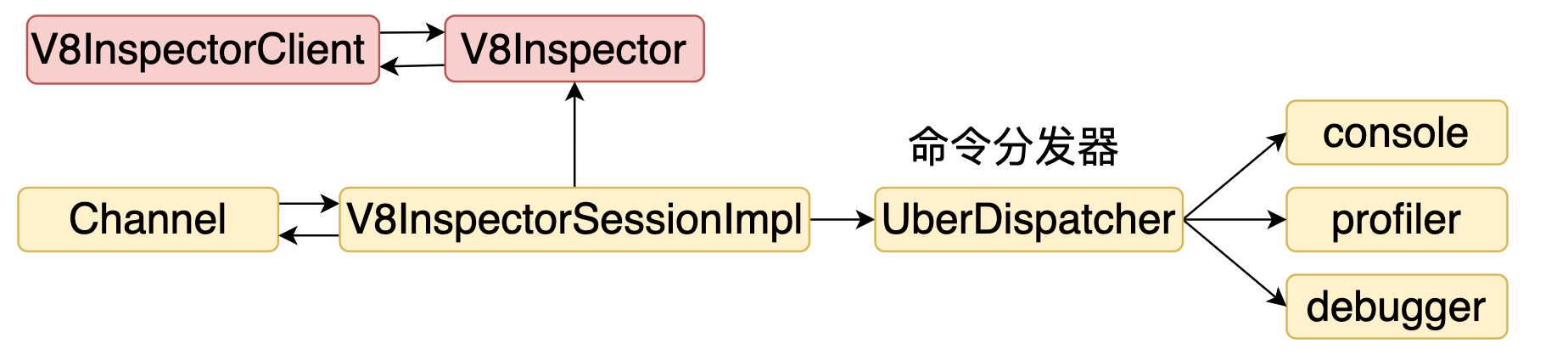
2. V8Inspector
class V8_EXPORT V8Inspector {public:// 静态方法,用于创建 V8Inspectorstatic std::unique_ptr<V8Inspector> create(v8::Isolate*, V8InspectorClient*);// 用于创建一个 V8InspectorSessionvirtual std::unique_ptr<V8InspectorSession> connect(int contextGroupId,Channel*,StringView state) = 0;
};
V8Inspector 是一个通信的总管,他不负责具体的通信,他只是负责管理通信者,Channel 才是负责通信的角色。下面看一下 V8Inspector 子类的实现 。
class V8InspectorImpl : public V8Inspector {public:V8InspectorImpl(v8::Isolate*, V8InspectorClient*);// 创建一个会话std::unique_ptr<V8InspectorSession> connect(int contextGroupId,V8Inspector::Channel*,StringView state) override;private:v8::Isolate* m_isolate;// 关联的 V8InspectorClient 对象,V8InspectorClient 封装了 V8Inspector,由调用方实现V8InspectorClient* m_client;// 保存所有的会话std::unordered_map<int, std::map<int, V8InspectorSessionImpl*>> m_sessions;
};
V8InspectorImpl 提供了创建会话的方法并保存了所有创建的会话,看一下创建会话的逻辑。
std::unique_ptr<V8InspectorSession> V8InspectorImpl::connect(int contextGroupId, V8Inspector::Channel* channel, StringView state) {int sessionId = ++m_lastSessionId;std::unique_ptr<V8InspectorSessionImpl> session = V8InspectorSessionImpl::create(this, contextGroupId, sessionId, channel, state);m_sessions[contextGroupId][sessionId] = session.get();return std::move(session);
}
connect 是创建了一个 V8InspectorSessionImpl 对象,并通过 id 保存到 map中。结构图如下。
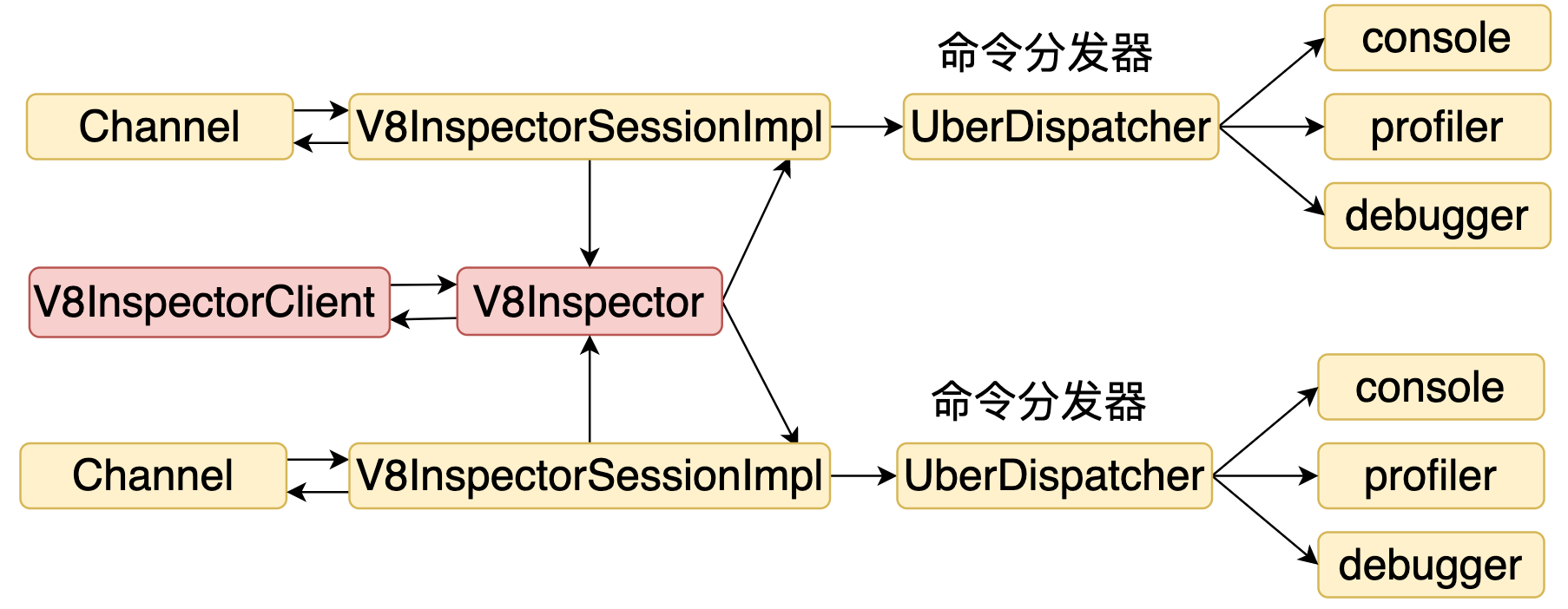
3. UberDispatcher
UberDispatcher 是一个命令分发器。
class UberDispatcher {public:// 表示分发结果的对象class DispatchResult {};// 分发处理函数DispatchResult Dispatch(const Dispatchable& dispatchable) const;// 注册命令和处理器 void WireBackend(span<uint8_t> domain,const std::vector<std::pair<span<uint8_t>, span<uint8_t>>>&,std::unique_ptr<DomainDispatcher> dispatcher);private:// 查找命令对应的处理器,Dispatch 中使用DomainDispatcher* findDispatcher(span<uint8_t> method);// 关联的 channelFrontendChannel* const frontend_channel_;std::vector<std::pair<span<uint8_t>, span<uint8_t>>> redirects_;// 命令处理器队列std::vector<std::pair<span<uint8_t>, std::unique_ptr<DomainDispatcher>>>dispatchers_;
};
下面看一下注册和分发的实现。
- 注册
void UberDispatcher::WireBackend(span<uint8_t> domain, std::unique_ptr<DomainDispatcher> dispatcher) {dispatchers_.insert(dispatchers_.end(), std::make_pair(domain, std::move(dispatcher))););
}
WireBackend 就是在队列里插入一个新的 domain 和 处理器组合。
2. 分发命令
UberDispatcher::DispatchResult UberDispatcher::Dispatch(const Dispatchable& dispatchable) const {span<uint8_t> method = FindByFirst(redirects_, dispatchable.Method(),/*default_value=*/dispatchable.Method());// 找到 . 的偏移,命令格式是 A.B size_t dot_idx = DotIdx(method);// 拿到 domain,即命令的第一部分span<uint8_t> domain = method.subspan(0, dot_idx);// 拿到命令span<uint8_t> command = method.subspan(dot_idx + 1);// 通过 domain 查找对应的处理器DomainDispatcher* dispatcher = FindByFirst(dispatchers_, domain);if (dispatcher) {// 交给 domain 对应的处理器继续处理std::function<void(const Dispatchable&)> dispatched =dispatcher->Dispatch(command);if (dispatched) {return DispatchResult(true, [dispatchable, dispatched = std::move(dispatched)]() {dispatched(dispatchable);});}}
}
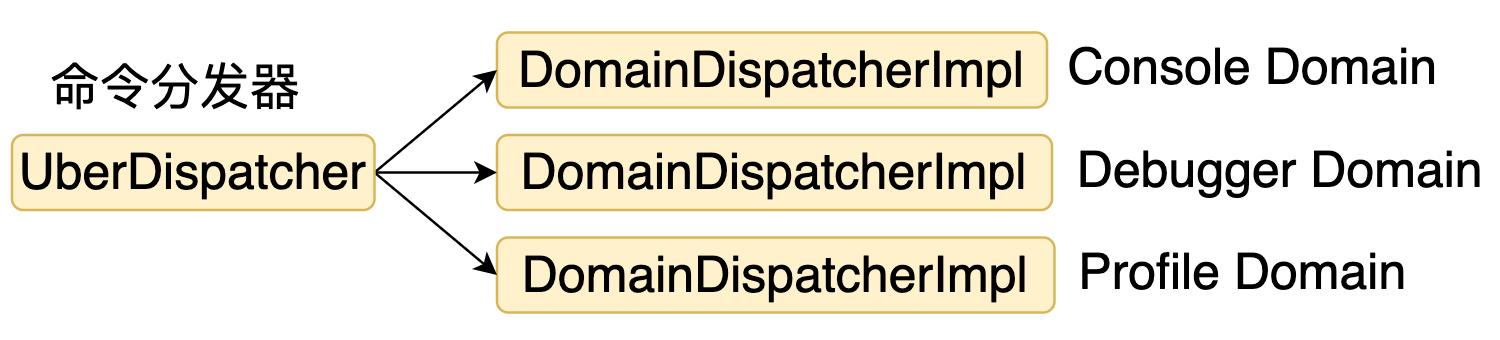
4. DomainDispatcher
刚才分析了 UberDispatcher,UberDispatcher 是一个命令一级分发器,因为命令是 domain.cmd 的格式,UberDispatcher 是根据 domain 进行初步分发,DomainDispatcher 则是找到具体命令对应的处理器。
class DomainDispatcher {// 分发逻辑,子类实现virtual std::function<void(const Dispatchable&)> Dispatch(span<uint8_t> command_name) = 0;// 处理完后响应void sendResponse(int call_id,const DispatchResponse&,std::unique_ptr<Serializable> result = nullptr);private:// 关联的 channelFrontendChannel* frontend_channel_;
};
DomainDispatcher 定义了命令分发和响应的逻辑,不同的 domain 的分发逻辑会有不同的实现,但是响应逻辑是一样的,所以基类实现了。
void DomainDispatcher::sendResponse(int call_id,const DispatchResponse& response,std::unique_ptr<Serializable> result) {std::unique_ptr<Serializable> serializable;if (response.IsError()) {serializable = CreateErrorResponse(call_id, response);} else {serializable = CreateResponse(call_id, std::move(result));}frontend_channel_->SendProtocolResponse(call_id, std::move(serializable));
}
通过 frontend_channel_ 返回响应。接下来看子类的实现,这里以 HeapProfiler 为例。
class DomainDispatcherImpl : public protocol::DomainDispatcher {
public:DomainDispatcherImpl(FrontendChannel* frontendChannel, Backend* backend): DomainDispatcher(frontendChannel), m_backend(backend) {}~DomainDispatcherImpl() override { }using CallHandler = void (DomainDispatcherImpl::*)(const v8_crdtp::Dispatchable& dispatchable);// 分发的实现std::function<void(const v8_crdtp::Dispatchable&)> Dispatch(v8_crdtp::span<uint8_t> command_name) override;// HeapProfiler 支持的命令void addInspectedHeapObject(const v8_crdtp::Dispatchable& dispatchable);void collectGarbage(const v8_crdtp::Dispatchable& dispatchable);void disable(const v8_crdtp::Dispatchable& dispatchable);void enable(const v8_crdtp::Dispatchable& dispatchable);void getHeapObjectId(const v8_crdtp::Dispatchable& dispatchable);void getObjectByHeapObjectId(const v8_crdtp::Dispatchable& dispatchable);void getSamplingProfile(const v8_crdtp::Dispatchable& dispatchable);void startSampling(const v8_crdtp::Dispatchable& dispatchable);void startTrackingHeapObjects(const v8_crdtp::Dispatchable& dispatchable);void stopSampling(const v8_crdtp::Dispatchable& dispatchable);void stopTrackingHeapObjects(const v8_crdtp::Dispatchable& dispatchable);void takeHeapSnapshot(const v8_crdtp::Dispatchable& dispatchable);protected:Backend* m_backend;
};
DomainDispatcherImpl 定义了 HeapProfiler 支持的命令,下面分析一下命令的注册和分发的处理逻辑。下面是 HeapProfiler 注册 domain 和 处理器的逻辑(创建 V8InspectorSessionImpl 时)
// backend 是处理命令的具体对象,对于 HeapProfiler domain 是 V8HeapProfilerAgentImpl
void Dispatcher::wire(UberDispatcher* uber, Backend* backend)
{ // channel 是通信的对端auto dispatcher = std::make_unique<DomainDispatcherImpl>(uber->channel(), backend);// 注册 domain 对应的处理器uber->WireBackend(v8_crdtp::SpanFrom("HeapProfiler"), std::move(dispatcher));
}
接下来看一下收到命令时具体的分发逻辑。
std::function<void(const v8_crdtp::Dispatchable&)> DomainDispatcherImpl::Dispatch(v8_crdtp::span<uint8_t> command_name) {// 根据命令查找处理函数CallHandler handler = CommandByName(command_name);// 返回个函数,外层执行return [this, handler](const v8_crdtp::Dispatchable& dispatchable) {(this->*handler)(dispatchable);};
}
看一下查找的逻辑。
DomainDispatcherImpl::CallHandler CommandByName(v8_crdtp::span<uint8_t> command_name) {static auto* commands = [](){auto* commands = new std::vector<std::pair<v8_crdtp::span<uint8_t>, DomainDispatcherImpl::CallHandler>>{// 太多,不一一列举{v8_crdtp::SpanFrom("enable"),&DomainDispatcherImpl::enable},};return commands;}();return v8_crdtp::FindByFirst<DomainDispatcherImpl::CallHandler>(*commands, command_name, nullptr);
}
再看一下 DomainDispatcherImpl::enable 的实现。
void DomainDispatcherImpl::enable(const v8_crdtp::Dispatchable& dispatchable)
{std::unique_ptr<DomainDispatcher::WeakPtr> weak = weakPtr();// 调用 m_backend 也就是 V8HeapProfilerAgentImpl 的 enableDispatchResponse response = m_backend->enable();if (response.IsFallThrough()) {channel()->FallThrough(dispatchable.CallId(), v8_crdtp::SpanFrom("HeapProfiler.enable"), dispatchable.Serialized());return;}if (weak->get())weak->get()->sendResponse(dispatchable.CallId(), response);return;
}
DomainDispatcherImpl 只是封装,具体的命令处理交给 m_backend 所指向的对象,这里是 V8HeapProfilerAgentImpl。下面是 V8HeapProfilerAgentImpl enable 的实现。
Response V8HeapProfilerAgentImpl::enable() {m_state->setBoolean(HeapProfilerAgentState::heapProfilerEnabled, true);return Response::Success();
}
结构图如下。
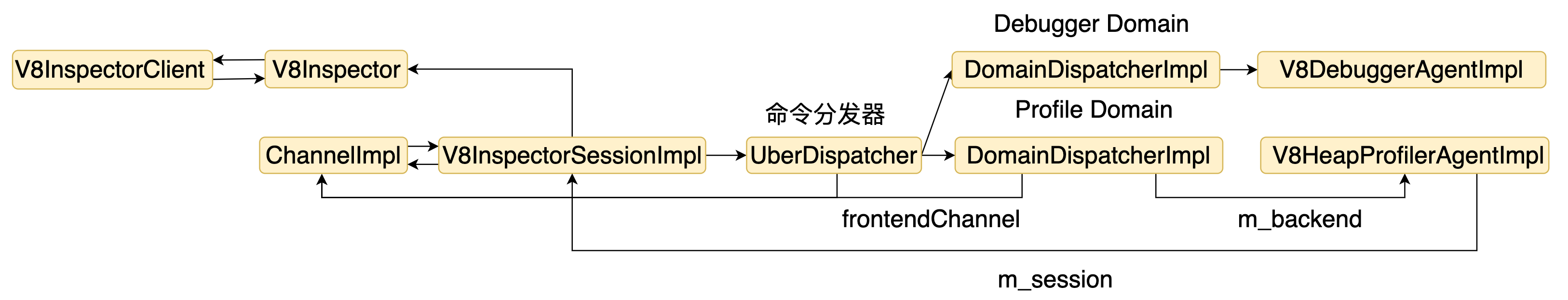
5. V8HeapProfilerAgentImpl
刚才分析了 V8HeapProfilerAgentImpl 的 enable 函数,这里以 V8HeapProfilerAgentImpl 为例子分析一下命令处理器类的逻辑。
class V8HeapProfilerAgentImpl : public protocol::HeapProfiler::Backend {public:V8HeapProfilerAgentImpl(V8InspectorSessionImpl*, protocol::FrontendChannel*,protocol::DictionaryValue* state);private:V8InspectorSessionImpl* m_session;v8::Isolate* m_isolate;// protocol::HeapProfiler::Frontend 定义了支持哪些事件protocol::HeapProfiler::Frontend m_frontend;protocol::DictionaryValue* m_state;
};
V8HeapProfilerAgentImpl 通过 protocol::HeapProfiler::Frontend 定义了支持的事件,因为 Inspector 不仅可以处理调用方发送的命令,还可以主动给调用方推送消息,这种推送就是以事件的方式触发的。
class Frontend {
public:explicit Frontend(FrontendChannel* frontend_channel) : frontend_channel_(frontend_channel) {}void addHeapSnapshotChunk(const String& chunk);void heapStatsUpdate(std::unique_ptr<protocol::Array<int>> statsUpdate);void lastSeenObjectId(int lastSeenObjectId, double timestamp);void reportHeapSnapshotProgress(int done, int total, Maybe<bool> finished = Maybe<bool>());void resetProfiles();void flush();void sendRawNotification(std::unique_ptr<Serializable>);private:// 指向 V8InspectorSessionImpl 对象FrontendChannel* frontend_channel_;
};
下面看一下 addHeapSnapshotChunk,这是获取堆快照时用到的逻辑。
void Frontend::addHeapSnapshotChunk(const String& chunk)
{v8_crdtp::ObjectSerializer serializer;serializer.AddField(v8_crdtp::MakeSpan("chunk"), chunk);frontend_channel_->SendProtocolNotification(v8_crdtp::CreateNotification("HeapProfiler.addHeapSnapshotChunk", serializer.Finish()));
}
最终触发了 HeapProfiler.addHeapSnapshotChunk 事件。另外 V8HeapProfilerAgentImpl 继承了 Backend 定义了支持哪些请求命令和 DomainDispatcherImpl 中的函数对应,比如获取堆快照。
class Backend {
public:virtual ~Backend() { }// 不一一列举virtual DispatchResponse takeHeapSnapshot(Maybe<bool> in_reportProgress, Maybe<bool> in_treatGlobalObjectsAsRoots, Maybe<bool> in_captureNumericValue) = 0;
};
结构图如下。
6. Node.js 对 V8 Inspector 的封装
接下来看一下 Node.js 中是如何使用 V8 Inspector 的,V8 Inspector 的使用方需要实现 V8InspectorClient 和 V8Inspector::Channel。下面看一下 Node.js 的实现。
class NodeInspectorClient : public V8InspectorClient {public:explicit NodeInspectorClient() {// 创建一个 V8Inspectorclient_ = V8Inspector::create(env->isolate(), this);}int connectFrontend(std::unique_ptr<InspectorSessionDelegate> delegate,bool prevent_shutdown) {int session_id = next_session_id_++;channels_[session_id] = std::make_unique<ChannelImpl>(env_,client_,getWorkerManager(),// 收到数据后由 delegate 处理std::move(delegate),getThreadHandle(),prevent_shutdown);return session_id;}std::unique_ptr<V8Inspector> client_;std::unordered_map<int, std::unique_ptr<ChannelImpl>> channels_;
};
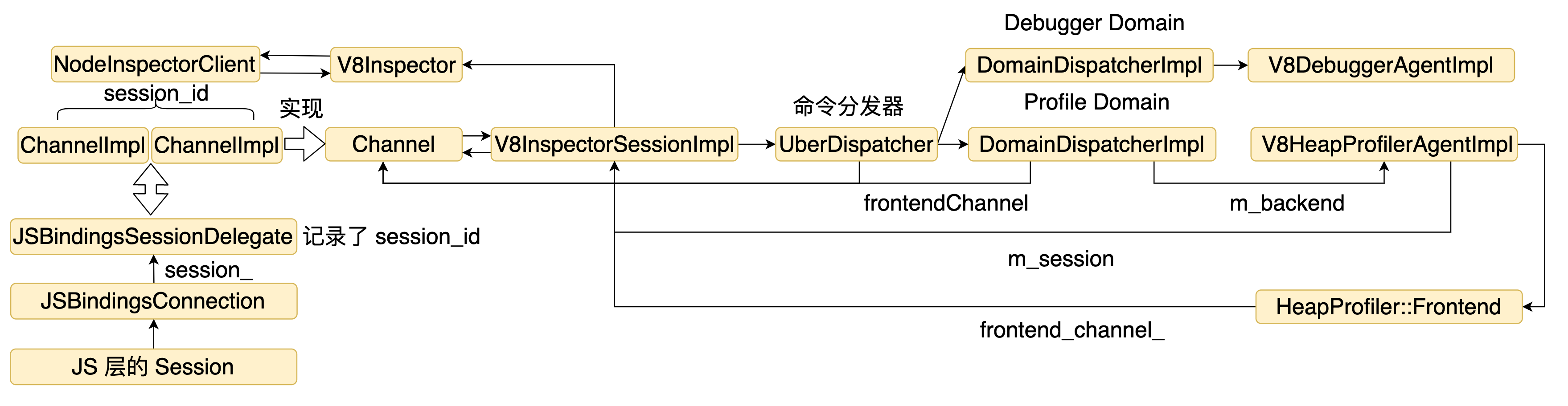
NodeInspectorClient 封装了 V8Inspector,并且维护了多个 channel。Node.js 的上层代码可以通过 connectFrontend 连接到 V8 Inspector,并拿到 session_id,这个连接用 ChannelImpl 来实现,来看一下 ChannelImpl 的实现。
explicit ChannelImpl(const std::unique_ptr<V8Inspector>& inspector, std::unique_ptr<InspectorSessionDelegate> delegate): // delegate_ 负责处理 V8 发过来的数据delegate_(std::move(delegate)) {session_ = inspector->connect(CONTEXT_GROUP_ID, this, StringView());
}
ChannelImpl 是对 V8InspectorSession 的封装,通过 V8InspectorSession 实现发送命令,ChannelImpl 自己实现了接收响应和接收 V8 推送数据的逻辑。了解了封装 V8 Inspector 的能力后,通过一个例子看一下整个处理过程。通常我们通过以下方式和 V8 Inspector 通信。
const { Session } = require('inspector');
new Session().connect();
我们从 connect 开始分析。
connect() {this[connectionSymbol] =new Connection((message) => this[onMessageSymbol](message));}
新建一个 C++ 层的对象 JSBindingsConnection。
JSBindingsConnection(Environment* env,Local<Object> wrap,Local<Function> callback): AsyncWrap(env, wrap, PROVIDER_INSPECTORJSBINDING),callback_(env->isolate(), callback) {Agent* inspector = env->inspector_agent();session_ = LocalConnection::Connect(inspector, std::make_unique<JSBindingsSessionDelegate>(env, this));
}static std::unique_ptr<InspectorSession> Connect(Agent* inspector, std::unique_ptr<InspectorSessionDelegate> delegate) {return inspector->Connect(std::move(delegate), false);
}std::unique_ptr<InspectorSession> Agent::Connect(std::unique_ptr<InspectorSessionDelegate> delegate,bool prevent_shutdown) {int session_id = client_->connectFrontend(std::move(delegate),prevent_shutdown);return std::unique_ptr<InspectorSession>(new SameThreadInspectorSession(session_id, client_));
}
JSBindingsConnection 初始化时会通过 agent->Connect 最终调用 Agent::Connect 建立到 V8 的通道,并传入 JSBindingsSessionDelegate 作为数据处理的代理(channel 中使用)。最后返回一个 SameThreadInspectorSession 对象保存到 session_ 中,后续就可以开始通信了,继续看一下 通过 JS 层的 post 发送请求时的逻辑。
post(method, params, callback) {const id = this[nextIdSymbol]++;const message = { id, method };if (params) {message.params = params;}if (callback) {this[messageCallbacksSymbol].set(id, callback);}this[connectionSymbol].dispatch(JSONStringify(message));}
为每一个请求生成一个 id,因为是异步返回的,最后调用 dispatch 函数。
static void Dispatch(const FunctionCallbackInfo<Value>& info) {Environment* env = Environment::GetCurrent(info);JSBindingsConnection* session;ASSIGN_OR_RETURN_UNWRAP(&session, info.Holder());if (session->session_) {session->session_->Dispatch(ToProtocolString(env->isolate(), info[0])->string());}}
看一下 SameThreadInspectorSession::Dispatch (即session->session_->Dispatch)。
void SameThreadInspectorSession::Dispatch(const v8_inspector::StringView& message) {auto client = client_.lock();if (client)client->dispatchMessageFromFrontend(session_id_, message);
}
SameThreadInspectorSession 中维护了一个sessionId,继续调用 client->dispatchMessageFromFrontend, client 是 NodeInspectorClient 对象。
void dispatchMessageFromFrontend(int session_id, const StringView& message) {channels_[session_id]->dispatchProtocolMessage(message);}
dispatchMessageFromFrontend 通过 sessionId 找到对应的 channel。继续调 channel 的 dispatchProtocolMessage。
void dispatchProtocolMessage(const StringView& message) {std::string raw_message = protocol::StringUtil::StringViewToUtf8(message);std::unique_ptr<protocol::DictionaryValue> value =protocol::DictionaryValue::cast(protocol::StringUtil::parseMessage(raw_message, false));int call_id;std::string method;node_dispatcher_->parseCommand(value.get(), &call_id, &method);if (v8_inspector::V8InspectorSession::canDispatchMethod(Utf8ToStringView(method)->string())) {session_->dispatchProtocolMessage(message);}}
最终调用 V8InspectorSessionImpl 的 session_->dispatchProtocolMessage(message),后面的内容前面就讲过了,就不再分析。最后看一下数据响应或者推送时的逻辑。下面代码来自 ChannelImpl。
void sendResponse(int callId,std::unique_ptr<v8_inspector::StringBuffer> message) override {sendMessageToFrontend(message->string());
}void sendNotification(std::unique_ptr<v8_inspector::StringBuffer> message) override {sendMessageToFrontend(message->string());
}void sendMessageToFrontend(const StringView& message) {delegate_->SendMessageToFrontend(message);
}
我们看到最终调用了 delegate_->SendMessageToFrontend, delegate 是 JSBindingsSessionDelegate对象。
void SendMessageToFrontend(const v8_inspector::StringView& message)override {Isolate* isolate = env_->isolate();HandleScope handle_scope(isolate);Context::Scope context_scope(env_->context());MaybeLocal<String> v8string =String::NewFromTwoByte(isolate, message.characters16(),NewStringType::kNormal, message.length());Local<Value> argument = v8string.ToLocalChecked().As<Value>();connection_->OnMessage(argument);
}
接着调用 connection_->OnMessage(argument),connection 是 JSBindingsConnection 对象。
void OnMessage(Local<Value> value) {MakeCallback(callback_.Get(env()->isolate()), 1, &value);
}
C++ 层回调 JS 层。
[onMessageSymbol](message) {const parsed = JSONParse(message);try {// 通过有没有 id 判断是响应还是推送if (parsed.id) {const callback = this[messageCallbacksSymbol].get(parsed.id);this[messageCallbacksSymbol].delete(parsed.id);if (callback) {if (parsed.error) {return callback(new ERR_INSPECTOR_COMMAND(parsed.error.code,parsed.error.message));}callback(null, parsed.result);}} else {this.emit(parsed.method, parsed);this.emit('inspectorNotification', parsed);}} catch (error) {process.emitWarning(error);}}
以上就完成了整个链路的分析。整体结构图如下。
7. 总结
V8 Inspector 的设计和实现上比较复杂,对象间关系错综复杂。因为 V8 提供调试和诊断 JS 的文档似乎不多,也不是很完善,就是简单描述一下命令是干啥的,很多时候不一定够用,了解了具体实现后,后续碰到问题,可以自己去看具体实现。
